Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 21, 2023; 29(15): 2283-2293
Published online Apr 21, 2023. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i15.2283
Published online Apr 21, 2023. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i15.2283
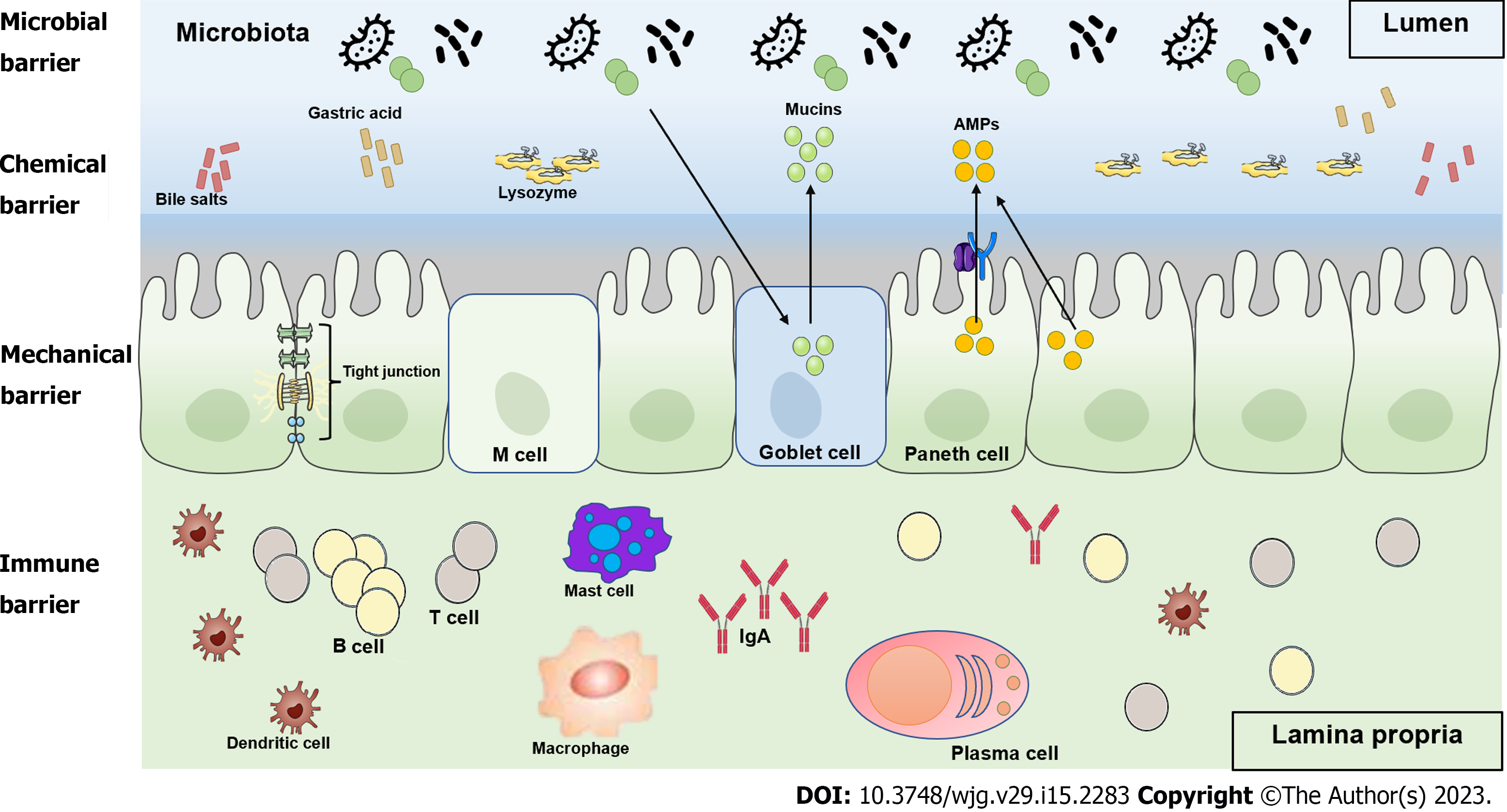
Figure 1 Schematic diagram of the intestinal barrier.
The intestinal barrier is composed of biological, chemical, mechanical, and immune barriers. The intestinal lumen contains antimicrobial peptides, mucins, gastric acid, bile salts, lysozyme, and commensal bacteria, which together provide a protective barrier effect and inhibit pathogen colonization. The epithelial layer consists of a single layer of epithelial cells with tight junctions that prevent paracellular passage. In addition, this layer also harbors M cells, Goblet cells, and Paneth cells. The lamina propria contains a large number of immune cells, including B cells, T cells, plasma cells, macrophages, dendritic cells, and mast cells.
- Citation: Xue W, Honda M, Hibi T. Mechanisms of gastrointestinal barrier dysfunction in COVID-19 patients. World J Gastroenterol 2023; 29(15): 2283-2293
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v29/i15/2283.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v29.i15.2283