Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 14, 2023; 29(14): 2188-2201
Published online Apr 14, 2023. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i14.2188
Published online Apr 14, 2023. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i14.2188
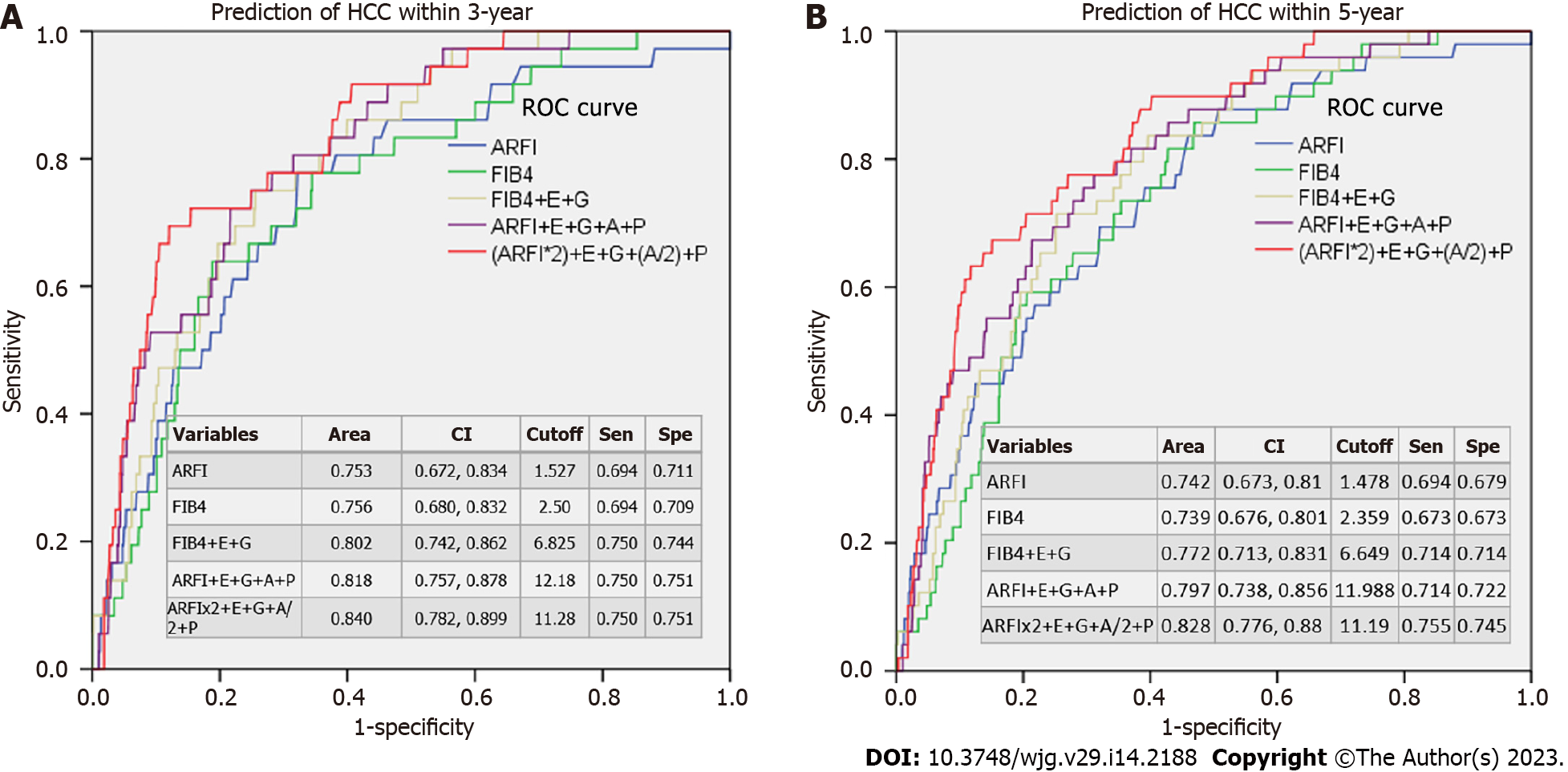
Figure 3 Area under the receiver operating characteristic curve of hepatocellular carcinoma prediction in different non-invasive scoring models.
A: Within 3-year period after enrollment; B: Within 5-year period after enrollment. The area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUROC) shows that acoustic radiation force impulse (ARFI) or FIB4 alone give similar 3- or 5-year predictions of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) (AUROC around 0.739-0.756). After adding G (gender score), E (etiology score), A (age score), and P (platelet score), the AUROC may increase to 0.772-0.840. Both ARFI and FIB4 models predict 3- or 5-year HCC quite satisfactorily, suggesting that fibrosis is the main risk factor for HCC. ARFI: Acoustic radiation force impulse; FIB4: Fibrosis index based on four factors; G: Gender score, male = 2, female = 0; E: Etiology score, hepatitis B virus (HBV) = 3, HCV = 2, NBNC = 1; A: Age score (year), 0-35 = 0, 35-40 = 1, 40-45 = 2, 45-50 = 3, 50-55 = 4, 55-60 = 5; > 60 = 6; P: Platelet score (109), 0-100 = 3, 100-150 = 2, > 150 = 1; Sen: Sensitivity; Spe: specificity; HCC: Hepatocellular carcinoma; ARFI: Acoustic radiation force impulse; FIB4: Fibrosis-4 index.
- Citation: Tai J, Harrison AP, Chen HM, Hsu CY, Hsu TH, Chen CJ, Jeng WJ, Chang ML, Lu L, Tai DI. Acoustic radiation force impulse predicts long-term outcomes in a large-scale cohort: High liver cancer, low comorbidity in hepatitis B virus. World J Gastroenterol 2023; 29(14): 2188-2201
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v29/i14/2188.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v29.i14.2188