Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 14, 2023; 29(14): 2188-2201
Published online Apr 14, 2023. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i14.2188
Published online Apr 14, 2023. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i14.2188
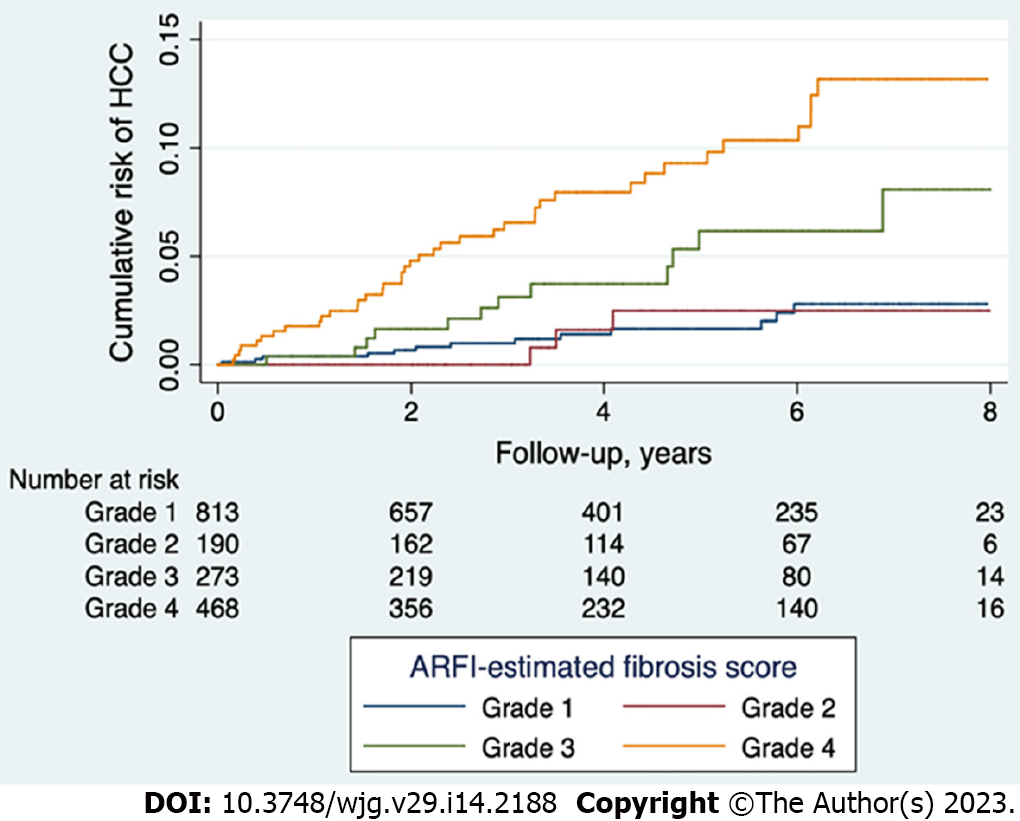
Figure 2 Cumulative risk of hepatocellular carcinoma after enrollment in different acoustic radiation force impulse-fibrosis grades.
Higher risk of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) was found in acoustic radiation force impulse (ARFI)-severe fibrosis and -cirrhosis grades than in none to moderate fibrosis grades. The 5-year risk of HCC was 9.8 % for ARFI fibrosis graded as cirrhosis; 5.9% for that graded as severe fibrosis; and only 1.7%-2.0% for that lower or equal to moderate fibrosis. Purple: Cirrhosis; Yellow: Severe fibrosis; Green: Moderate fibrosis, Blue: None or mild fibrosis [Log rank test: P = 0.026 (3 vs 4); P = 0.015 (3 vs 1 + 2); P < 0.001 (4 vs 1 + 2)]. HCC: Hepatocellular carcinoma; ARFI: Acoustic radiation force impulse.
- Citation: Tai J, Harrison AP, Chen HM, Hsu CY, Hsu TH, Chen CJ, Jeng WJ, Chang ML, Lu L, Tai DI. Acoustic radiation force impulse predicts long-term outcomes in a large-scale cohort: High liver cancer, low comorbidity in hepatitis B virus. World J Gastroenterol 2023; 29(14): 2188-2201
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v29/i14/2188.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v29.i14.2188