Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 14, 2023; 29(14): 2153-2171
Published online Apr 14, 2023. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i14.2153
Published online Apr 14, 2023. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i14.2153
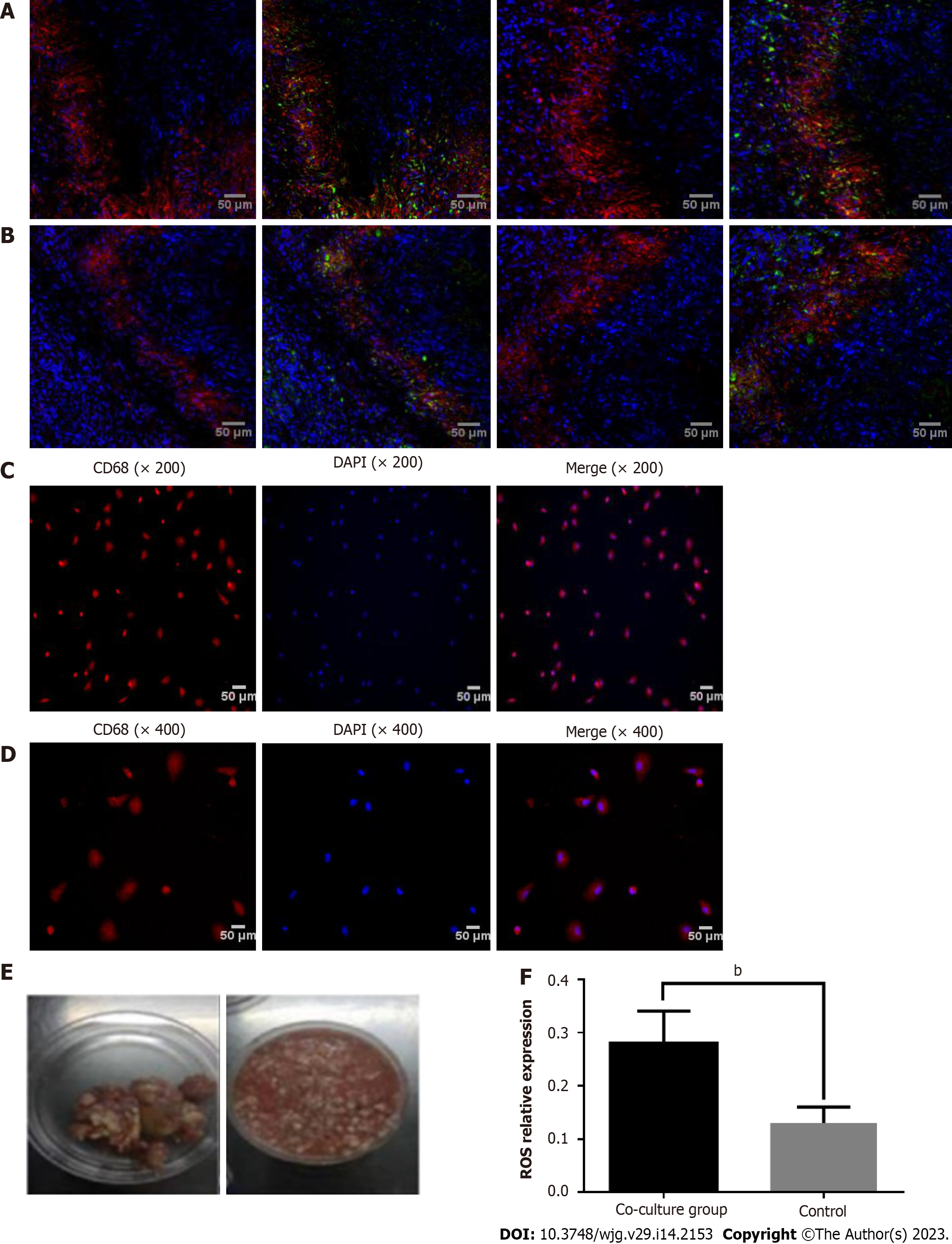
Figure 4 Echinococcus multilocularis activation of the NOD-like receptor family pyrin domain-containing 3-caspase-1-interleukin-1β pathways in Kupffer cells.
A: Cellular localisation of NOD-like receptor family pyrin domain-containing 3 (NLRP3) in the marginal zone (red denotes NLRP3 inflammasomes, blue denotes 4’,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI) stained nuclei, and green denotes the macrophage marker, CD68); B: Cellular localisation of caspase-1 in the marginal zone (red denotes caspase-1, blue denotes DAPI stained nuclei, and green denotes CD68); C: The identification of Kupffer cells at 200 × magnification and; D: The identification of Kupffer cells at 400× magnification (red denotes CD68 and blue denotes DAPI stained nuclei; the final image is a fusion image); E: Isolation of E. multilocularis; F: Relative expression in the co-culture and control groups. Scale bar, 50 μm. F, n = 3. bP < 0.01. NLRP3: NOD-like receptor family pyrin domain-containing 3; DAPI: 4’,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole.
- Citation: Chen CS, Zhang YG, Wang HJ, Fan HN. Effect and mechanism of reactive oxygen species-mediated NOD-like receptor family pyrin domain-containing 3 inflammasome activation in hepatic alveolar echinococcosis. World J Gastroenterol 2023; 29(14): 2153-2171
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v29/i14/2153.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v29.i14.2153