Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 7, 2023; 29(13): 1942-1954
Published online Apr 7, 2023. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i13.1942
Published online Apr 7, 2023. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i13.1942
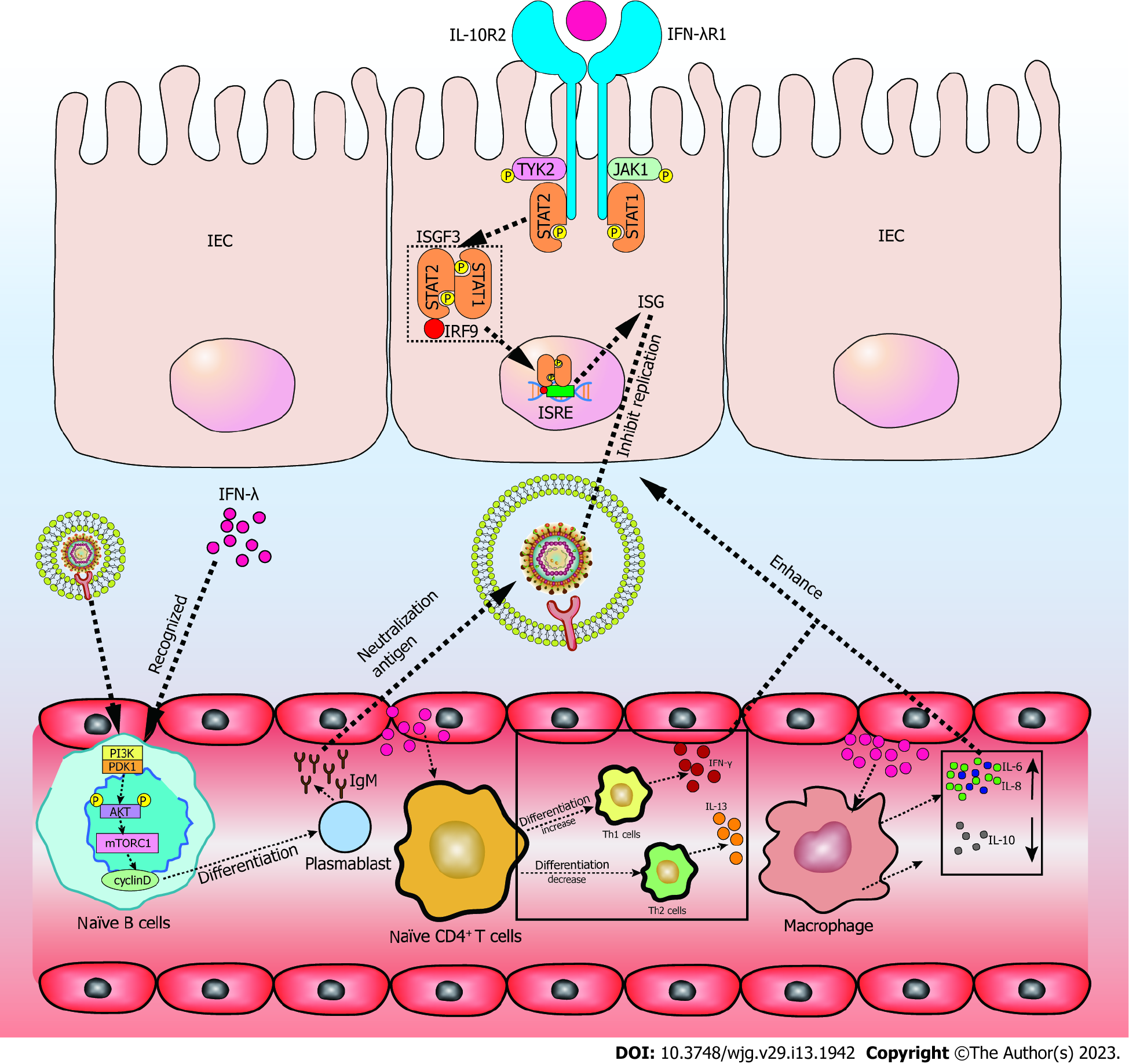
Figure 2 When interferon-λ is recognized in intestinal epithelial cells, JAK1 and TYK2 phosphorylate and activate phosphorylated signal transducer and activator of transcription 1 and signal transducer and activator of transcription 2.
Interferon (IFN)-stimulated gene factor 3 is formed by phosphorylated signal transducer and activator of transcription 1, signal transducer and activator of transcription 2, and interferon regulatory factor 9. It then binds to IFN-stimulated response elements in the nucleus to promote the transcription of IFN-stimulated genes (ISGs). ISGs inhibit the RNA replication of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2). Recognition of IFN-λ in naïve T cells promotes the differentiation of Th1 cells while inhibiting Th2 cells, resulting in increased IFN-γ and lower interleukin (IL)-13. In peripheral mononuclear blood cells (PMBCs), IFN-λ induces higher IL-6 and IL-8, while reducing IL-10. The effects of IFN-λ on naïve T cells and PMBCs enhance the antiviral effect of ISGs in intestinal epithelial cells. IFN-λ and pathogens are co-recognized by naïve B cells, and promote the differentiation of naïve B cells to plasmablasts through the phosphoinositide 3-kinase-phosphoinositide dependent kinase-1 pathway. This action produces large amounts of immunoglobulin M (IgM). IgM acts as a neutralizing antibody in the intestinal tract of SARS-CoV-2 infection. STAT1: Signal transducer and activator of transcription 1; STAT2: Signal transducer and activator of transcription 2; IL: Interleukin; IFN-λ: Interferon-λ; IEC: Intestinal epithelial cell; ISGF3: IFN-stimulated gene factor 3; IRF9: Interferon regulatory factor 9; ISRE: IFN-stimulated response element; ISG: IFN-stimulated genes; PI3K: Phosphoinositide 3-kinase; PDK1: Phosphoinositide dependent kinase-1; mTORC1: Mechanistic target of rapamycin complex 1; IgM: Immunoglobulin M.
- Citation: Pan YY, Wang LC, Yang F, Yu M. Interferon-lambda: New role in intestinal symptoms of COVID-19. World J Gastroenterol 2023; 29(13): 1942-1954
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v29/i13/1942.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v29.i13.1942