Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Gastroenterol. Mar 28, 2023; 29(12): 1875-1898
Published online Mar 28, 2023. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i12.1875
Published online Mar 28, 2023. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i12.1875
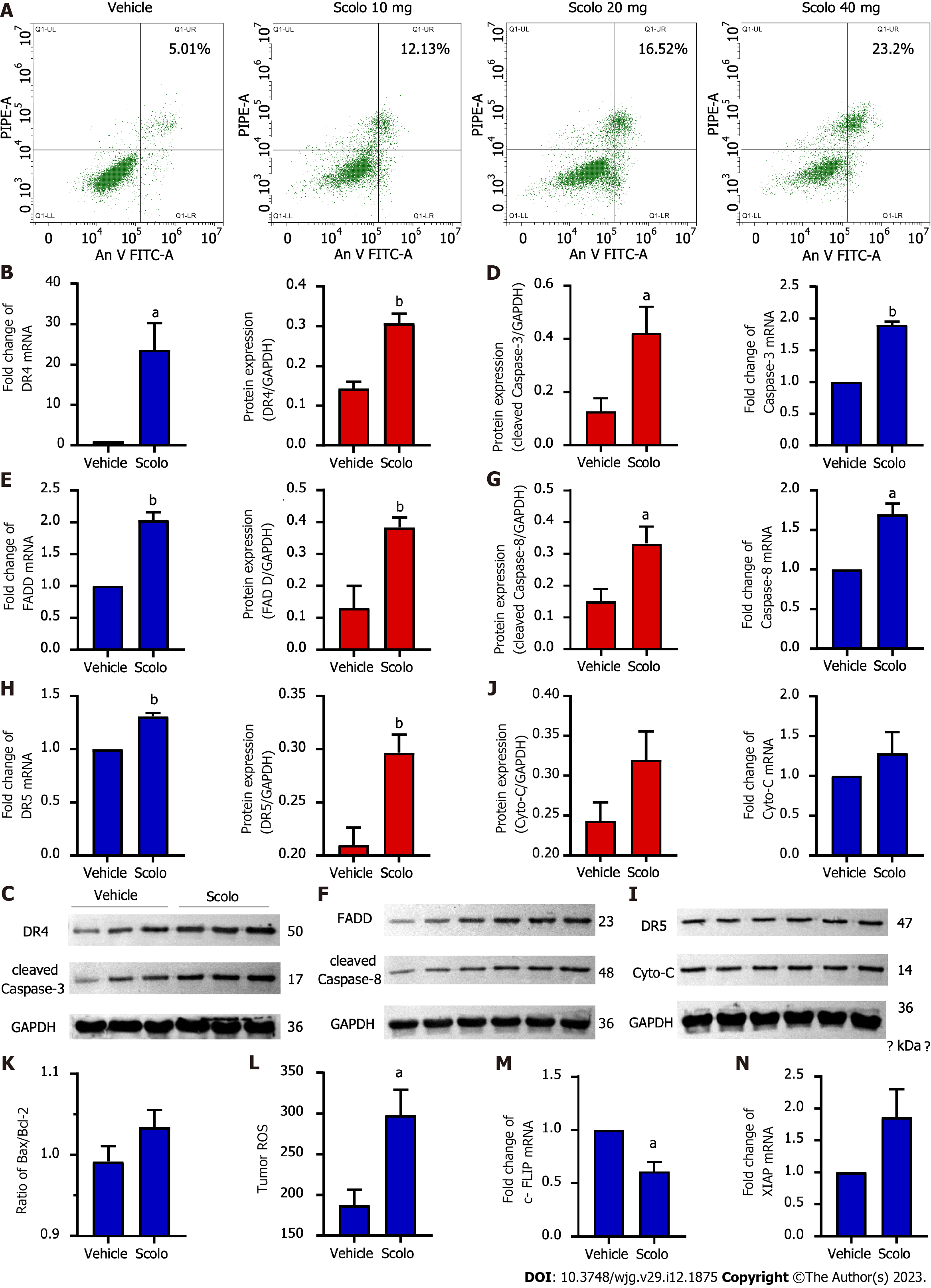
Figure 6 Antihepatoma mechanism of scolopentide.
A: Flow cytometry suggested that apoptosis occurred in HepG2 cells after treatment with extracted scolopentide in vitro. B-I: Quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) and western blotting showed that the expression of DR4 (B and C), DR5 (H and I), FADD (E and F), caspase-8 (F and G), and caspase-3 (C and D) was significantly upregulated in the scolopentide group. DR4 was the most considerably upregulated; I-K: qRT-PCR and western blotting showed that the expression of Cyto-C (I and J) and Bax/Bcl-2 (K) was not upregulated, which are key indicators of mitochondria dependence; L: Tumor ROS levels in the scolopentide group were higher than those in the vehicle group; M: c-FLIP, an inhibitory protein of caspase-8, was significantly downregulated in qRT-PCR; N: XIAP, an inhibitory protein of caspase-3, was insignificantly upregulated in qRT-PCR. DR4: Death receptor 4; DR5: Death receptor 5; FADD: Fas-associated death domain protein. n = 4 per group in qRT-PCR, n = 3 per group in Western blotting, n = 4 per group in ROS; aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01.
- Citation: Hu YX, Liu Z, Zhang Z, Deng Z, Huang Z, Feng T, Zhou QH, Mei S, Yi C, Zhou Q, Zeng PH, Pei G, Tian S, Tian XF. Antihepatoma peptide, scolopentide, derived from the centipede scolopendra subspinipes mutilans. World J Gastroenterol 2023; 29(12): 1875-1898
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v29/i12/1875.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v29.i12.1875