Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Gastroenterol. Mar 28, 2023; 29(12): 1875-1898
Published online Mar 28, 2023. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i12.1875
Published online Mar 28, 2023. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i12.1875
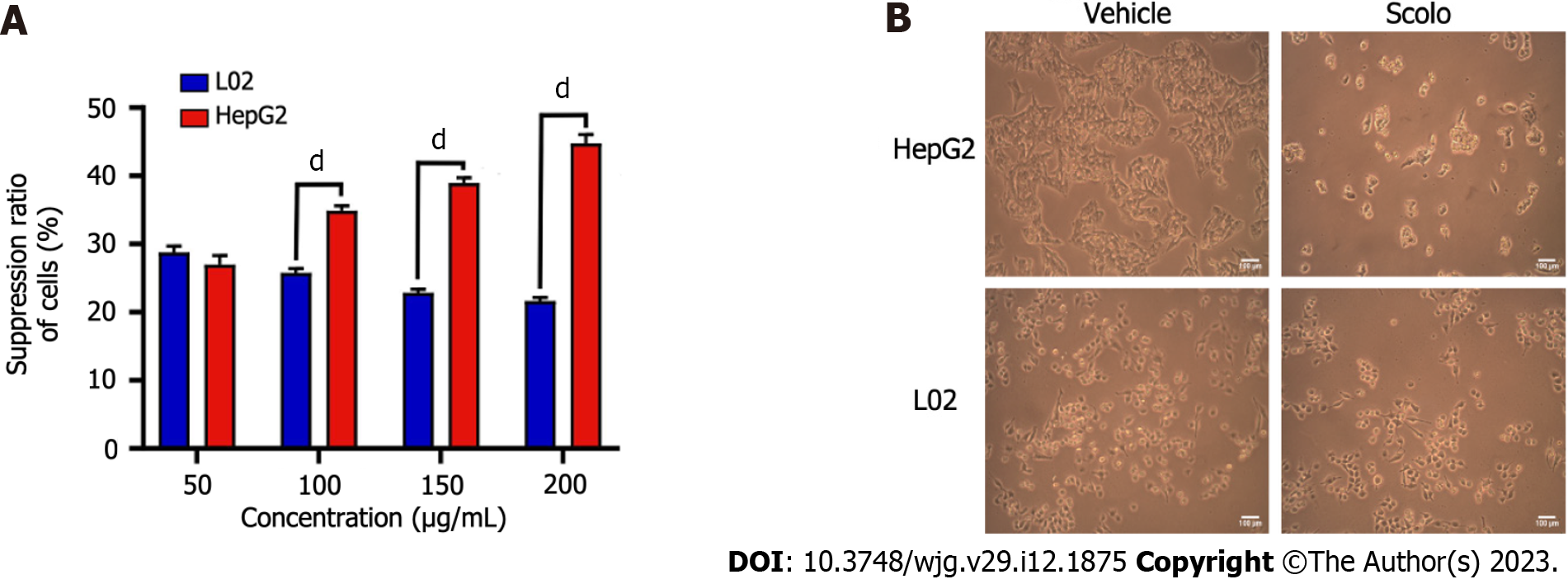
Figure 4 Cytotoxicity of synthetic scolopentide to L02 cells and HepG2 cells.
A: The CCK8 assay showed that cytotoxicity to L02 cells was significantly lower than that to HepG2 cells after treatment with synthetic scolopentide for 12 h (100 μg/mL, 150 μg/mL, and 200 μg/mL); B: Morphological changes in HepG2 and L02 cells under a light microscope after treatment with synthetic scolopentide for 12 h (× 100). Compared to cells in the vehicle group (0 μg/mL), most HepG2 cells in the scolopentide group (100 μg/mL) died, while some L02 cells survived. dP < 0.0001.
- Citation: Hu YX, Liu Z, Zhang Z, Deng Z, Huang Z, Feng T, Zhou QH, Mei S, Yi C, Zhou Q, Zeng PH, Pei G, Tian S, Tian XF. Antihepatoma peptide, scolopentide, derived from the centipede scolopendra subspinipes mutilans. World J Gastroenterol 2023; 29(12): 1875-1898
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v29/i12/1875.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v29.i12.1875