Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Gastroenterol. Mar 21, 2023; 29(11): 1721-1734
Published online Mar 21, 2023. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i11.1721
Published online Mar 21, 2023. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i11.1721
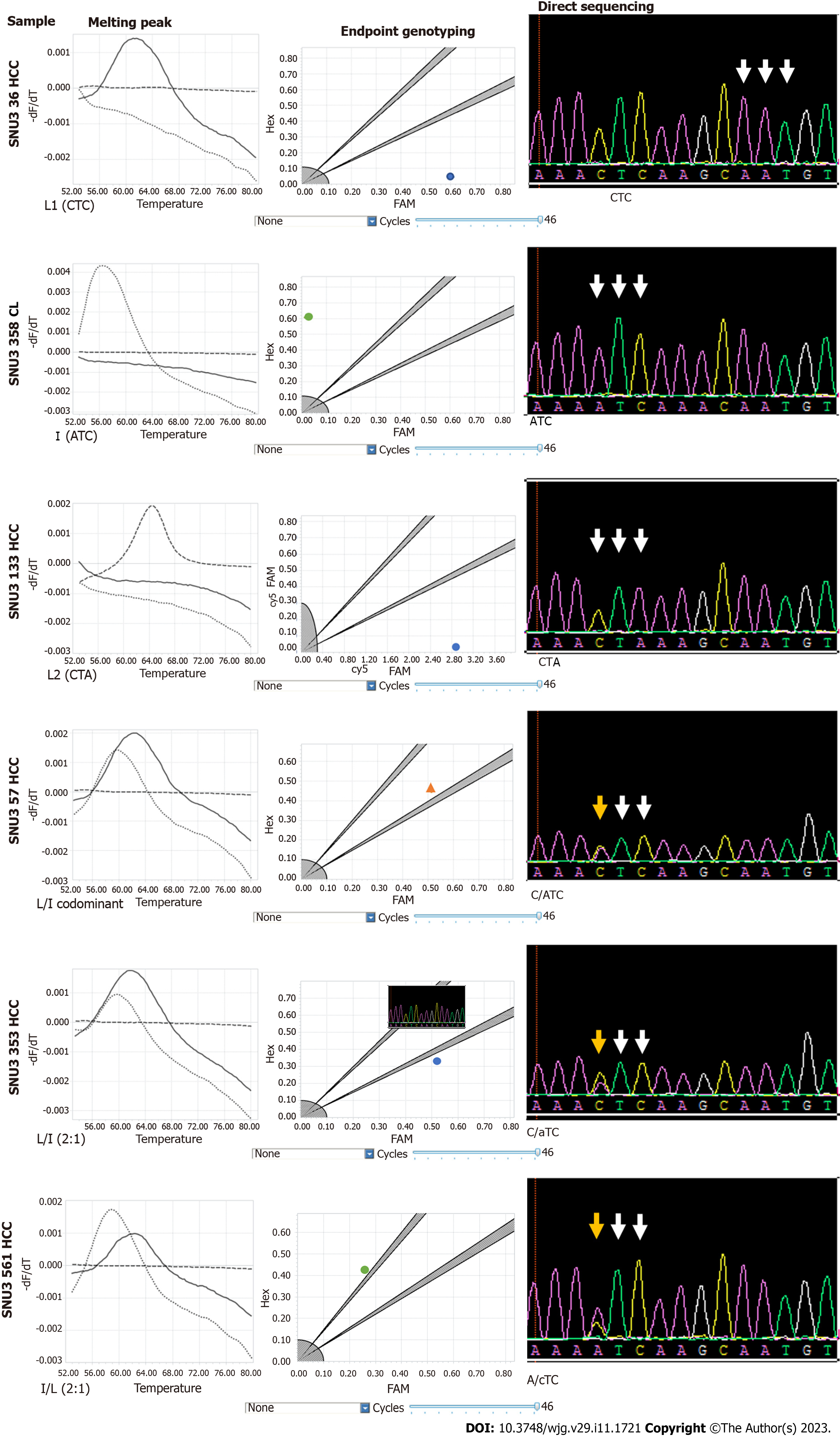
Figure 4 Confirmation of multiprobe locked nucleic acid real-time polymerase chain reaction identification results of hepatitis B virus rtL269 variants by direct sequencing.
Nucleotide bases are shown in the parentheses. Lowercase letters represent the base present in a lower amount relative to the dominant variant. Bold indicates the dominant amino acids and bases. Arrows represent the codon sequence positions for leucine or isoleucine; yellow, mixed bases.
- Citation: Kim K, Choi YM, Kim DH, Jang J, Choe WH, Kim BJ. Locked nucleic acid real-time polymerase chain reaction method identifying two polymorphisms of hepatitis B virus genotype C2 infections, rt269L and rt269I. World J Gastroenterol 2023; 29(11): 1721-1734
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v29/i11/1721.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v29.i11.1721