Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Gastroenterol. Mar 21, 2023; 29(11): 1708-1720
Published online Mar 21, 2023. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i11.1708
Published online Mar 21, 2023. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i11.1708
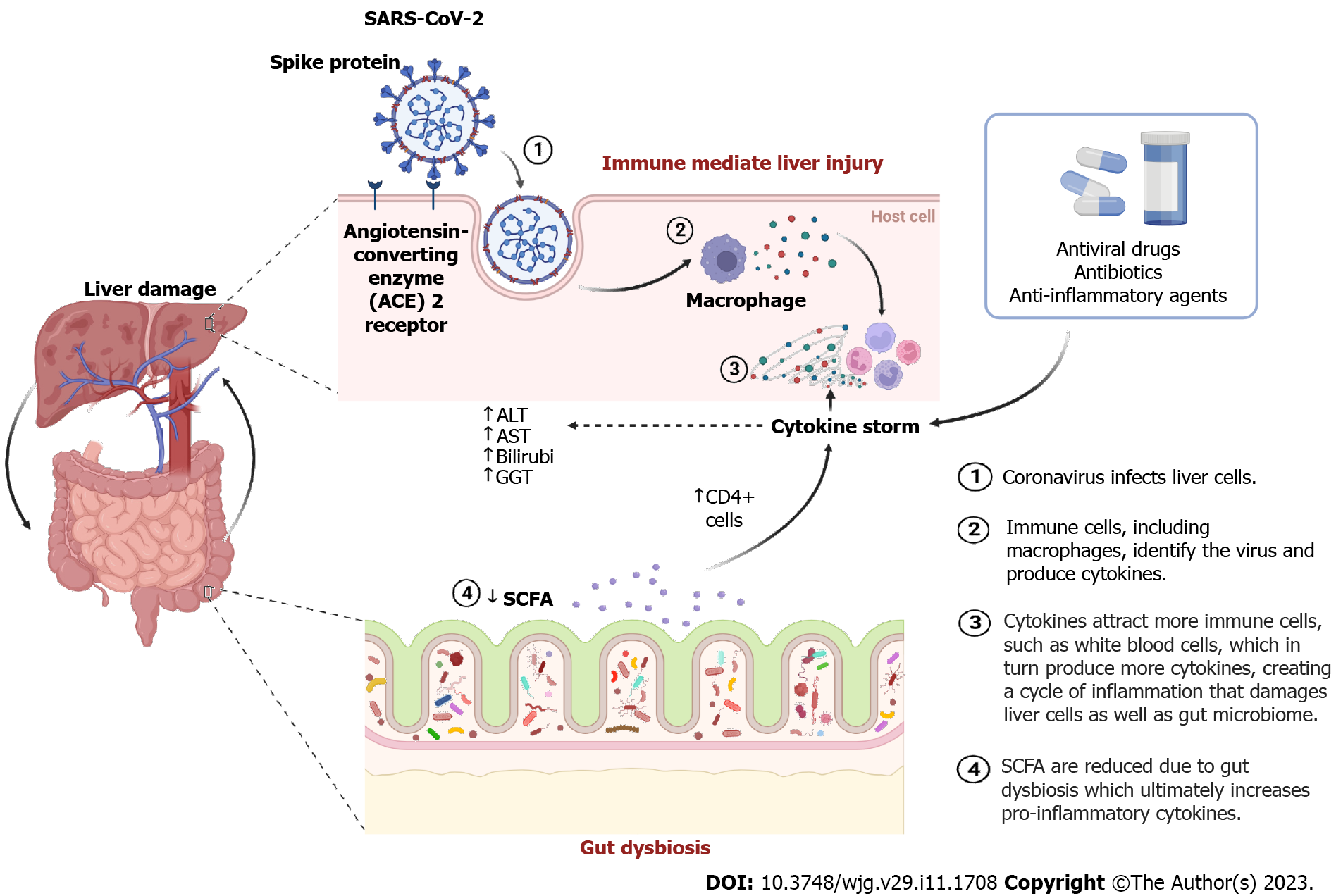
Figure 1 Potential causes of liver injury during coronavirus disease 2019.
Following severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 infection, liver injury may arise due to direct viral entry [via angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) receptors on hepatocytes] or gut microbial dysbiosis leading to cytokine storm in the liver. ALT: Alanine aminotransferase; AST: Aspartate aminotransferase; CD4+: Cluster of differentiation; GGT: Gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase; SCFA: Short-chain fatty acids.
- Citation: Ahsan K, Anwar MA, Munawar N. Gut microbiome therapeutic modulation to alleviate drug-induced hepatic damage in COVID-19 patients. World J Gastroenterol 2023; 29(11): 1708-1720
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v29/i11/1708.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v29.i11.1708