Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Gastroenterol. Jan 7, 2023; 29(1): 126-143
Published online Jan 7, 2023. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i1.126
Published online Jan 7, 2023. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i1.126
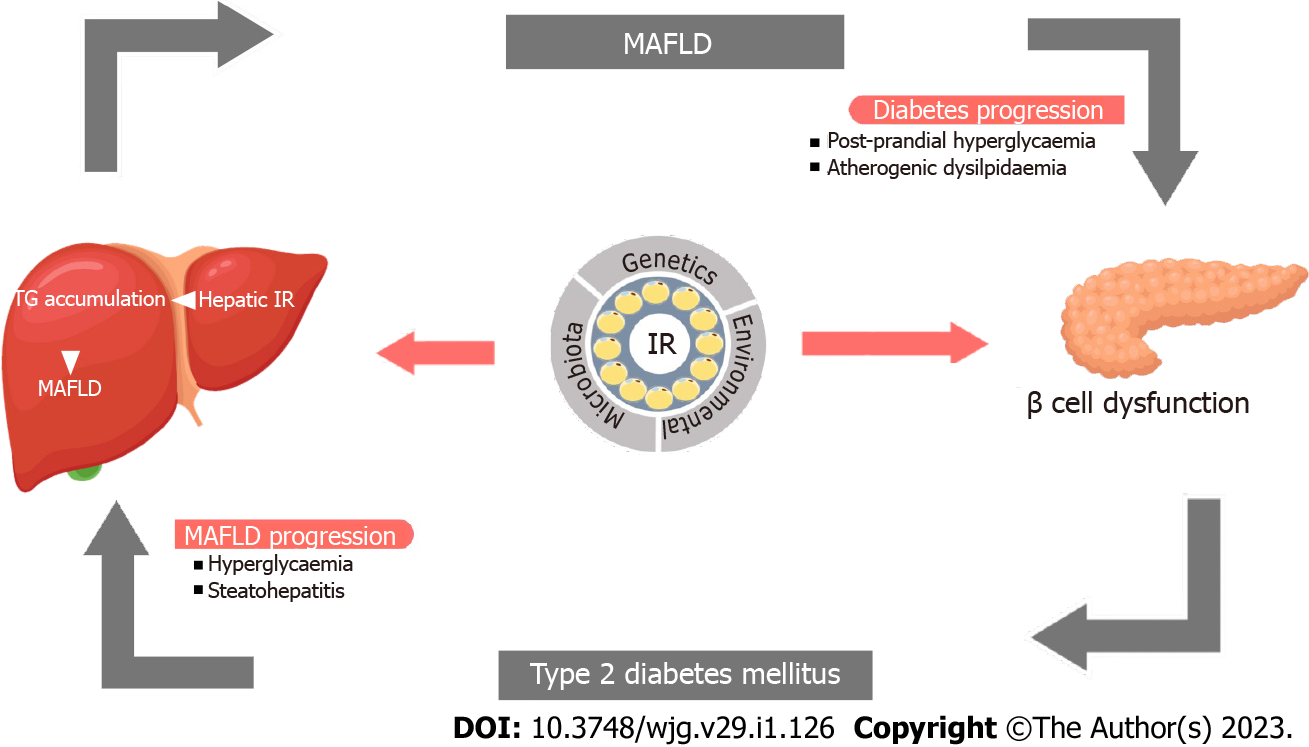
Figure 1 Pathobiological link between metabolic-associated fatty live disease and type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Metabolic-associated fatty live disease (MAFLD) may increase the risk for hyperglycemia and dyslipidemia and cause β-cell dysfunction leading to insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes which in turn may aggravate MAFLD progression to nonalcoholic steatohepatitis and fibrosis. IR: Insulin resistance; MAFLD: Metabolic-associated fatty live disease; TG: Triglycerides.
- Citation: Jeeyavudeen MS, Khan SKA, Fouda S, Pappachan JM. Management of metabolic-associated fatty liver disease: The diabetology perspective. World J Gastroenterol 2023; 29(1): 126-143
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v29/i1/126.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v29.i1.126