Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Gastroenterol. Mar 7, 2022; 28(9): 897-908
Published online Mar 7, 2022. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i9.897
Published online Mar 7, 2022. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i9.897
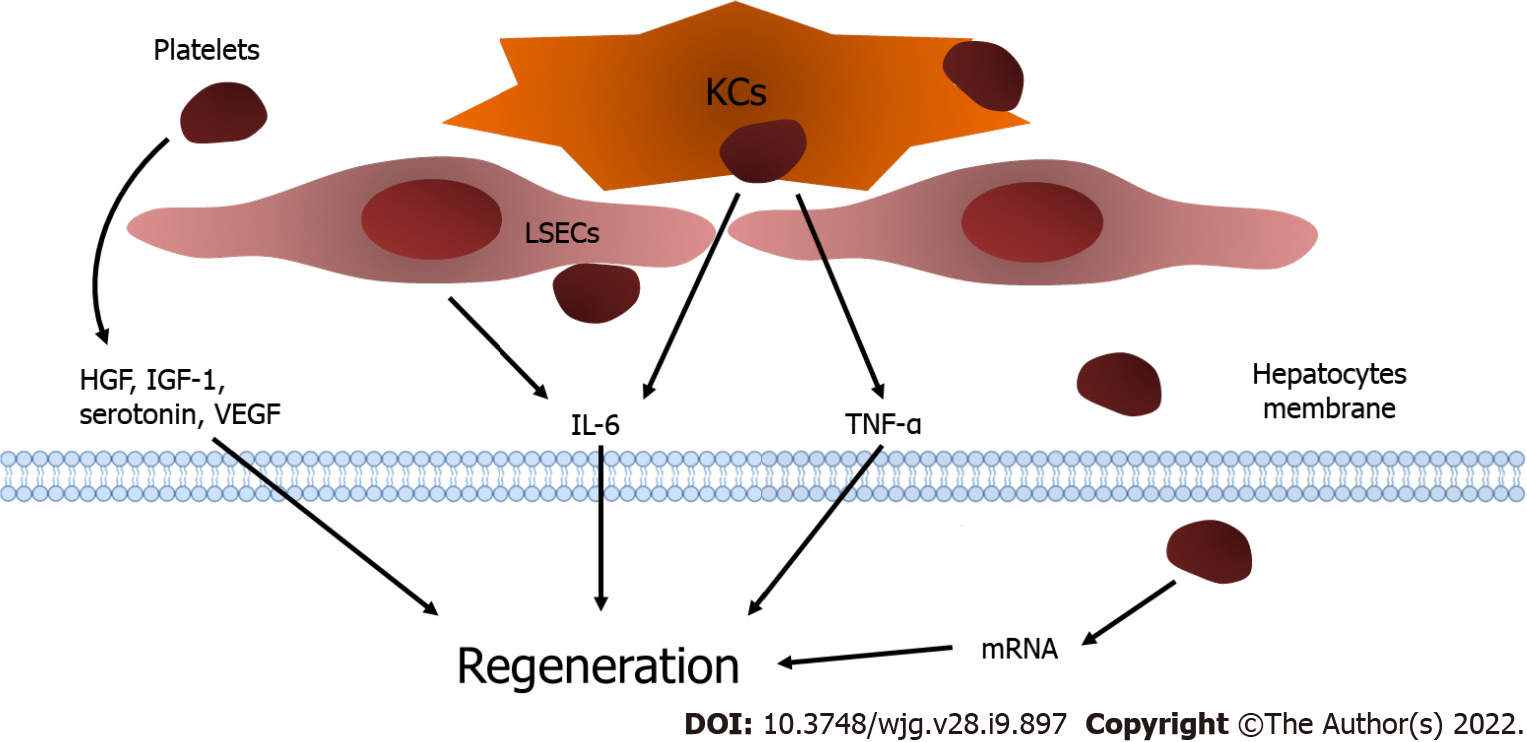
Figure 1 Platelets and liver regeneration.
Platelets translocate into the space of Disse and release insulin-like growth factor-1, hepatocyte growth factor, and vascular endothelial growth factor. The direct contact of platelets with liver sinusoidal endothelial cells (LSECs) results in the excretion of interleukin-6 (IL-6) from LSECs. In addition, the attachment of platelets activates Kupffer cells (KCs) and enhances the release of tumor necrosis factor-alpha and IL-6 from KCs to promote liver regeneration. Moreover, platelets are internalized into hepatocytes and trigger the functional transfer of messenger RNA stored in platelets, which stimulates hepatocyte proliferation. KCs: Kupffer cells; LSECs: Liver sinusoidal endothelial cells; IGF-1: Insulin-like growth factor-1; HGF: Hepatocyte growth factor; VEGF: Vascular endothelial growth factor; LSECs: Liver sinusoidal endothelial cells; IL-6: Interleukin-6; KCs: Kupffer cells; TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor-alpha.
- Citation: Liang C, Takahashi K, Furuya K, Ohkohchi N, Oda T. Dualistic role of platelets in living donor liver transplantation: Are they harmful? World J Gastroenterol 2022; 28(9): 897-908
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v28/i9/897.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v28.i9.897