Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Gastroenterol. Feb 28, 2022; 28(8): 775-793
Published online Feb 28, 2022. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i8.775
Published online Feb 28, 2022. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i8.775
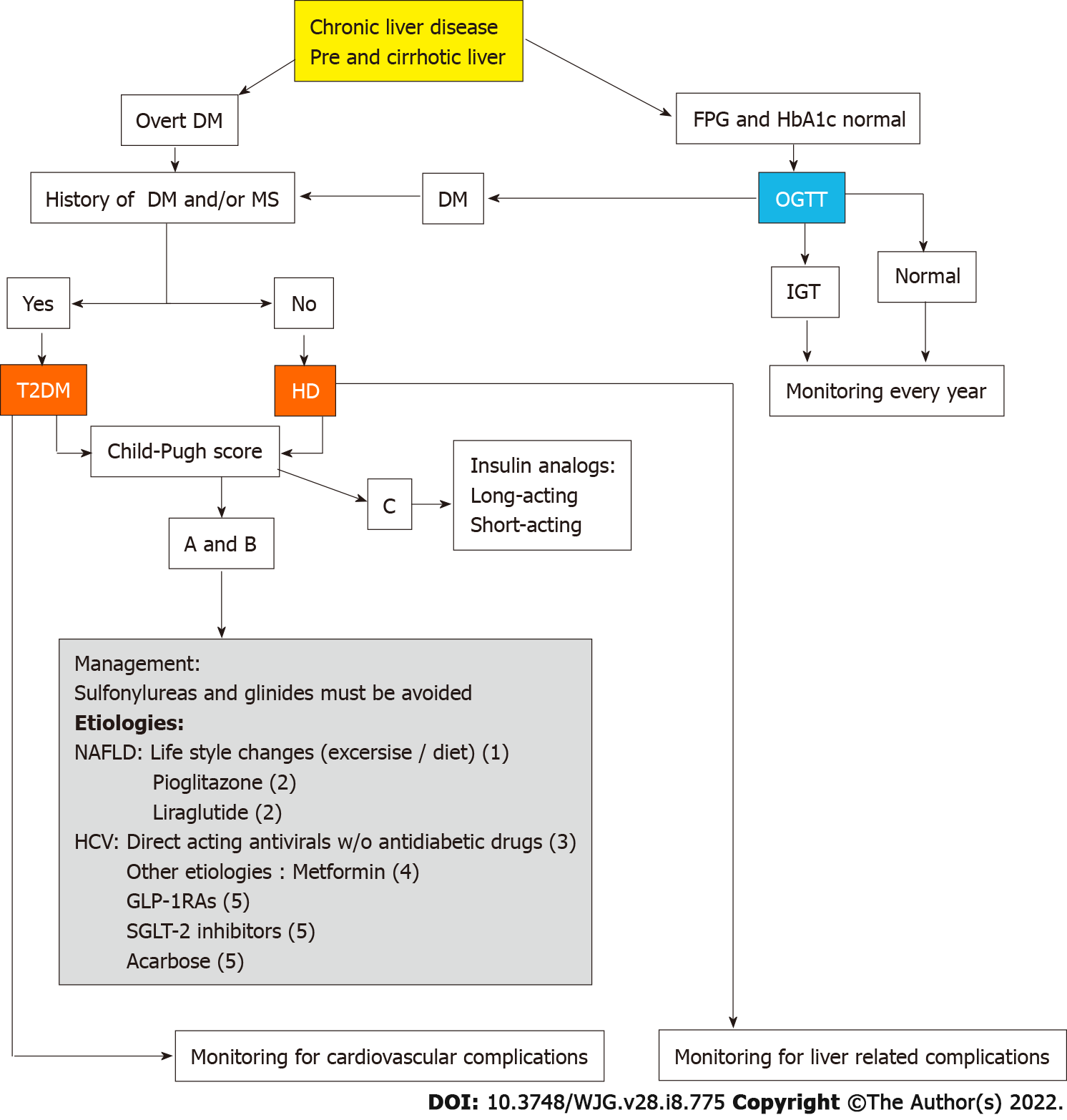
Figure 3 Algorithm for diagnosis and management of diabetes mellitus and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease based on the published evidences.
As follows: (1) This treatment has been evaluated only in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD); (2) These drugs have been evaluated in NAFLD showing improvement of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis and fibrosis; (3) Direct-acting antiviral have demonstrated improvement of short and long term glycemic control after hepatitis C virus eradication; (4) Long term administration of metformin has demonstrated association to significant reduction of liver related complications, hepatocellular carcinoma and mortality; and (5) GLP-1 receptor agonists and sodium-glucose co-transporter-2 inhibitor drugs have demonstrated effectiveness for glycemic control and good tolerance in liver cirrhosis patients. NAFLD: Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease; DM: Diabetes mellitus; GLP-1Ras: GLP-1 receptor agonists; SGLT-2: Sodium-glucose co-transporter-2; HCV: Hepatitis C virus; FPG: Fasting plasma glucose; HbA1c: Glycated hemoglobin; HD: Hepatogenous diabetes; MS: Metabolic syndrome; OGTT: Oral glucose tolerance test; IGT: Impaired glucose tolerance.
- Citation: García-Compeán D, Orsi E, Kumar R, Gundling F, Nishida T, Villarreal-Pérez JZ, Del Cueto-Aguilera ÁN, González-González JA, Pugliese G. Clinical implications of diabetes in chronic liver disease: Diagnosis, outcomes and management, current and future perspectives. World J Gastroenterol 2022; 28(8): 775-793
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v28/i8/775.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v28.i8.775