Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Gastroenterol. Dec 28, 2022; 28(48): 6935-6949
Published online Dec 28, 2022. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i48.6935
Published online Dec 28, 2022. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i48.6935
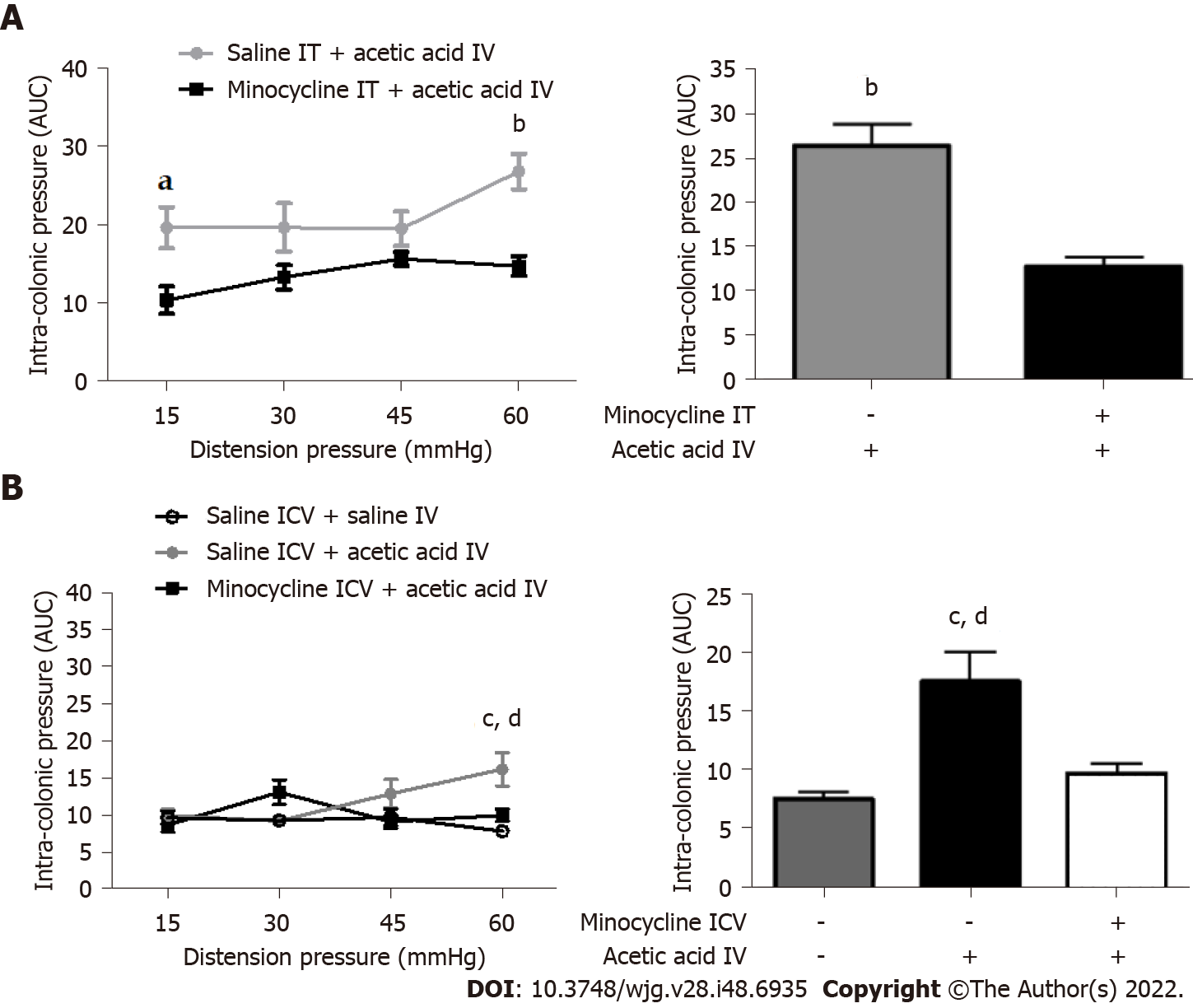
Figure 5 Effect of minocycline injection at the central level on visceral sensitivity.
A and B: Changes in intracolonic pressure in response to isobaric colorectal distensions (15, 30, 45 and 60 mmHg) intrathecal (IT) injections of saline (NaCl 0.9%) (A) or minocycline (1.25 mg/kg) prior to intravesical (IV) injections of acetic acid 0.75% and after intracerebroventricular (ICV) injections of saline or minocycline (1.25 mg/kg) (B) prior to IV injections of saline or acetic acid 0.75% in mice at day 7, both with details of the comparison at 60 mmHg of distension on the right. n = 6-8 mice per group. aP < 0.05 and bP < 0.001 (compared to the minocycline IT + acetic acid IV group); cP < 0.0001 (compared to the saline ICV + saline IV group); dP < 0.05 (compared to the minocycline ICV + acetic acid IV group). Variability in the results is represented by the standard error of the mean (area under the curve ± standard error of the mean). AUC: Area under the curve.
- Citation: Atmani K, Wuestenberghs F, Baron M, Bouleté I, Guérin C, Bahlouli W, Vaudry D, do Rego JC, Cornu JN, Leroi AM, Coëffier M, Meleine M, Gourcerol G. Bladder-colon chronic cross-sensitization involves neuro-glial pathways in male mice. World J Gastroenterol 2022; 28(48): 6935-6949
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v28/i48/6935.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v28.i48.6935