Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Gastroenterol. Dec 28, 2022; 28(48): 6811-6826
Published online Dec 28, 2022. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i48.6811
Published online Dec 28, 2022. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i48.6811
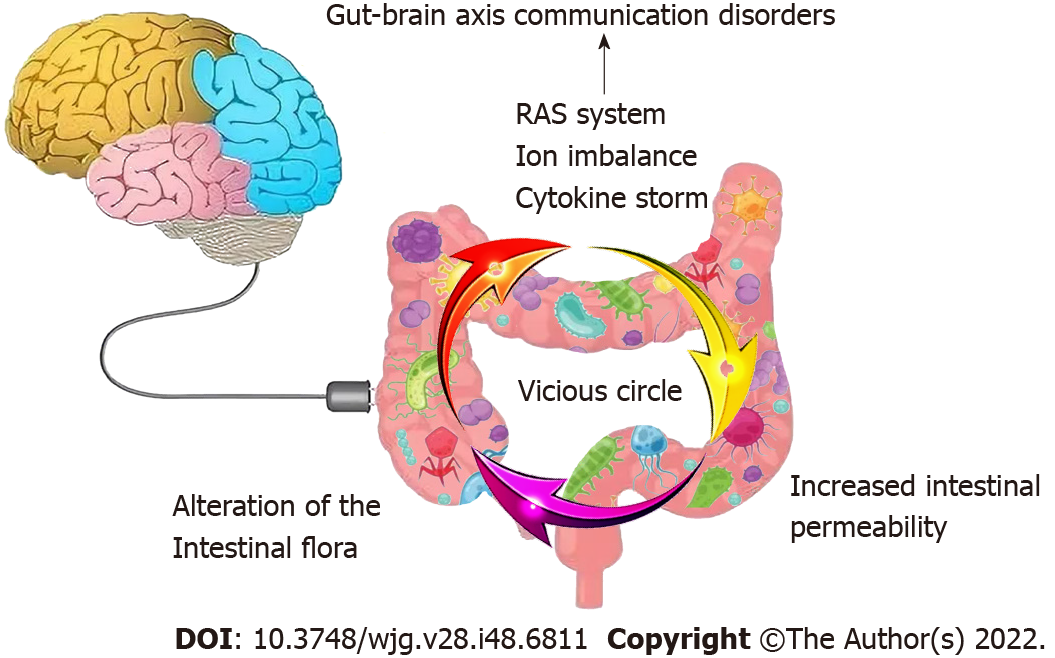
Figure 3 Main mechanisms involved in coronavirus disease 2019-induced gastrointestinal syndromes.
Gut infection of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) results in cytokine storm, increased intestinal permeability and alteration of the intestinal flora, and forming a vicious circle, extending the recovery time. Moreover, COVID-19 binding to gastrointestinal angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 also leads to ion imbalance and activation of renin-angiotensin system. Abnormal enteric neurotransmitters may further lead to gut-brain axis communication disorders. RAS: Renin-angiotensin system.
- Citation: Yao Y, Liu ZJ, Zhang YK, Sun HJ. Mechanism and potential treatments for gastrointestinal dysfunction in patients with COVID-19. World J Gastroenterol 2022; 28(48): 6811-6826
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v28/i48/6811.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v28.i48.6811