Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Gastroenterol. Dec 21, 2022; 28(47): 6769-6787
Published online Dec 21, 2022. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i47.6769
Published online Dec 21, 2022. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i47.6769
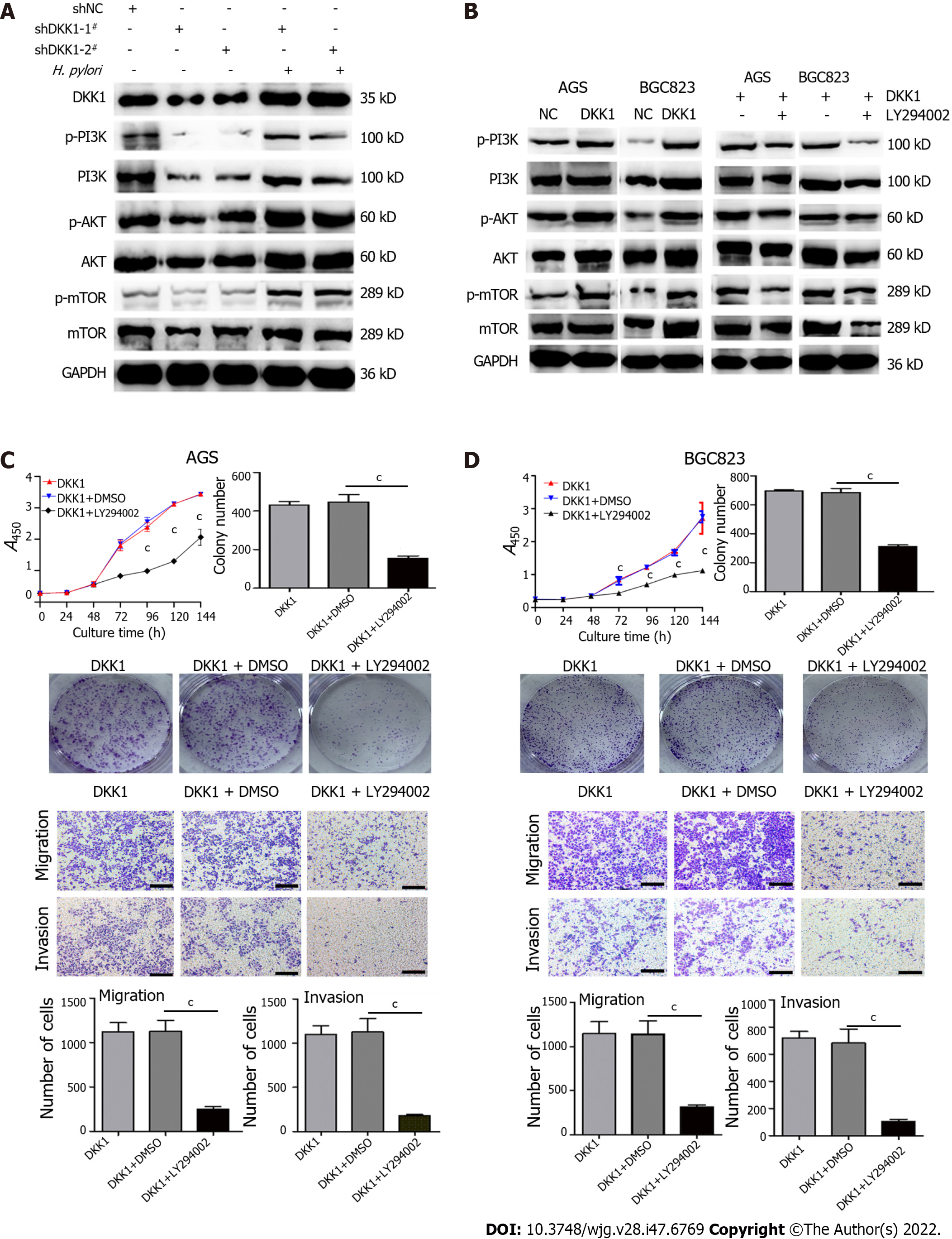
Figure 6 Dickkopf-related protein 1 promotes the growth, migration, and invasion of AGS and BGC823 cells by activating the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/AKT/ mammalian target of rapamycin pathway.
A and B: Western blotting for phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K), p-PI3K, AKT, p-AKT, mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR), and p-mTOR in dickkopf-related protein 1 (DKK1) knockdown and/or Helicobacter pylori-infected AGS cells (A) and DKK1 overexpression and/or LY294002 (50 μmol/L)-treated AGS and BGC823 cells (B); C and D: LY294002 treatment (50 μmol/L) decreases cell proliferation, colony formation, migration, and invasion in DKK1 overexpression AGS (C) and BGC823 (D) cells. Bar graphs show the quantitation of colony numbers or migrated and invaded cell numbers. Scale bar = 200 μm. cP < 0.001. DKK1: Dickkopf-related protein 1; H. pylori: Helicobacter pylori; PI3K: Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase; mTOR: Mammalian target of rapamycin.
- Citation: Luo M, Chen YJ, Xie Y, Wang QR, Xiang YN, Long NY, Yang WX, Zhao Y, Zhou JJ. Dickkopf-related protein 1/cytoskeleton-associated protein 4 signaling activation by Helicobacter pylori-induced activator protein-1 promotes gastric tumorigenesis via the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway. World J Gastroenterol 2022; 28(47): 6769-6787
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v28/i47/6769.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v28.i47.6769