Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Gastroenterol. Dec 21, 2022; 28(47): 6752-6768
Published online Dec 21, 2022. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i47.6752
Published online Dec 21, 2022. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i47.6752
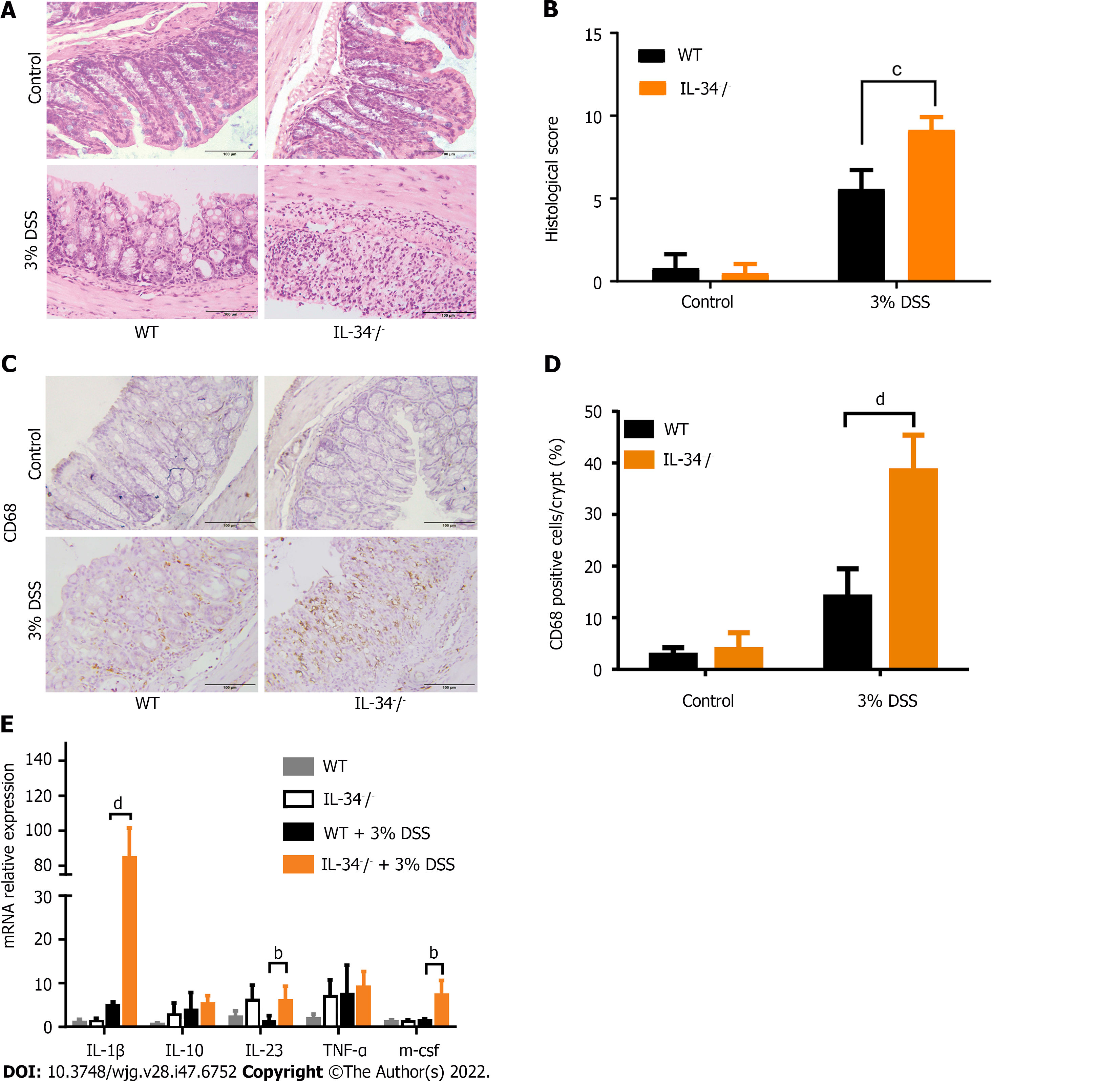
Figure 3 Interleukin-34 deficiency aggravates acute colitis and increase proinflammatory cytokines.
A: Representative microscopic pictures of hematoxylin and eosin-stained colon sections of Interleukin-34 (IL-34)-/- and WT mice fed with 3% DSS for 7 d (n = 6 or 7 per group); B: Histological score for IL-34-/- and WT mice fed with 3% dextran sodium sulfate (DSS); C: Representative photomicrographs of macrophage staining in colon sections of IL-34-/- and WT mice treated with DSS; D: Statistical analysis of CD68-positive cells in IL-34-/- and WT mice treated with DSS; E: mRNA expression of proinflammatory cytokines including IL-1β, IL-10, IL-23, TNF-α, and M-CSF in IL-34-/- and WT mice fed with 3% DSS. DSS: Dextran sodium sulfate; IL: Interleukin; M-CSF: Macrophage colony-stimulating factor; TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor-α; WT: Wild-type. Scale bars = 100 μm. Data depict the mean ± SD. bP < 0.01, cP < 0.005, dP < 0.001.
- Citation: Liu ZX, Chen WJ, Wang Y, Chen BQ, Liu YC, Cheng TC, Luo LL, Chen L, Ju LL, Liu Y, Li M, Feng N, Shao JG, Bian ZL. Interleukin-34 deficiency aggravates development of colitis and colitis-associated cancer in mice. World J Gastroenterol 2022; 28(47): 6752-6768
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v28/i47/6752.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v28.i47.6752