Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Gastroenterol. Dec 14, 2022; 28(46): 6564-6572
Published online Dec 14, 2022. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i46.6564
Published online Dec 14, 2022. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i46.6564
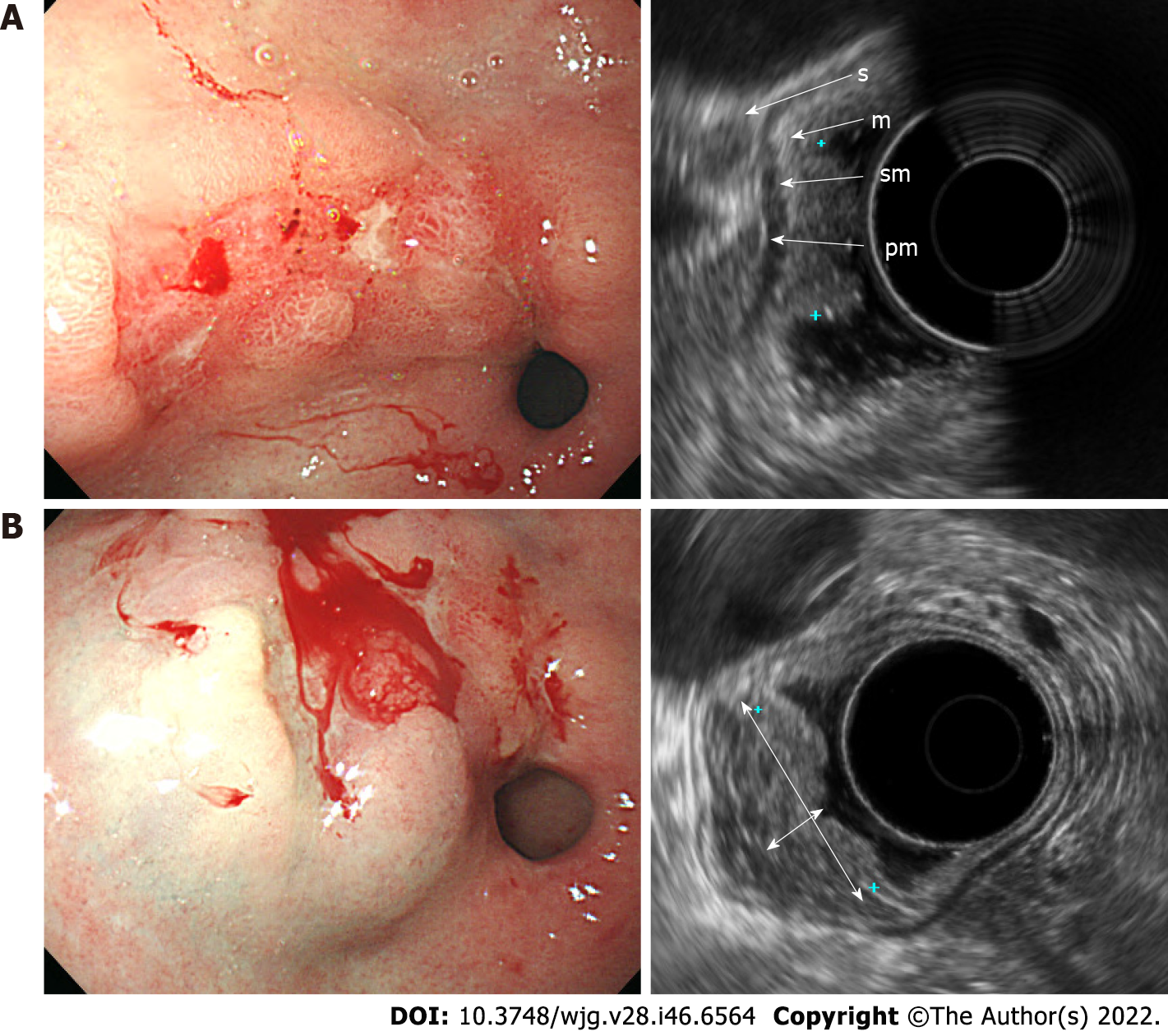
Figure 3 Endoscopic and ultrasonographic images and associated schematic diagrams of T1a early gastric cancer.
A: With the use of standard endoscopic ultrasonography (EUS), the boundary between the lesion and the submucosal layer was unclear. The distance between the mucosa and the submucosa was short. This lesion was diagnosed as T1b as it appeared to partially invade the submucosa when observed with standard EUS; B: With the use of endoscopic ultrasonography after submucosal saline injection (EUS-SSI), the boundary between the lesion and the submucosal layer was apparent. It was much easier to determine whether the lesion had invaded the submucosal layer due to the increased thickness of the gastric wall and an effect of increasing echoic contrast by saline cushion. This lesion was diagnosed as T1a as the submucosal layer was intact when observed with EUS-SSI. m: Mucosa; sm: Submucosa; pm: Proper muscle; s: Serosa; double arrow, saline layer.
- Citation: Park JY, Jeon TJ. Diagnostic evaluation of endoscopic ultrasonography with submucosal saline injection for differentiating between T1a and T1b early gastric cancer. World J Gastroenterol 2022; 28(46): 6564-6572
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v28/i46/6564.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v28.i46.6564