Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Gastroenterol. Dec 14, 2022; 28(46): 6522-6536
Published online Dec 14, 2022. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i46.6522
Published online Dec 14, 2022. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i46.6522
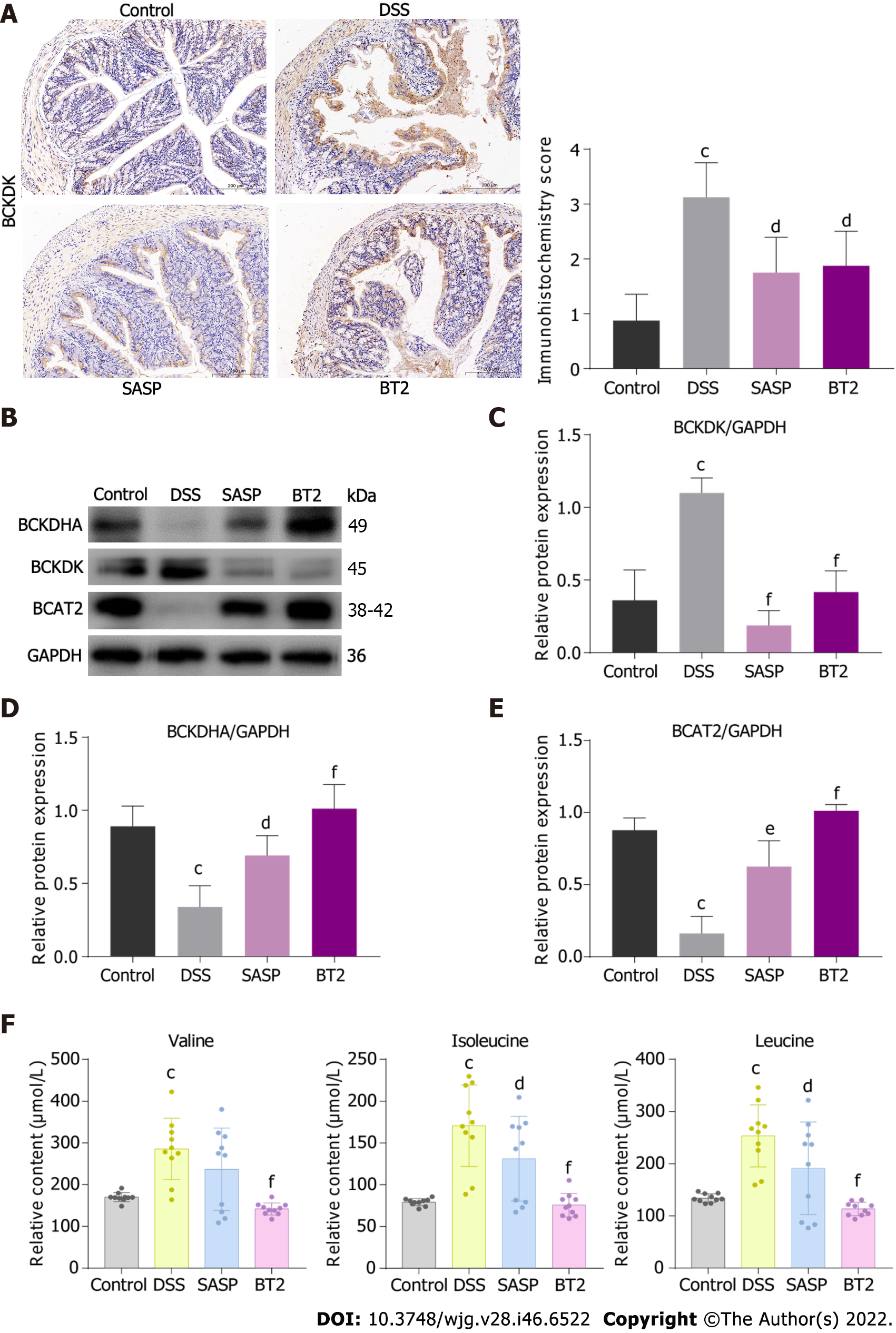
Figure 3 3,6-dichlorobenzo[b]thiophene-2-carboxylic acid improved branched-chain amino acid catabolism in dextran sodium sulfate-induced colitis mice.
A: The expression of branched-chain α-keto acid dehydrogenase kinase in colon sections was detected by immunohistochemical assays (n = 4, 200 × magnification); B-E: Western blot images and quantitative data of branched-chain amino acid (BCAA) catabolic enzymes in colon tissues (n = 3-4); F: The contents of BCAAs, including valine, leucine and isoleucine, in mouse serum were determined by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (n = 10). dP < 0.05, eP < 0.01, and fP < 0.001 vs the dextran sodium sulfate group; cP < 0.001 vs the control group. The data are shown as the mean ± SD. BCKDK: Branched-chain α-keto acid dehydrogenase kinase; DSS: Dextran sodium sulfate; SASP: Salazosulfapyridine; BT2: 3,6-dichlorobenzo[b]thiophene-2-carboxylic acid.
- Citation: He QZ, Wei P, Zhang JZ, Liu TT, Shi KQ, Liu HH, Zhang JW, Liu SJ. 3,6-dichlorobenzo[b]thiophene-2-carboxylic acid alleviates ulcerative colitis by suppressing mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1 activation and regulating intestinal microbiota. World J Gastroenterol 2022; 28(46): 6522-6536
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v28/i46/6522.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v28.i46.6522