Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Gastroenterol. Nov 28, 2022; 28(44): 6249-6257
Published online Nov 28, 2022. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i44.6249
Published online Nov 28, 2022. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i44.6249
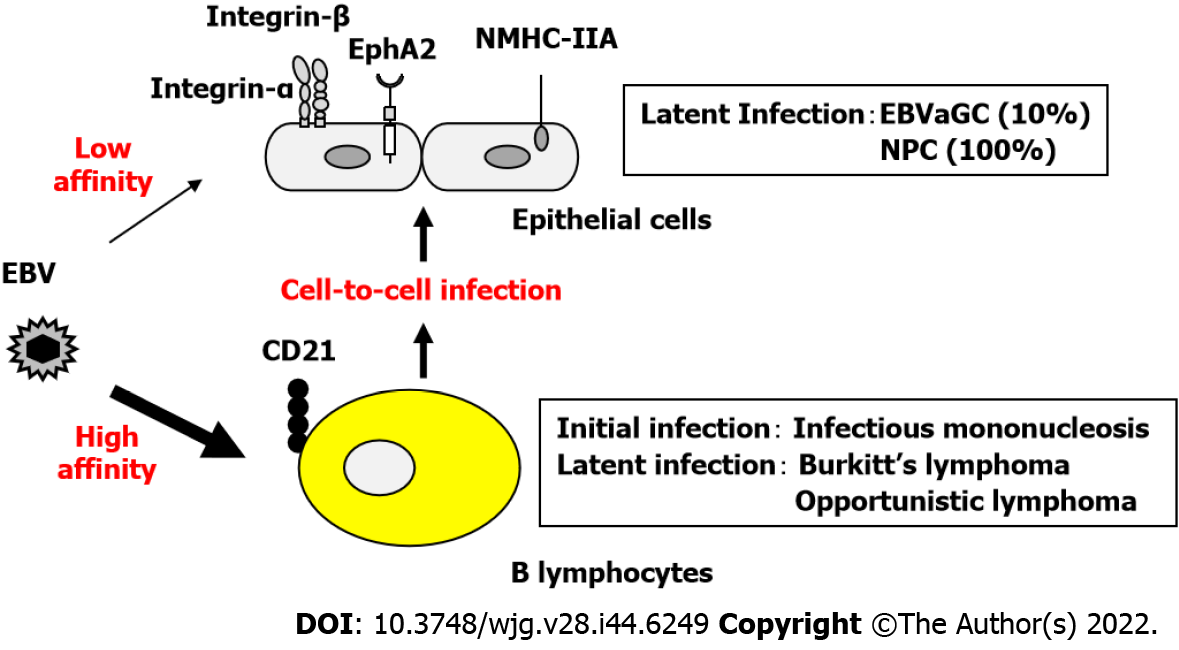
Figure 1 Epstein-Barr virus infects B lymphocytes and epithelial cells to form tumors.
Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) infects B lymphocytes and epithelial cells via the CD21 receptor and co-receptors, respectively. Although the efficiency of epithelial cell infection is extremely low, approximately 1000000 times lower than that of B lymphocytes, cell-to-cell EBV infection by B lymphocytes increased the efficiency of EBV infection by more than 1000-fold. The squares show the EBV infection status and disease names that are established differently depending on the cell type. EBV: Epstein-Barr virus; EBVaGC: Epstein-Barr virus-associated gastric cancer; NPC: Nasopharyngeal carcinoma.
- Citation: Iizasa H, Kartika AV, Fekadu S, Okada S, Onomura D, Wadi AFAA, Khatun MM, Moe TM, Nishikawa J, Yoshiyama H. Development of Epstein-Barr virus-associated gastric cancer: Infection, inflammation, and oncogenesis. World J Gastroenterol 2022; 28(44): 6249-6257
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v28/i44/6249.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v28.i44.6249