Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 28, 2022; 28(40): 5827-5844
Published online Oct 28, 2022. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i40.5827
Published online Oct 28, 2022. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i40.5827
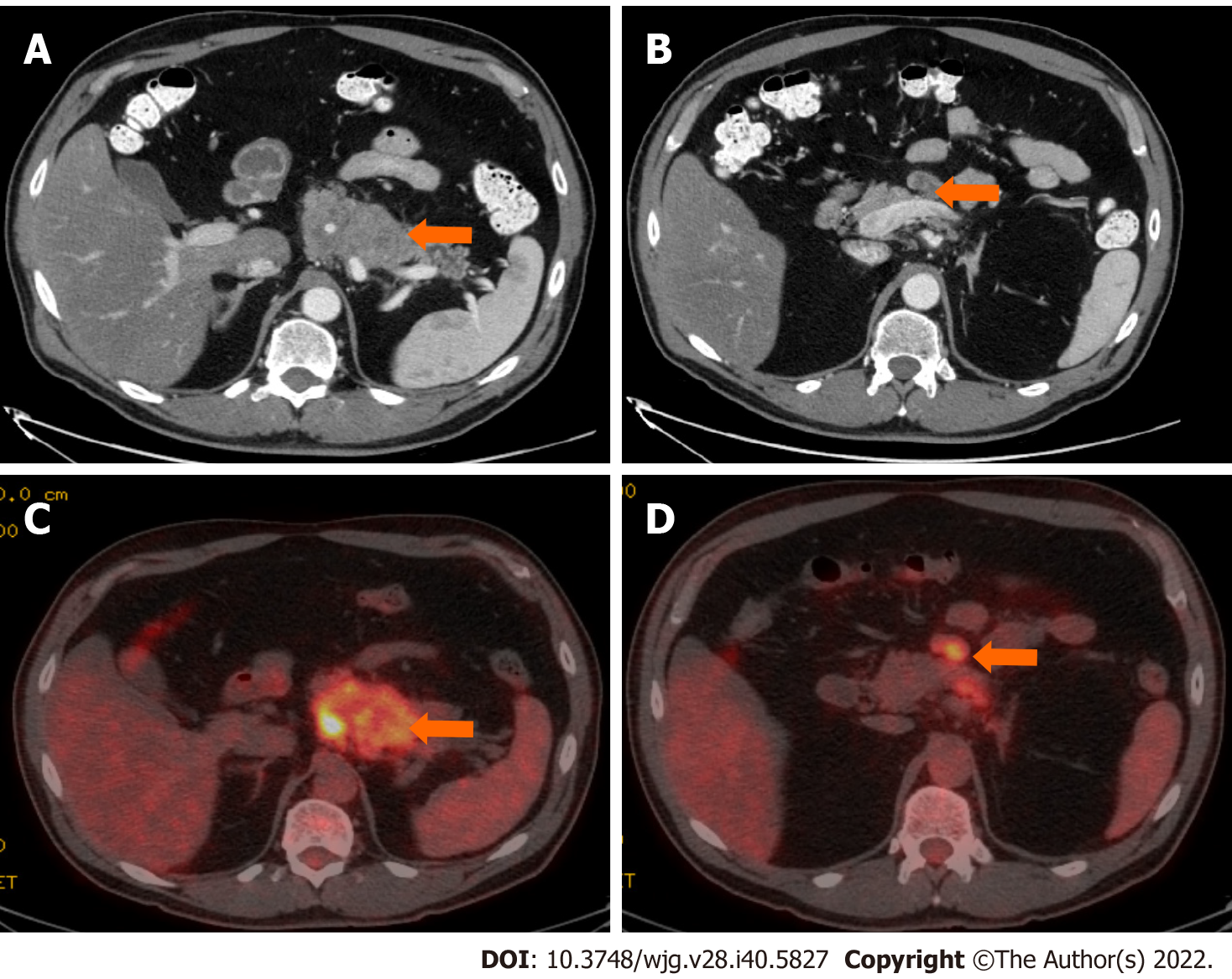
Figure 6 Stage IIB (T3, N1, M0).
A 61-year-old patient with acinar cell carcinoma. A: Axial post-contrast computed tomography (CT) image in the portovenous phase shows an infiltrative mass arising from the pancreatic body and tail (arrow); B: axial post-contrast CT images in the portovenous phase shows an enlarged mesenteric lymph node (arrow) measuring 2.6 cm × 1.2 cm; C: Axial positron emission tomography/CT image in the portovenous phase shows hypermetabolic pancreatic body and tail mass (arrow); D: Axial post-contrast CT images in the portovenous phase shows hypermetabolic enlarged mesenteric lymph node (arrow). Pathology of the mass revealed Acinar cell carcinoma with a metastatic mesenteric lymph node.
- Citation: Calimano-Ramirez LF, Daoud T, Gopireddy DR, Morani AC, Waters R, Gumus K, Klekers AR, Bhosale PR, Virarkar MK. Pancreatic acinar cell carcinoma: A comprehensive review. World J Gastroenterol 2022; 28(40): 5827-5844
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v28/i40/5827.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v28.i40.5827