Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 28, 2022; 28(40): 5784-5800
Published online Oct 28, 2022. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i40.5784
Published online Oct 28, 2022. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i40.5784
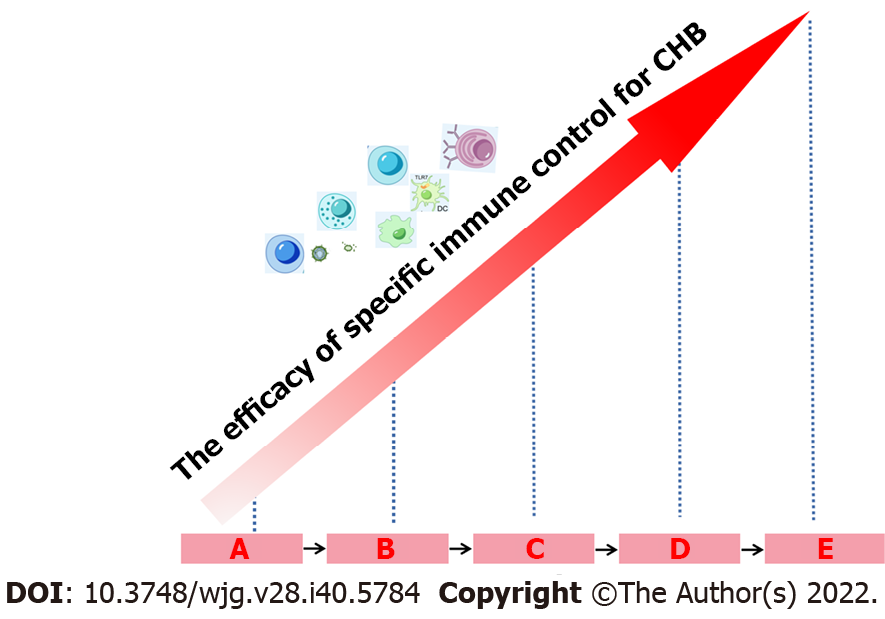
Figure 4 Interferon-α retreatment improves the efficacy of hepatitis B virus-specific immune control.
Interferon-α (IFN-α) retreatment can lead to various treatment outcomes, namely no response, hepatitis B virus (HBV) decline, partial cure and functional cure. Multiple frequencies of IFN-α treatment can potentially restore specific immune control to HBV infection and simultaneously increase the rate of partial cure and functional cure. A: Exhausted immune control to HBV before IFN-α therapy (Baseline); B: Without HBV decline following IFN-α therapy; C: HBV decline; D: Partial cure; E: Functional cure. CHB: Chronic hepatitis B.
- Citation: Yin GQ, Chen KP, Gu XC. Heterogeneity of immune control in chronic hepatitis B virus infection: Clinical implications on immunity with interferon-α treatment and retreatment. World J Gastroenterol 2022; 28(40): 5784-5800
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v28/i40/5784.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v28.i40.5784