Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 21, 2022; 28(39): 5707-5722
Published online Oct 21, 2022. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i39.5707
Published online Oct 21, 2022. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i39.5707
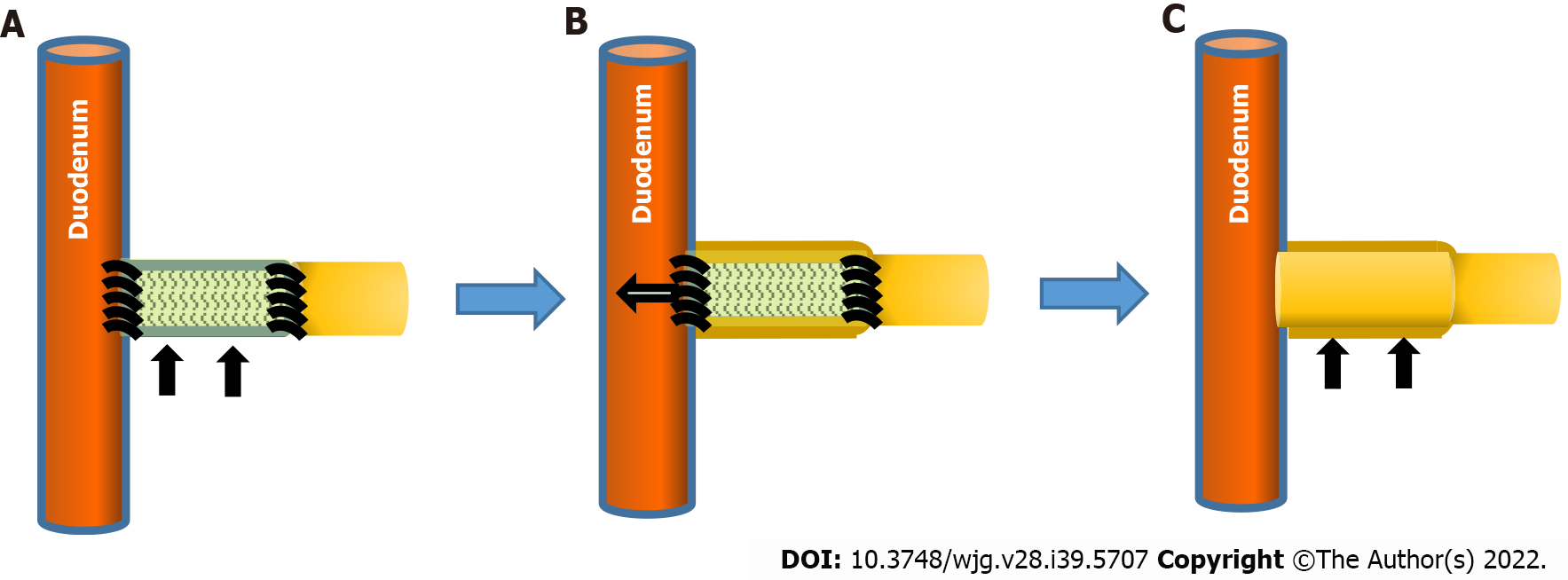
Figure 4 Regeneration of the neo-bile duct outside the short-term absorption type bile duct substitute.
A: Bile duct substitute (BDS) (black arrows) is anastomosed to the native extrahepatic bile duct; B: Immature cells attach around the BDS, forming a cylindrical cell mass outside the BDS. The bioabsorbable polymer that comprise BDS becomes fragile in the living body from approximately 3 wk and sheds to the duodenal side; C: After BDS is no longer present at the transplant site, immature cell clusters mature as bile duct cells and the bile ducts are regenerated as tissue (black arrows).
- Citation: Miyazawa M, Aikawa M, Takashima J, Kobayashi H, Ohnishi S, Ikada Y. Pitfalls and promises of bile duct alternatives: A narrative review. World J Gastroenterol 2022; 28(39): 5707-5722
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v28/i39/5707.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v28.i39.5707