Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 21, 2022; 28(39): 5707-5722
Published online Oct 21, 2022. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i39.5707
Published online Oct 21, 2022. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i39.5707
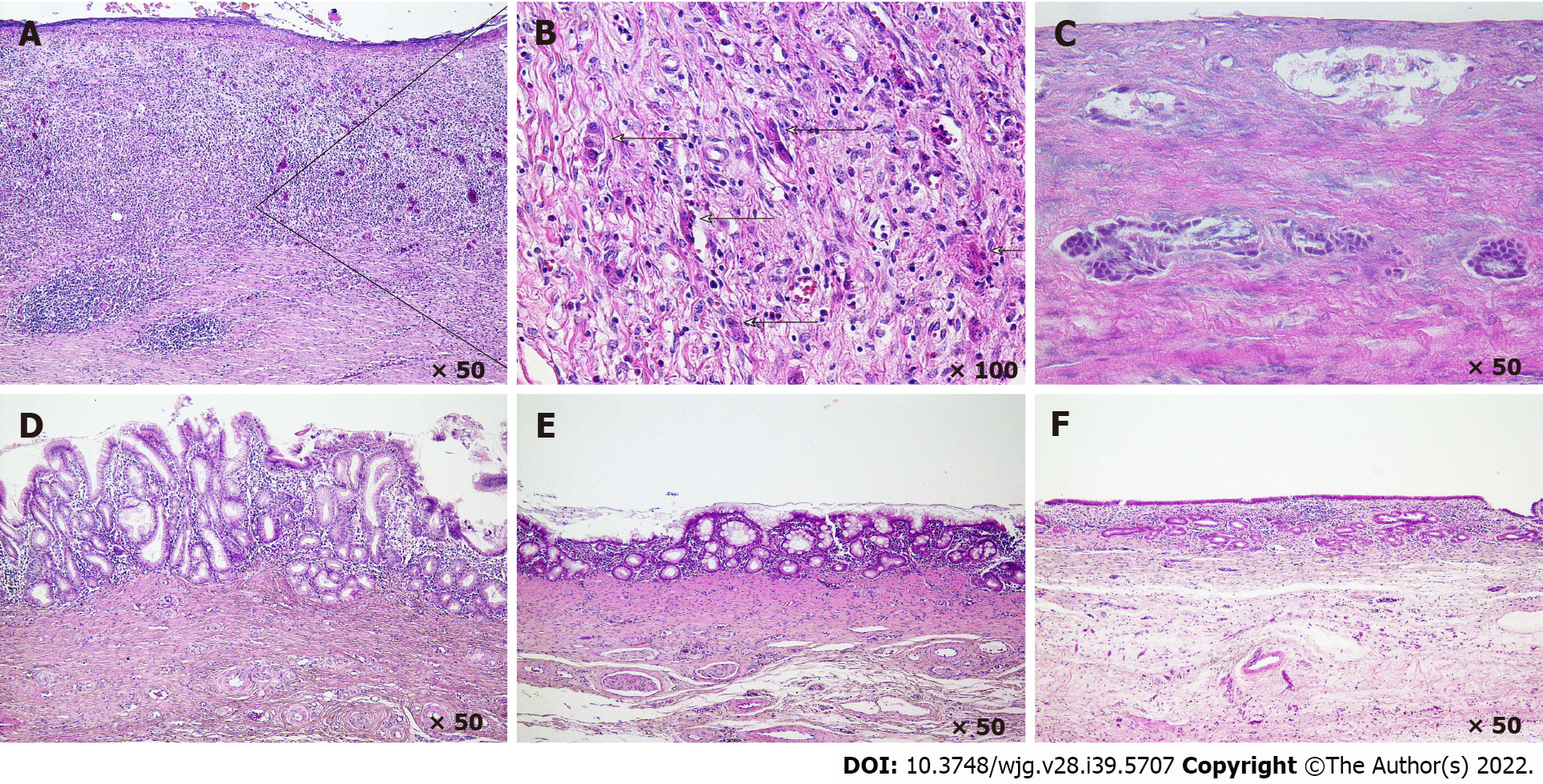
Figure 2 Histology of bile duct regeneration on the outside of the short-term absorption type bile duct substitute.
A and B: At 3 wk after bile duct substitute (BDS) implantation, a cell population in the stroma that may comprise the origin of the peribiliary gland is observed; C: At 5 wk after BDS implantation, a ring-shaped biliary gland-like structure is observed in which cell masses that are thought to form peribiliary glands are fused; D: At 7 wk after BDS implantation, many bile duct appendages are observed on the bile passage surface, and the epithelial surface exhibits a high papillary morphology; E: At 12 wk after BDS implantation, the number of peribiliary gland on the bile passage surface is decreased, the appendages begin to fuse, and the epithelial surface becomes more even; F: At 6 mo after BDS implantation, the epithelial surface becomes a single layer of cubic columnar epithelium, similar to the native bile duct.
- Citation: Miyazawa M, Aikawa M, Takashima J, Kobayashi H, Ohnishi S, Ikada Y. Pitfalls and promises of bile duct alternatives: A narrative review. World J Gastroenterol 2022; 28(39): 5707-5722
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v28/i39/5707.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v28.i39.5707