Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 14, 2022; 28(38): 5614-5625
Published online Oct 14, 2022. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i38.5614
Published online Oct 14, 2022. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i38.5614
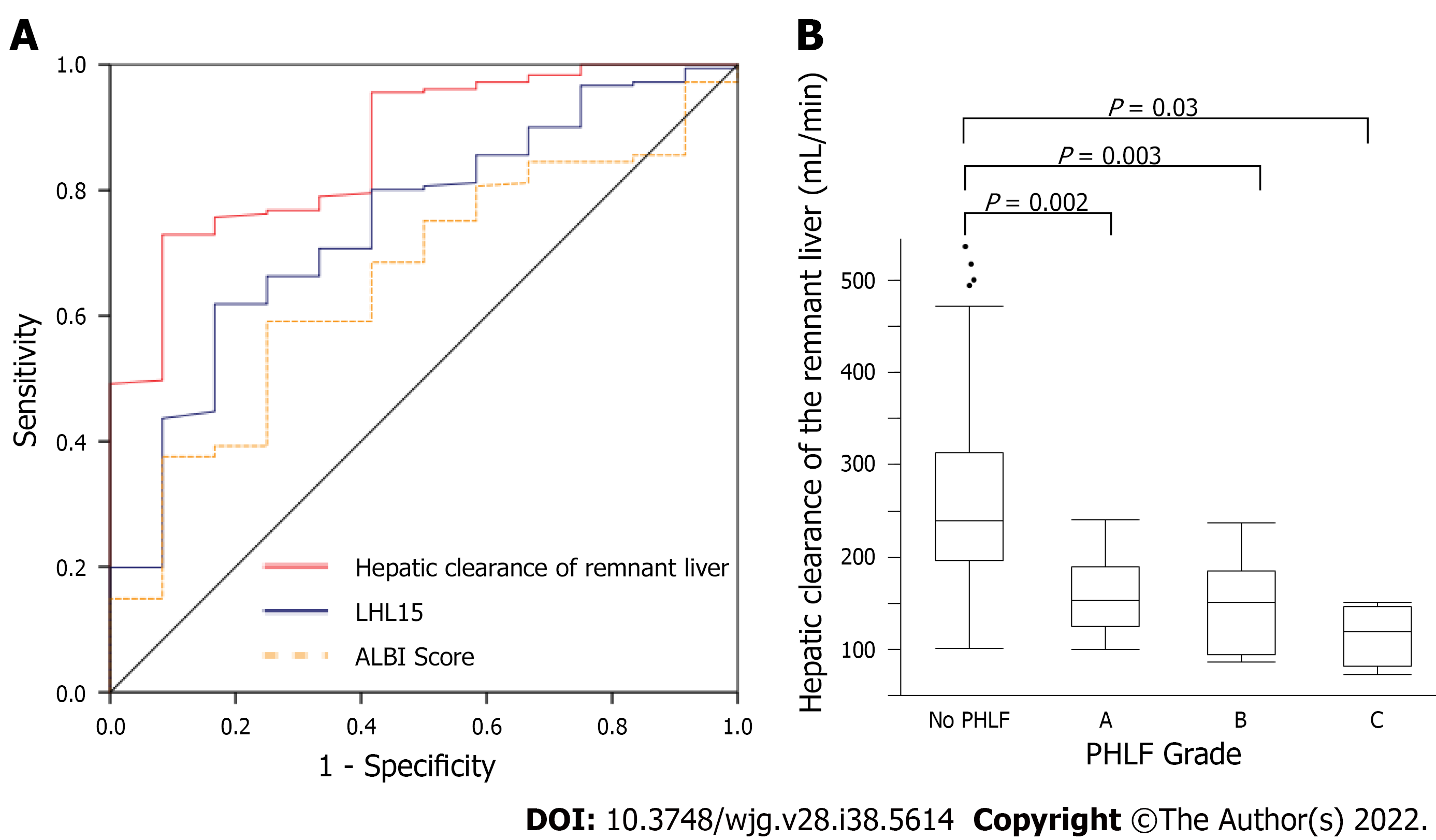
Figure 2 Analysis of hepatic clearance for post hepatectomy liver failure.
A: Receiver-operating characteristic curve analysis of hepatic clearance of the remnant liver, LHL15, and albumin–bilirubin (ALBI) score in predicting PHLF. The area under the receiver-operating characteristic curve values for analysis of hepatic clearance of the remnant liver, LHL15, and ALBI score in predicting PHLF were 0.868, 0.629, and 0.655, respectively; B: Hepatic clearance of the remnant liver for each PHLF. The median hepatic clearances of the remnant liver were 239, 153, 150.5, and 119.5 mL/min for normal, Grades A, B, and C, respectively. LHL15: liver to heart-plus-liver radioactivity at 15 min; ALBI score: Albumin–bilirubin score; PHLF: Post hepatectomy liver failure.
- Citation: Miki A, Sakuma Y, Ohzawa H, Saito A, Meguro Y, Watanabe J, Morishima K, Endo K, Sasanuma H, Shimizu A, Lefor AK, Yasuda Y, Sata N. Clearance of the liver remnant predicts short-term outcome in patients undergoing resection of hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol 2022; 28(38): 5614-5625
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v28/i38/5614.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v28.i38.5614