Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 14, 2022; 28(38): 5557-5572
Published online Oct 14, 2022. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i38.5557
Published online Oct 14, 2022. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i38.5557
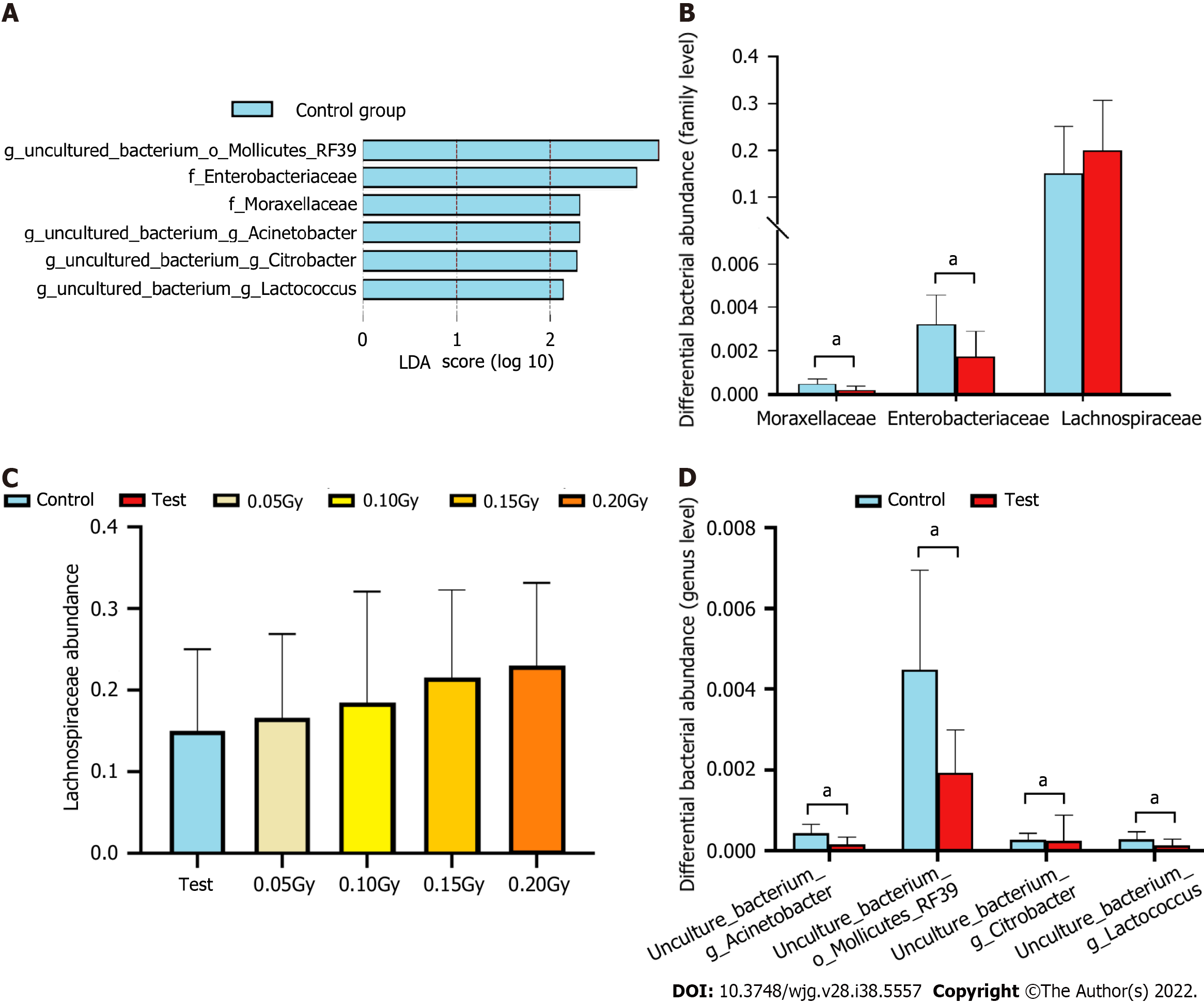
Figure 7 Altered gut microbiota composition in the radiation-exposed group compared with the control group.
A: Identification of the significantly different species in the radiation-exposed group and controls at the family and genus levels as determined by linear discriminant analysis (LDA) effect size (LEfSe). Only taxa meeting a significant linear discriminant analysis threshold value of > 2.0 and P < 0.05 are shown; B: Comparison of Moraxellaceae, Enterobacteriaceae, and Lachnospiraceae abundances between the test group and control group at the family level; C: Histogram of the abundance of Lachnospiraceae in the control and test subgroups; D: Comparison of the differential bacterial abundances between the test group and controls at the genus level, including uncultured_bacterium_g_Acinetobacter, uncultured_bacterium_o_Mollicutes_RF39, uncultured_bacterium_g_Citrobacter, and uncultured_bacterium_g_Lactococcus. aP < 0.05.
- Citation: Tong JY, Jiang W, Yu XQ, Wang R, Lu GH, Gao DW, Lv ZW, Li D. Effect of low-dose radiation on thyroid function and the gut microbiota. World J Gastroenterol 2022; 28(38): 5557-5572
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v28/i38/5557.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v28.i38.5557