Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 14, 2022; 28(38): 5547-5556
Published online Oct 14, 2022. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i38.5547
Published online Oct 14, 2022. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i38.5547
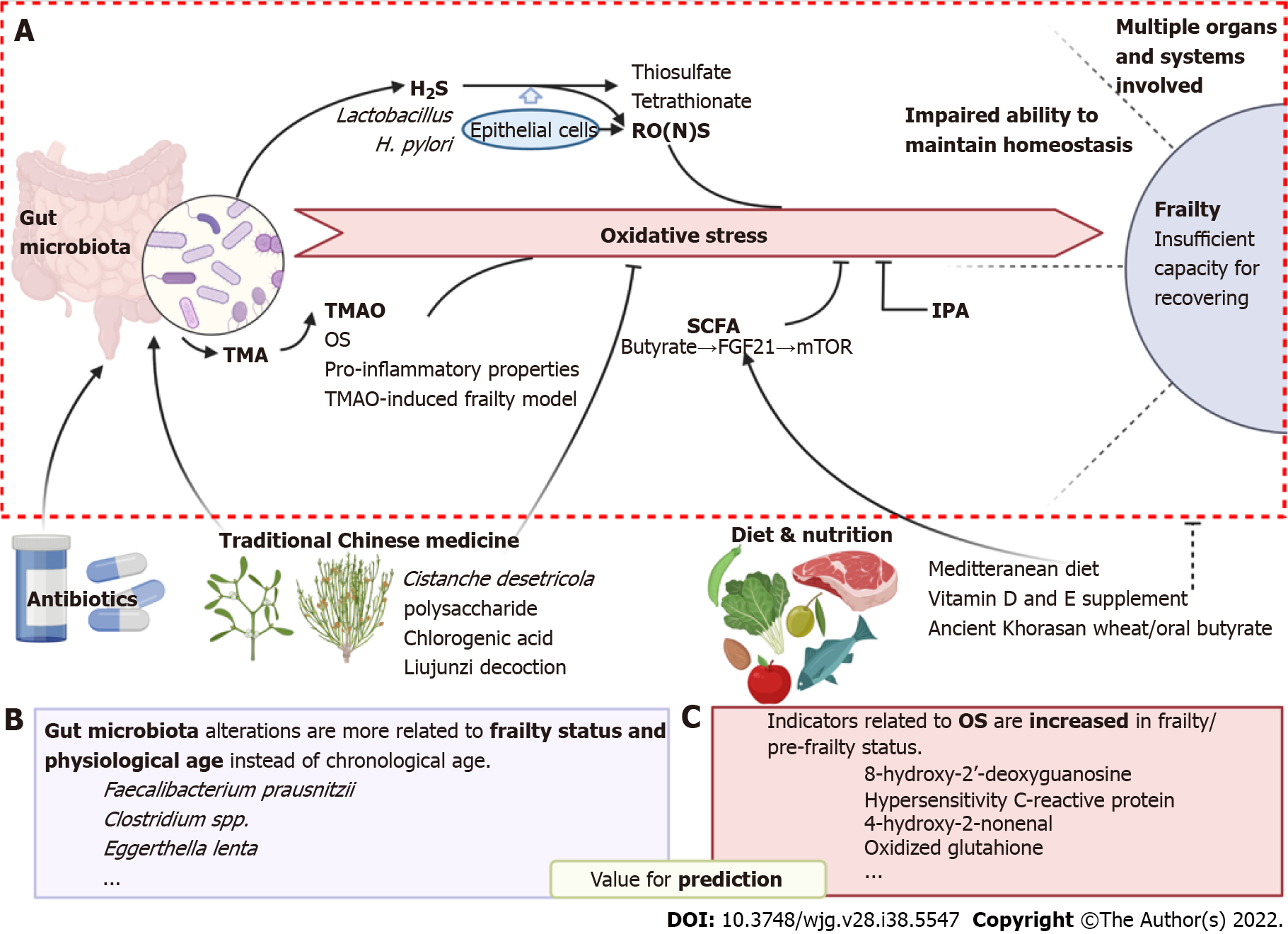
Figure 1 Oxidative stress is involved in the association between the gut microbiota and frailty syndrome.
A: Involving molecular and pathways of how oxidative stress bridges gut microbiota and frailty; B and C: Potential bacterial species and oxidative markers which are valuable for prediction of frailty are listed in B and C, respectively. In addition, possible intervene strategies including traditional Chinese medicine and diet & nutrition are shown at the bottom of the figure. Created with BioRender.com. OS: Oxidative stress; TMA: Trimethylamine; SCFA: Short-chain fatty acid; FGF21: Fibroblast growth factor 21; IPA: Indole-3-propionic acid; RONS: Reactive oxygen and nitrogen species; 8-OdG: 8-hydroxy-2’-deoxyguanosine; 4-HNE: 4-hydroxy-2-nonenal; GSSG: Glutathione.
- Citation: Chen SY, Wang TY, Zhao C, Wang HJ. Oxidative stress bridges the gut microbiota and the occurrence of frailty syndrome. World J Gastroenterol 2022; 28(38): 5547-5556
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v28/i38/5547.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v28.i38.5547