Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 7, 2022; 28(37): 5420-5443
Published online Oct 7, 2022. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i37.5420
Published online Oct 7, 2022. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i37.5420
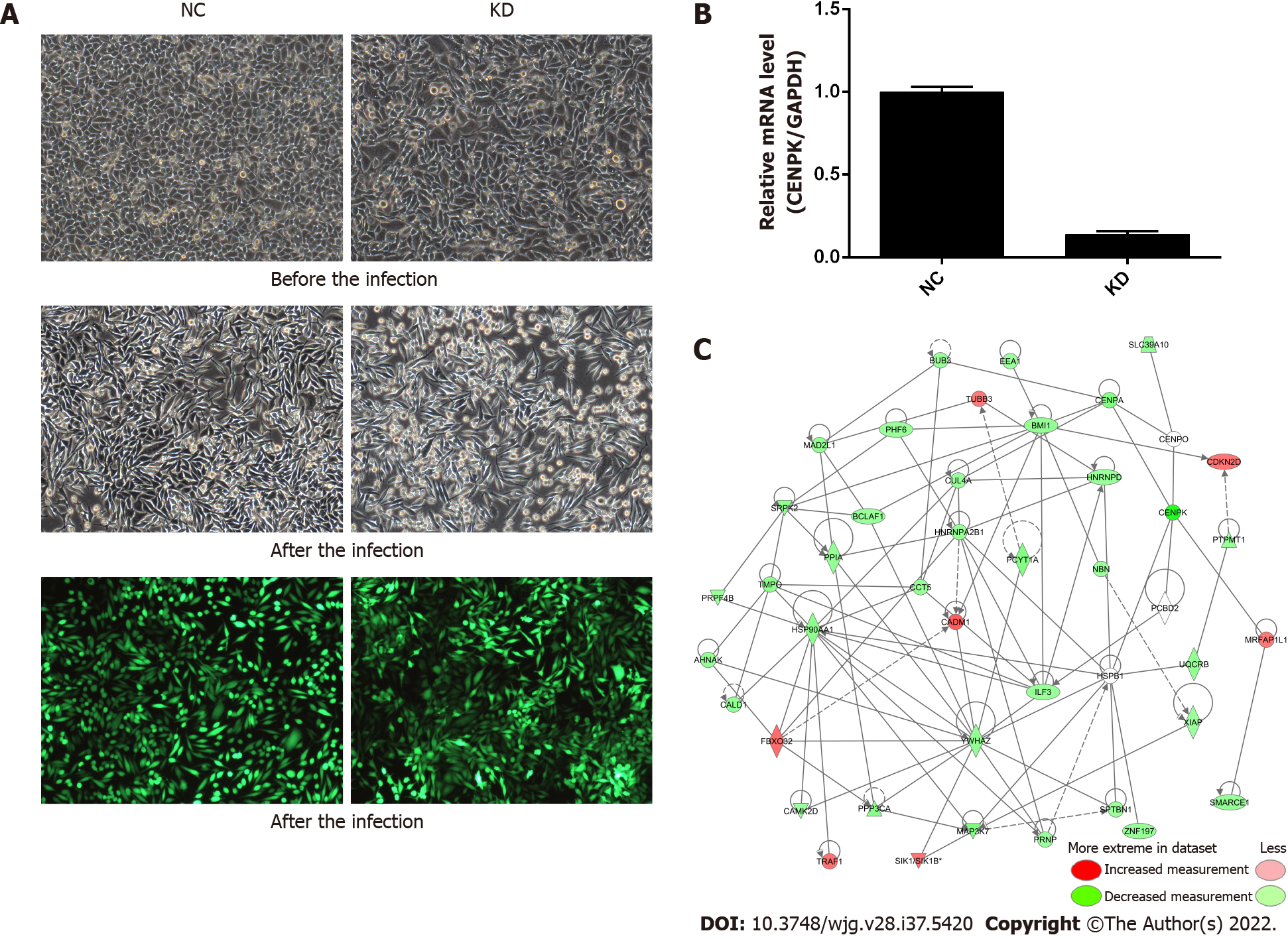
Figure 1 Centromere protein K affects the proliferation and invasion of colorectal cancer cells by acting on downstream genes.
A: Morphology of RKO cells in NC and KD groups before and after lentivirus infection as well as infection efficiency assessed using fluorescence microscopy (× 100 magnification); B: Relative expression level of centromere protein K by quantitative polymerase chain reaction in NC and KD groups; C: Gene interaction network diagram. Genes, proteins, and chemicals are represented by different shapes; color labeling of molecules is shown in the illustration. NC: RKO cells infected with centromere protein K negative control virus; KD: RKO cells with lentivirus-mediated short hairpin RNA interference of centromere protein K; CENPK: Centromere protein K.
- Citation: Li X, Han YR, Xuefeng X, Ma YX, Xing GS, Yang ZW, Zhang Z, Shi L, Wu XL. Lentivirus-mediated short hairpin RNA interference of CENPK inhibits growth of colorectal cancer cells with overexpression of Cullin 4A. World J Gastroenterol 2022; 28(37): 5420-5443
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v28/i37/5420.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v28.i37.5420