Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Gastroenterol. Sep 28, 2022; 28(36): 5250-5264
Published online Sep 28, 2022. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i36.5250
Published online Sep 28, 2022. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i36.5250
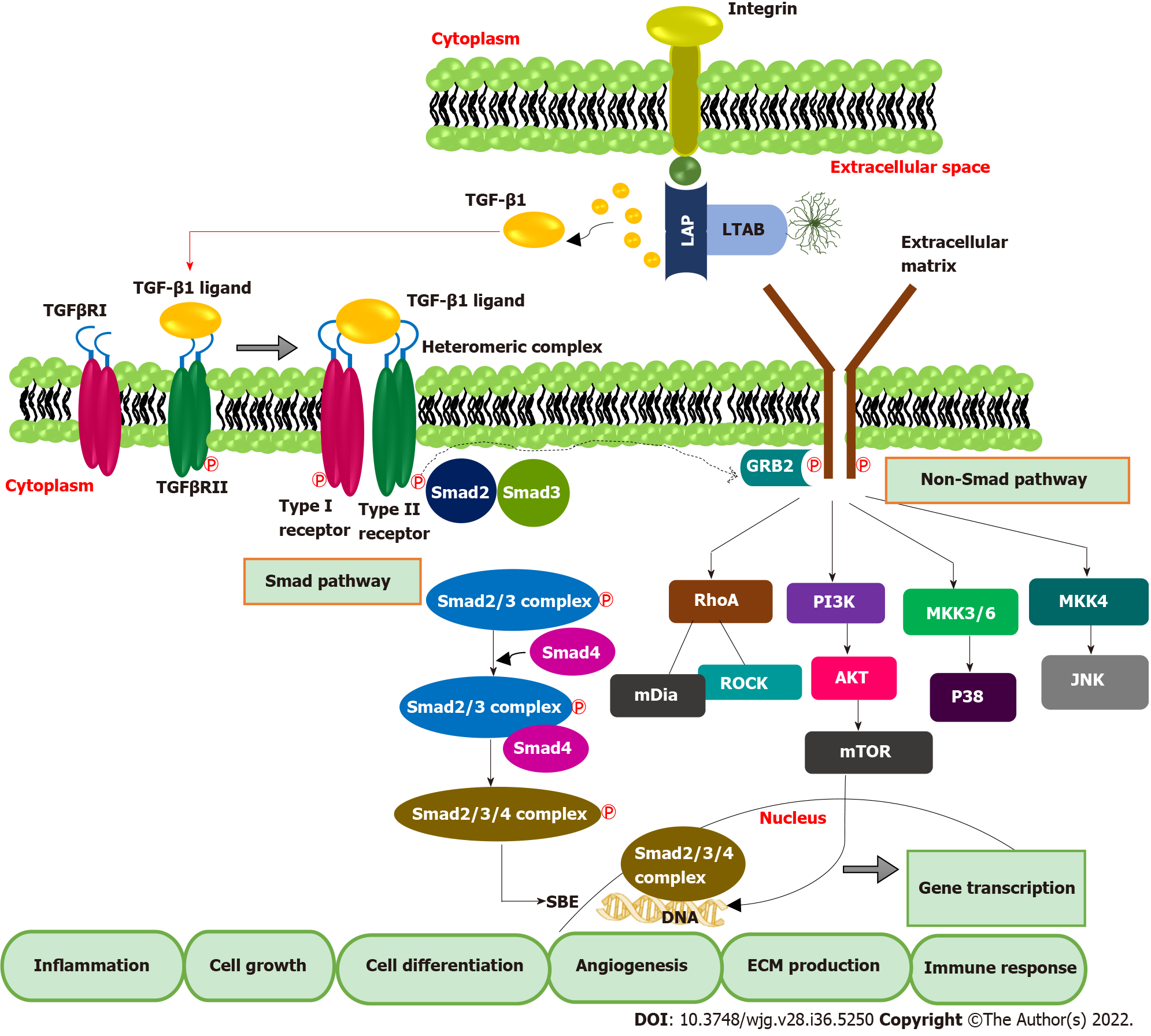
Figure 2 Transforming growth factor-beta 1 signaling pathway.
Smad and non-Smad pathways mainly regulate transforming growth factor-beta 1 (TGF-β1) signal transduction. Integrin signaling triggers the activation and release of TGF-β1 from LCC (large latent complex). Activated TGF-β1 binds TGF-β type II receptor, leading to phosphorylation of TGF-β type I receptor and associated Smad proteins, mainly Smad-2 and Smad-3. Phosphorylated Smad-2 and 3, complex with the co-Smad, Smad-7, form a ternary complex. This ternary complex then translocates into the nucleus, binds to Smad binding elements and regulates the transcription of TGF-β-related genes. TGF: Transforming growth factor; LAP: Latency associated protein; LTAB: Latent transforming growth factor-beta binding protein; SBE: Smad binding elements; ECM: Extracellular matrix; mTOR: Mammalian target of Rapamycin; PI3K: Phosphoinositide 3-kinase; AKT: AKT serine/threonine kinase 1; MKK: Mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase; JNK: C-Jun N-terminal kinase.
- Citation: Devan AR, Pavithran K, Nair B, Murali M, Nath LR. Deciphering the role of transforming growth factor-beta 1 as a diagnostic-prognostic-therapeutic candidate against hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol 2022; 28(36): 5250-5264
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v28/i36/5250.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v28.i36.5250