Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Gastroenterol. Sep 21, 2022; 28(35): 5154-5174
Published online Sep 21, 2022. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i35.5154
Published online Sep 21, 2022. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i35.5154
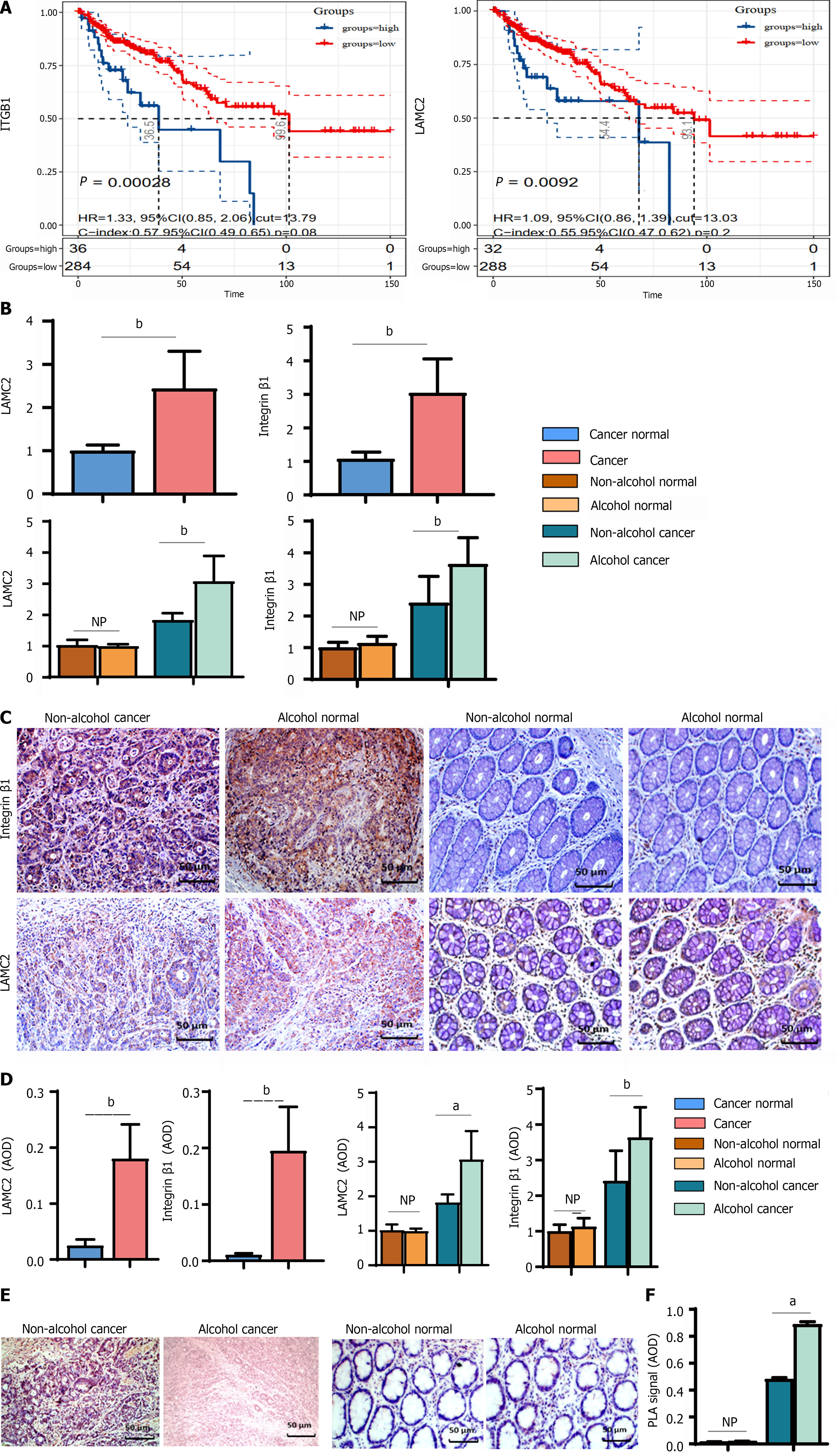
Figure 7 Alcohol consumption increased the expression and interaction of laminin-γ2 and integrin-β1 in colorectal cancer rats.
The bars represent the mean ± SD (n = 8). A: Survival analysis of integrin-β1 (ITGB1) and laminin-γ2 (LAMC2) in colorectal cancer; B: The mRNA levels of ITGB1 and LAMC2 determined by quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction in clinical samples; C: Representative immunohistochemical (IHC) images of ITGB1 and LAMC2 in clinical samples (× 400); D: The quantifications of the protein levels of ITGB1 and LAMC2 determined by IHC in clinical samples; E and F: Duolink proximity ligation assay (PLA) verified the interactions between ITGB1 and LAMC2 in clinical samples. The statistical analysis of PLA positive signals was performed by counting the average optical density under a light microscope. Compared with the non-alcohol group: bP < 0.01, aP < 0.05. LAMC2: Laminin-γ2; ITGB1: Integrin-β1; qRT-PCR: Quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction; PLA: Proximity ligation assay; IHC: Immunohistochemical staining; AOD: Average optical density. Cancer normal group: cancer adjacent tissue group. NP: No statistical difference.
- Citation: Nong FF, Liang YQ, Xing SP, Xiao YF, Chen HH, Wen B. Alcohol promotes epithelial mesenchymal transformation-mediated premetastatic niche formation of colorectal cancer by activating interaction between laminin-γ2 and integrin-β1. World J Gastroenterol 2022; 28(35): 5154-5174
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v28/i35/5154.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v28.i35.5154