Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Gastroenterol. Sep 21, 2022; 28(35): 5154-5174
Published online Sep 21, 2022. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i35.5154
Published online Sep 21, 2022. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i35.5154
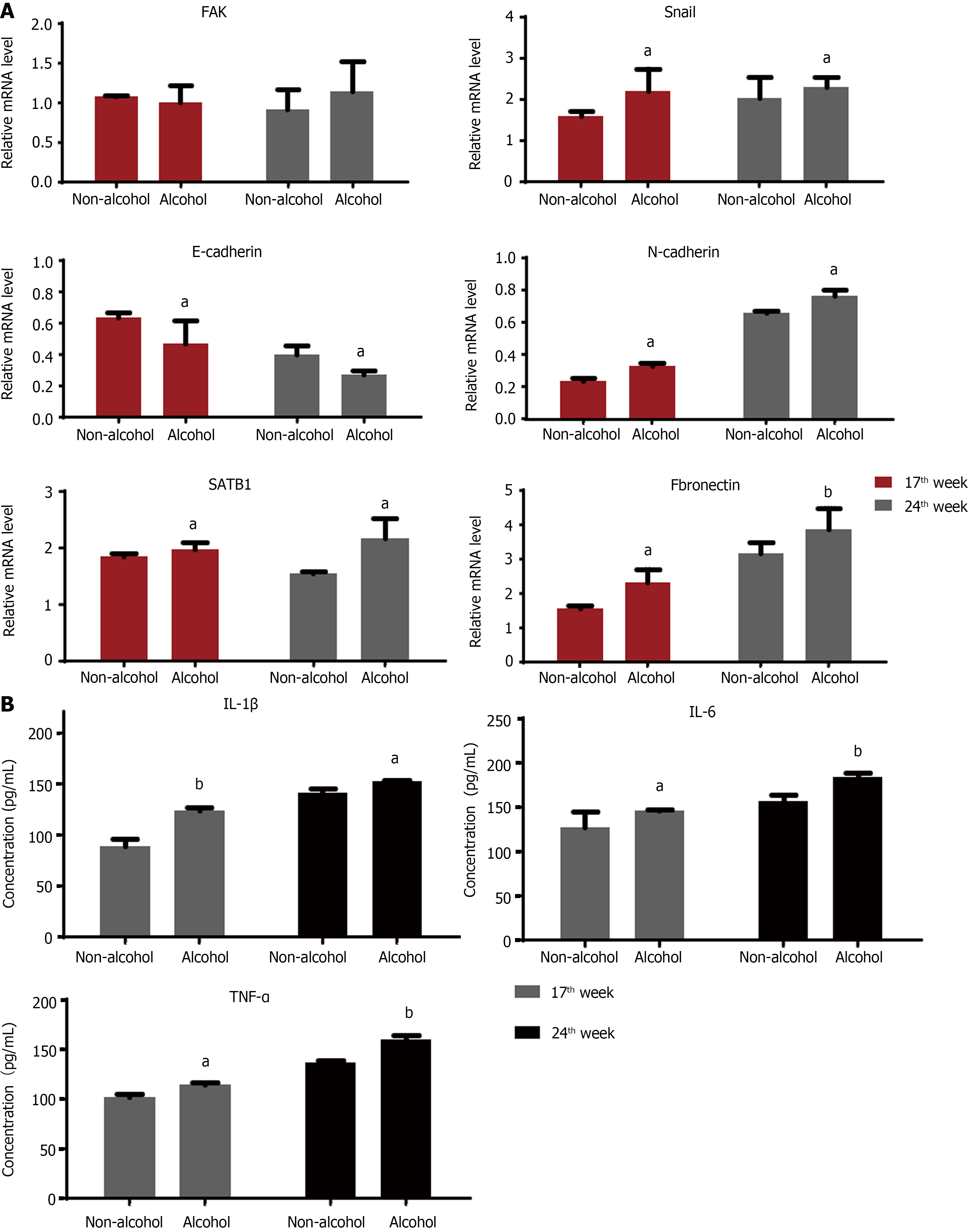
Figure 6 Alcohol consumption regulated the mRNA expression of epithelial mesenchymal transformation-related markers and proinflammatory factors in colorectal cancer rats.
The bars represent the mean ± SD (n = 8). A: Quantification of the mRNA levels of snail, focal adhesion kinase, fibronectin, N-cadherin, E-cadherin and special AT-rich sequence binding protein 1 in each group analyzed by quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction; B: Tumor necrosis factor-α, interleukin-6 (IL-6) and IL-1β levels in each group. Compared with the non-alcohol group: bP < 0.01, aP < 0.05. SATB1: Special AT-rich sequence binding protein 1; FAK: Focal adhesion kinase; IL-1β: Interleukin-1β; IL-6: Interleukin-6; TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor-α.
- Citation: Nong FF, Liang YQ, Xing SP, Xiao YF, Chen HH, Wen B. Alcohol promotes epithelial mesenchymal transformation-mediated premetastatic niche formation of colorectal cancer by activating interaction between laminin-γ2 and integrin-β1. World J Gastroenterol 2022; 28(35): 5154-5174
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v28/i35/5154.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v28.i35.5154