Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Gastroenterol. Sep 14, 2022; 28(34): 5058-5075
Published online Sep 14, 2022. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i34.5058
Published online Sep 14, 2022. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i34.5058
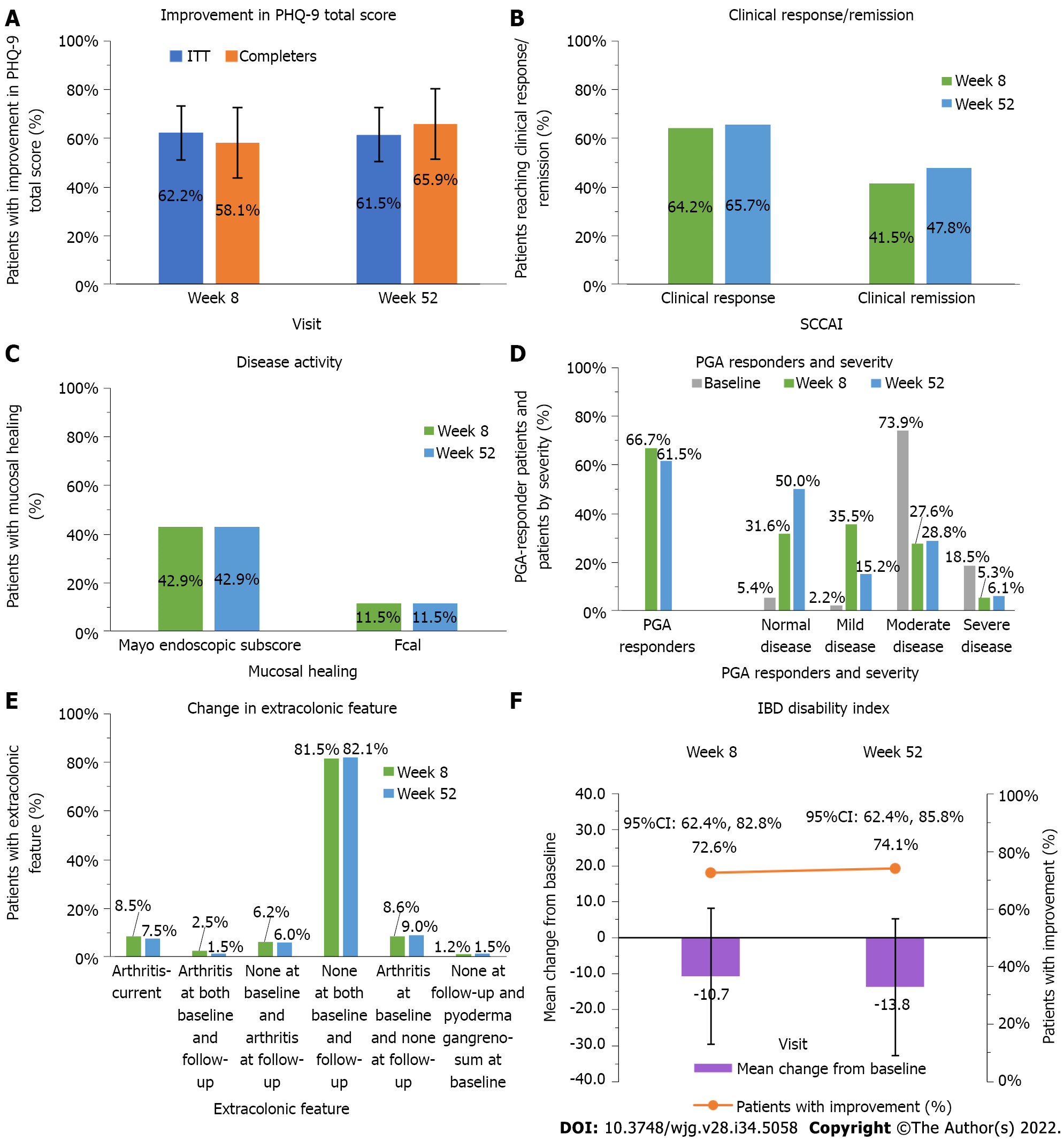
Figure 2 Effect of a real-world adalimumab treatment on effectiveness and patient-reported outcomes in moderate-to-severe ulcerative colitis patients.
A: Proportion of patients who improved in Patient Health Questionnaire–9 items total score at week 52 in the intent-to-treat and completers populations (%), improvement defined as change from baseline, bars show 95% confidence intervals; B: Proportion of patients achieving clinical response/remission at weeks 8 and 52 (%), measured by the simple clinical colitis activity index (SCCAI) ≤ 2; C: Proportion of patients with endoscopic healing at weeks 8 and 52 (%), healing measured as a Mayo endoscopic subscore of 0 or 1 or a fecal calprotectin concentration < 50 μg/g; D: Proportion of patients with extracolonic feature at weeks 8 and 52 (%), measured by the SCCAI; E: Proportion of physician’s global assessment responders and severity at weeks 8 and 52 (%), responders defined as with a decrease from baseline of ≥ 1 point; F: inflammatory bowel disease index mean change from baseline and proportion of patients who improved (%). Bars represent standard deviations. PRO: Patient-reported outcome; UC: Ulcerative colitis; PHQ-9: Patient Health Questionnaire–9; IBD: Inflammatory bowel disease; SCCAI: Simple clinical colitis activity index; ITT: Intent-to-treat; PGA: Physician’s global assessment.
- Citation: Bessissow T, Nguyen GC, Tarabain O, Peyrin-Biroulet L, Foucault N, McHugh K, Ruel J. Impact of adalimumab on disease burden in moderate-to-severe ulcerative colitis patients: The one-year, real-world UCanADA study. World J Gastroenterol 2022; 28(34): 5058-5075
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v28/i34/5058.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v28.i34.5058