Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Gastroenterol. Sep 7, 2022; 28(33): 4787-4811
Published online Sep 7, 2022. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i33.4787
Published online Sep 7, 2022. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i33.4787
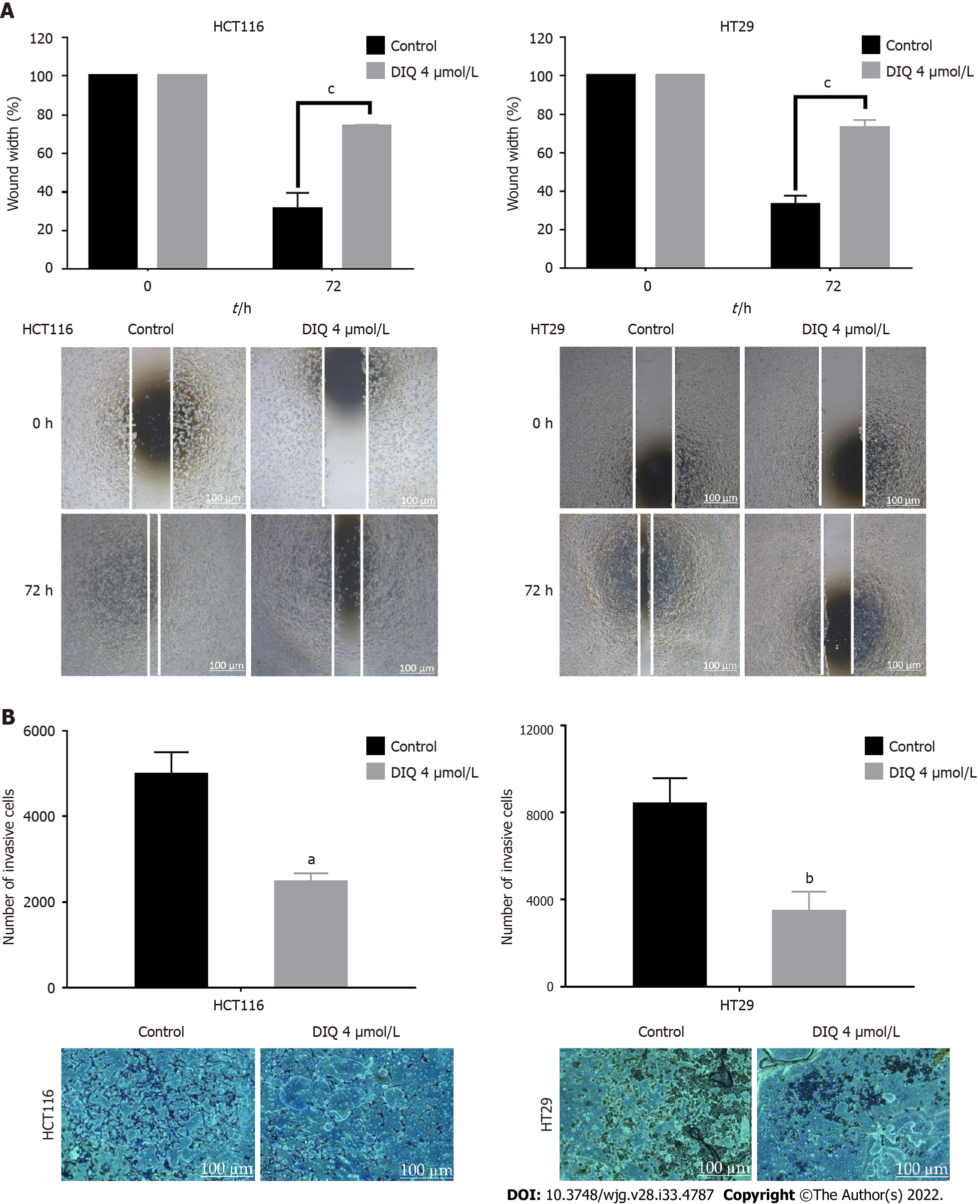
Figure 3 Diiminoquinone reduced the migration and the invasion of HCT116 and HT29 colorectal cancer cells.
A: HCT116 and HT29 cells were seeded in 24-well plates. A scratch was made on confluent cells using a 200 μL tip, and images were taken at 0 h and 72 h with or without the indicated treatment. Quantification of the distance of the wound closure was assessed over time. Representative images of wound healing assay at × 5 magnification (scale = 100 μm); B: Colorectal cancer cells were seeded onto the Matrigel-coated membrane in the top chamber of the transwell and were either treated or not with the indicated concentration in the presence of fetal bovine serum in the lower chamber. Cells that invaded to the lower chamber after 72 h were fixed, stained with hematoxylin and eosin, counted, and are represented as the number of invading cells compared to the control. Data represent an average of three independent experiments and is reported as mean ± standard error of the mean (aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, cP < 0.001). DIQ: Diiminoquinone.
- Citation: Monzer A, Wakimian K, Ballout F, Al Bitar S, Yehya A, Kanso M, Saheb N, Tawil A, Doughan S, Hussein M, Mukherji D, Faraj W, Gali-Muhtasib H, Abou-Kheir W. Novel therapeutic diiminoquinone exhibits anticancer effects on human colorectal cancer cells in two-dimensional and three-dimensional in vitro models. World J Gastroenterol 2022; 28(33): 4787-4811
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v28/i33/4787.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v28.i33.4787