Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Gastroenterol. Sep 7, 2022; 28(33): 4787-4811
Published online Sep 7, 2022. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i33.4787
Published online Sep 7, 2022. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i33.4787
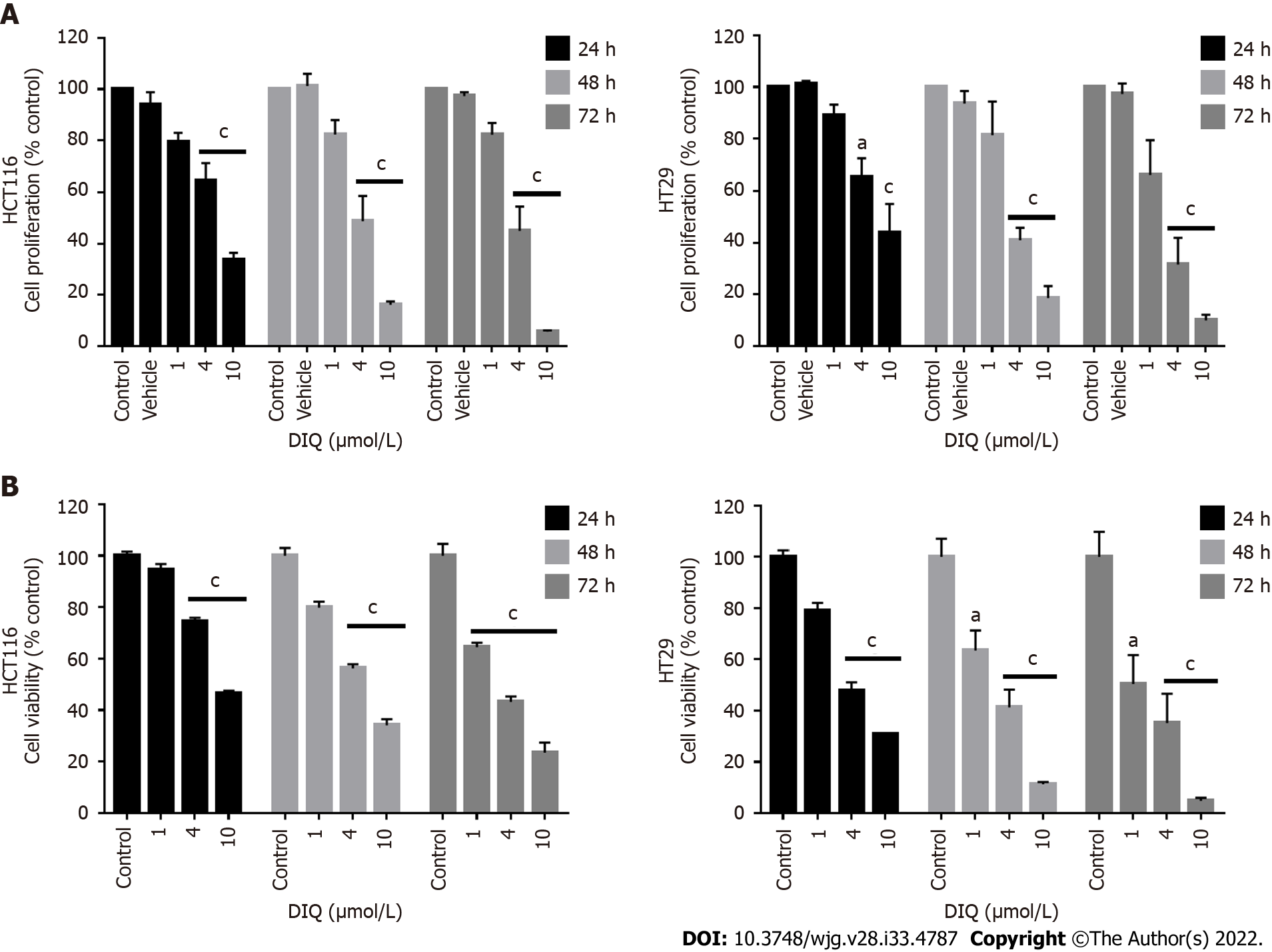
Figure 2 Diiminoquinone reduced the proliferation and the viability of HCT116 and HT29 colorectal cancer cell lines in a time- and dose-dependent manner.
A: The anticancer effect of different concentrations of diiminoquinone (DIQ) on the proliferation of HCT116 and HT29 cells using the MTT assay was determined in triplicates at 24, 48, and 72 h. Results were expressed as the percentage of proliferation of the treated group compared to the control at every time point; B: The anticancer effect of different concentrations of DIQ on the viability of HCT116 and HT29 cells using the trypan blue exclusion assay was determined in triplicates at 24, 48, and 72 h. Results were expressed as percentage of viable cells of the treated group compared to the control at every time point. Data represent an average of three independent experiments and is reported as mean ± standard error of the mean (aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, cP < 0.001).
- Citation: Monzer A, Wakimian K, Ballout F, Al Bitar S, Yehya A, Kanso M, Saheb N, Tawil A, Doughan S, Hussein M, Mukherji D, Faraj W, Gali-Muhtasib H, Abou-Kheir W. Novel therapeutic diiminoquinone exhibits anticancer effects on human colorectal cancer cells in two-dimensional and three-dimensional in vitro models. World J Gastroenterol 2022; 28(33): 4787-4811
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v28/i33/4787.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v28.i33.4787