Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 28, 2022; 28(32): 4620-4634
Published online Aug 28, 2022. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i32.4620
Published online Aug 28, 2022. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i32.4620
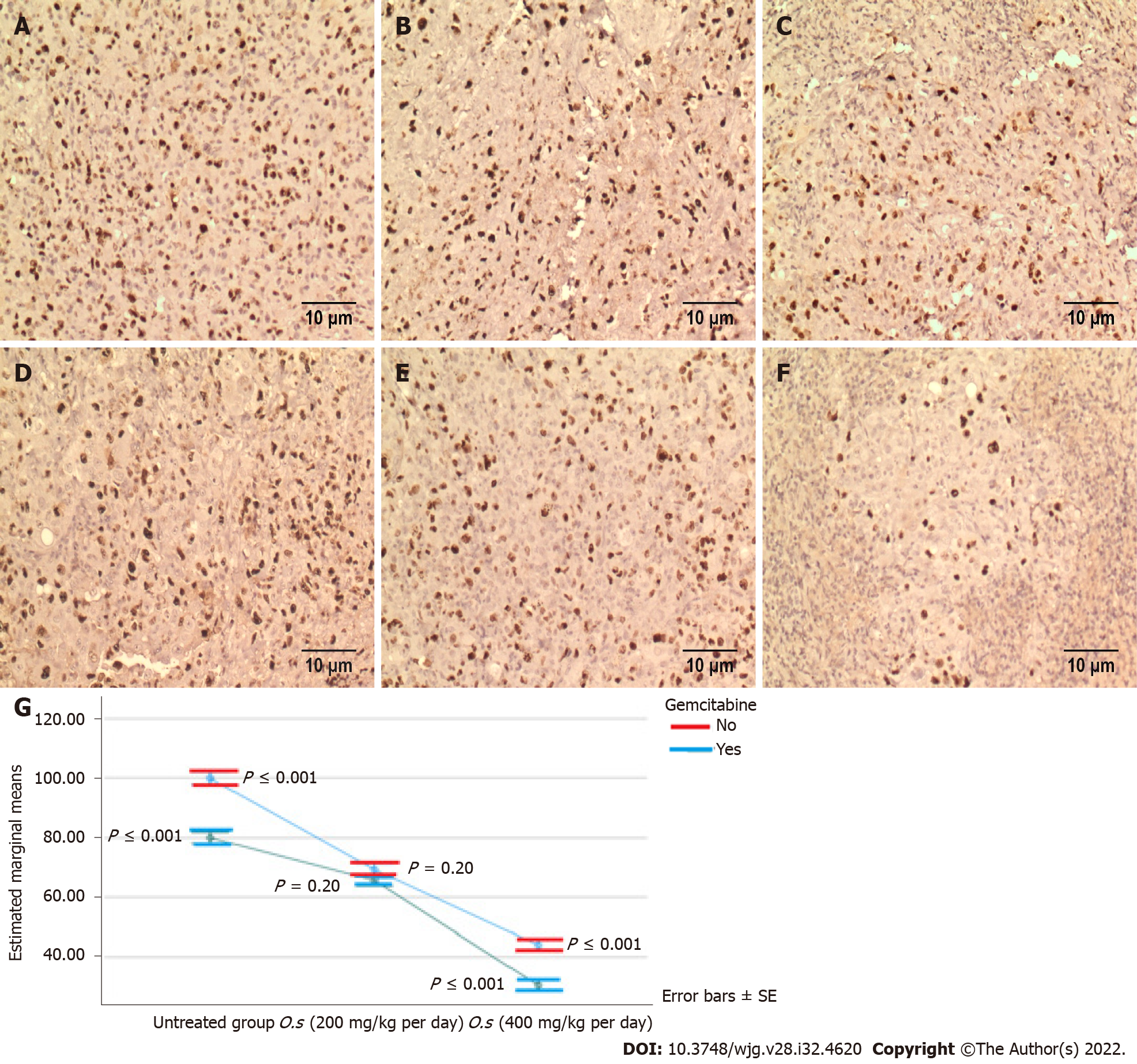
Figure 6 Ki67 proliferation protein expression in treated and untreated groups.
A: Untreated group; B: Orthosiphon stamineus (O.s) (200 mg/kg per day); C: O.s (400 mg/kg per day); D: Gemcitabine (10 mg/kg per 3 d); E: O.s (200 mg/kg per day) + gemcitabine (10 mg/kg per 3 d); F: O.s (400 mg/kg per day) + gemcitabine (10 mg/kg per 3 d); G: Estimated marginal means of Ki67. Single treatment either by C5EOSEW5050ESA or gemcitabine significantly reduced the Ki67 protein expression in tumour tissues compared to the untreated group. No significant reduction of Ki67 protein expression was noted between the groups treated by C5EOSEW5050ESA 200 mg/kg per day and the gemcitabine combination. Combination treatment of C5EOSEW5050ESA 400 mg/kg per day and gemcitabine synergistically reduced Ki67 protein expression in tumour tissue compared to a single treatment. Error bars represent standard deviations. Statistics analysis (Two-way ANOVA, n = 6 animals per group) using SPSS software. O.s: Orthosiphon stamineus.
- Citation: Yehya AHS, Subramaniam AV, Asif M, Kaur G, Abdul Majid AMS, Oon CE. Anti-tumour activity and toxicological studies of combination treatment of Orthosiphon stamineus and gemcitabine on pancreatic xenograft model. World J Gastroenterol 2022; 28(32): 4620-4634
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v28/i32/4620.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v28.i32.4620