Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 21, 2022; 28(31): 4338-4350
Published online Aug 21, 2022. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i31.4338
Published online Aug 21, 2022. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i31.4338
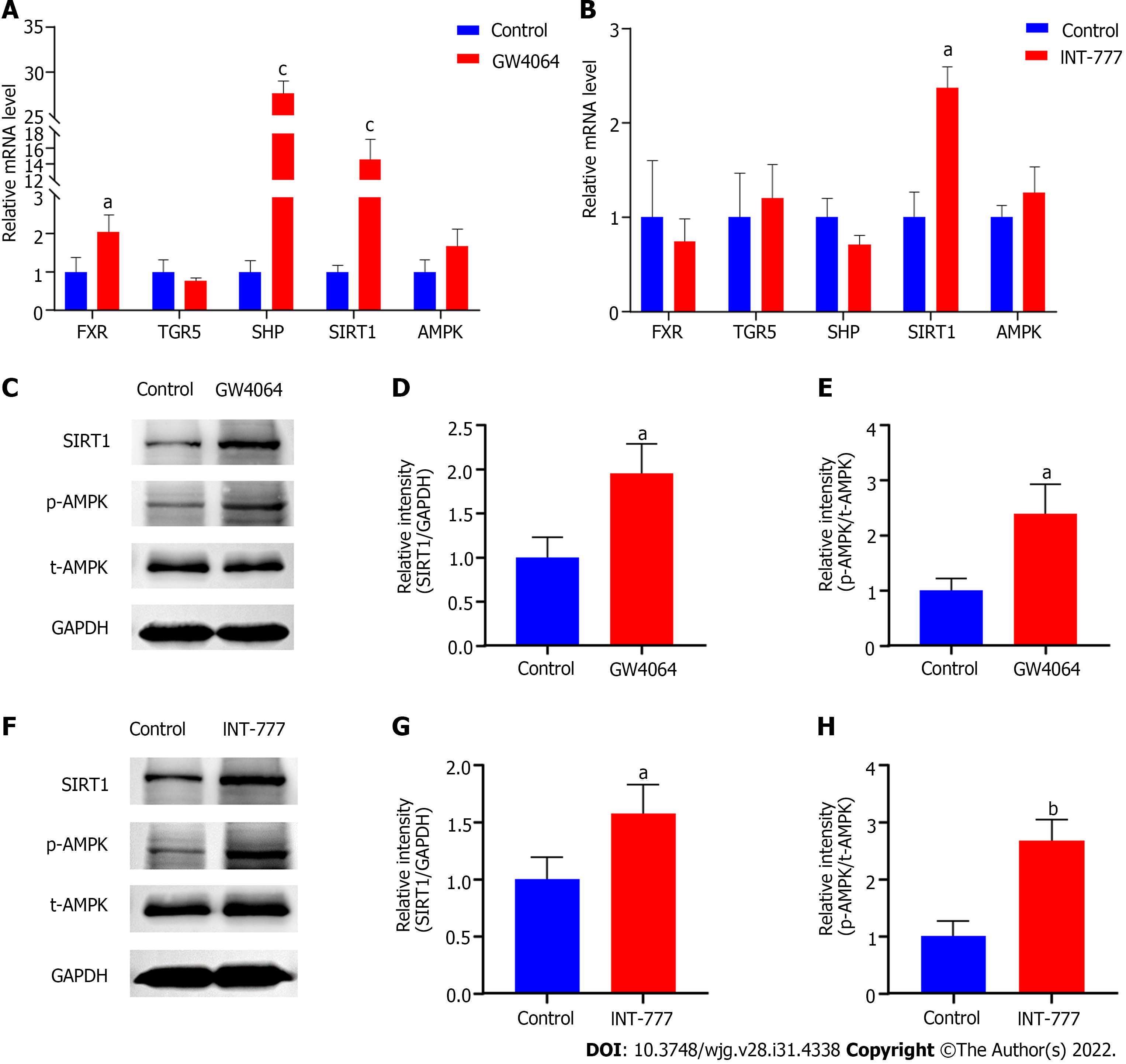
Figure 4 Activation of farnesoid X receptor and Takeda G-protein-coupled receptor 5 increased SIRT1 and promoted phosphorylation of AMPK in rat small intestine epithelial IEC-6 cells.
A and B: Effects of farnesoid X receptor (FXR) and Takeda G-protein-coupled receptor 5 (TGR5) activation on SIRT1, AMPK, and key genes involved in BA signaling pathway; C: Western blot images of SIRT1, phosphorylated AMPK (p-AMPK), and total AMPK (t-AMPK) in IEC-6 cells after FXR activation; D and E: The relative intensity of SIRT1 and p-AMPK/t-AMPK in IEC-6 cells after FXR activation. F: Western blot images of SIRT1, p-AMPK, and t-AMPK in IEC-6 cells after TGR5 activation; G and H: The relative intensity of SIRT1 and p-AMPK/t-AMPK in IEC-6 cells after TGR5 activation. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, cP < 0.001 GW4064 or INT-777 vs control group. p-AMPK: Phosphorylated AMPK; t-AMPK: Total AMPK; FXR: Farnesoid X receptor; SHP: Small heterodimer partner; TGR5: Takeda G-protein-coupled receptor 5.
- Citation: Han HF, Liu SZ, Zhang X, Wei M, Huang X, Yu WB. Duodenal-jejunal bypass increases intraduodenal bile acids and upregulates duodenal SIRT1 expression in high-fat diet and streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. World J Gastroenterol 2022; 28(31): 4338-4350
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v28/i31/4338.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v28.i31.4338