Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 14, 2022; 28(30): 4075-4088
Published online Aug 14, 2022. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i30.4075
Published online Aug 14, 2022. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i30.4075
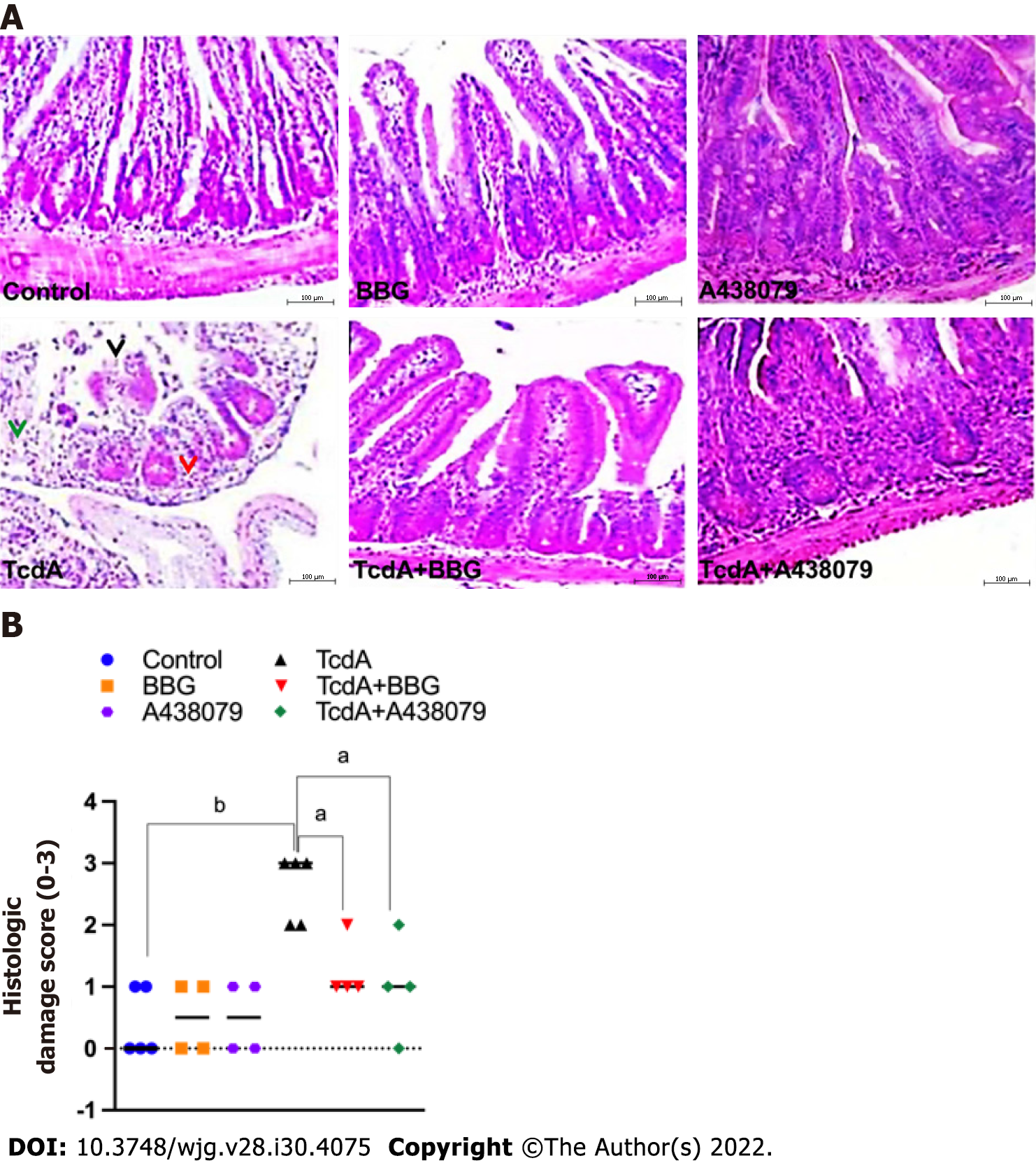
Figure 3 Inhibition of the P2X7 receptor decreases Clostridioides difficile toxin A-induced ileal damage in mice.
Mouse ileal loops were injected with TcdA [TcdA, 50 μg in phosphate-buffered saline (PBS)] or PBS alone (control) (n = 5), and the animals were pretreated with a P2X7 receptor antagonist [Brilliant Blue G (BBG) or A438079] one hour prior to TcdA challenge. A: Representative histological images (magnification of 200 ×) of TcdA-unchallenged (control, BBG, and A438079) and challenged (TcdA, TcdA + BBG, and TcdA + A438079) mice. TcdA induced epithelial disruption (black arrowhead), edema (green arrowhead), and neutrophil infiltration (red arrowhead); B: Histopathological score (median; 0 corresponds to-no damage and 3 corresponds to intense damage) performed by a blinded histopathological expert and based on epithelial damage, submucosal edema, and infiltration of inflammatory cells. Kruskal–Wallis nonparametric test followed by Dunn’s test. aP < 0.04; bP < 0.007. BBG: Brilliant Blue G.
- Citation: Santos AAQA, Costa DVS, Foschetti DA, Duarte ASG, Martins CS, Soares PMG, Castelucci P, Brito GAC. P2X7 receptor blockade decreases inflammation, apoptosis, and enteric neuron loss during Clostridioides difficile toxin A-induced ileitis in mice. World J Gastroenterol 2022; 28(30): 4075-4088
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v28/i30/4075.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v28.i30.4075