Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 14, 2022; 28(30): 4075-4088
Published online Aug 14, 2022. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i30.4075
Published online Aug 14, 2022. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i30.4075
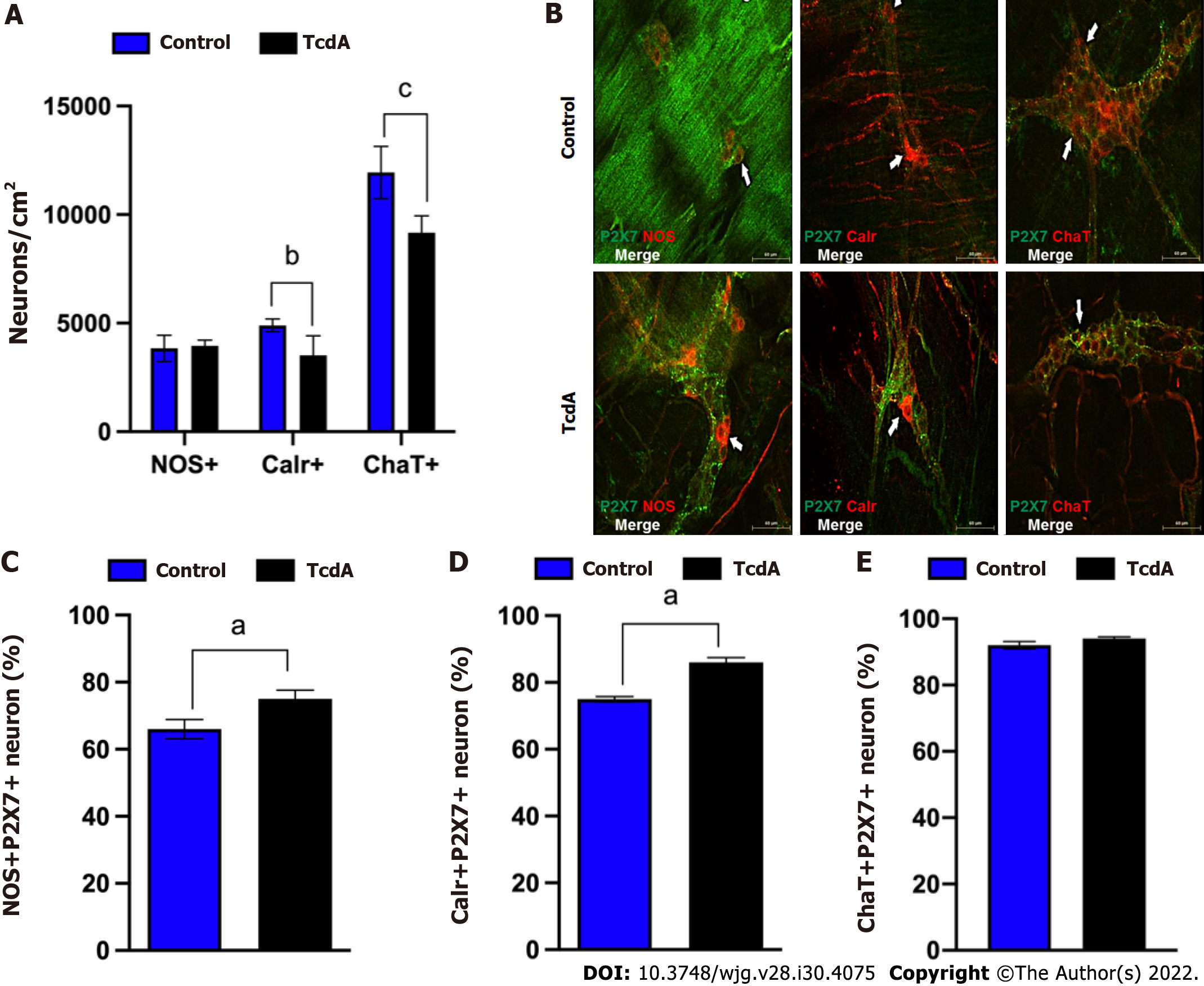
Figure 2 Clostridioides difficile toxin A induces alterations in enteric neuronal coding in the myenteric plexus in the ileum of mice.
A: Quantification of the number of neuronal nitric oxide synthase+ (nNOS+), calretinin+ (Calr+), and choline acetyltransferase+ (ChaT+) neurons/cm2 [mean ± standard error of the mean (SEM)] in the ileum myenteric plexus in control and TcdA-challenged mice; B: Representative photomicrographs of the P2X7 receptor (green), nNOS (left panels, red), Calr (center panels, red), and ChaT (right panel, red) immunostaining and DAPI (blue) nuclear staining in control and TcdA-challenged mice. White arrows indicate positive immunostaining. Scale bars, 50 μm; C-E: Percentage of NOS+P2X7+ neurons (C), Calr+P2RX7+ neurons (D), and ChaT+P2RX7+ neurons (E) (mean ± SEM) in the ileum myenteric plexus of control and TcdA-challenged mice (n = 4); A, C, D and E: Unpaired two-tailed Student's t test (aP < 0.05; bP < 0.03; cP < 0.002 ). NOS: Nitric oxide synthase; Calr: Calretinin; ChaT: Choline acetyltransferase.
- Citation: Santos AAQA, Costa DVS, Foschetti DA, Duarte ASG, Martins CS, Soares PMG, Castelucci P, Brito GAC. P2X7 receptor blockade decreases inflammation, apoptosis, and enteric neuron loss during Clostridioides difficile toxin A-induced ileitis in mice. World J Gastroenterol 2022; 28(30): 4075-4088
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v28/i30/4075.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v28.i30.4075