Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 7, 2022; 28(29): 3903-3916
Published online Aug 7, 2022. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i29.3903
Published online Aug 7, 2022. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i29.3903
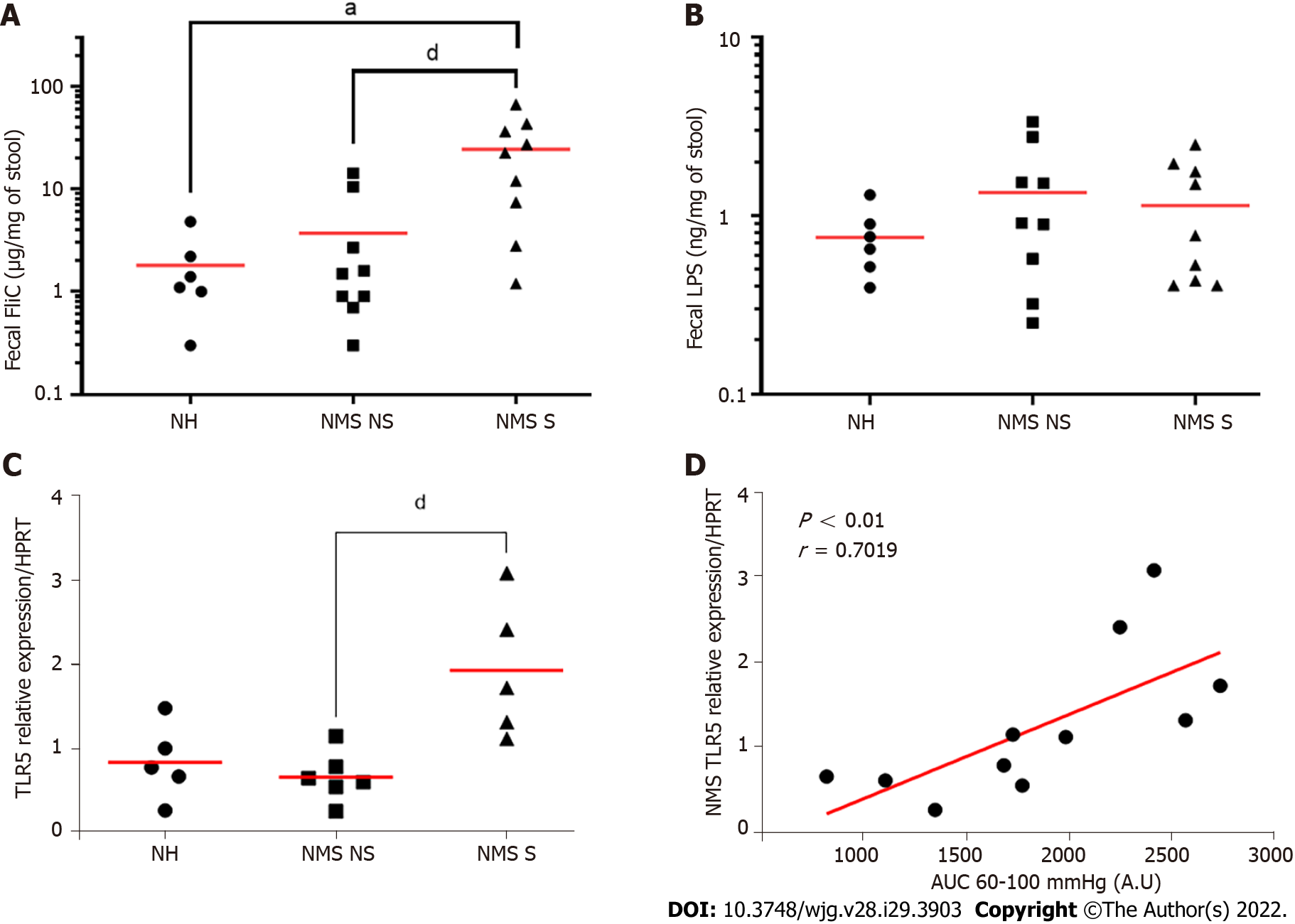
Figure 4 Neonatal maternal separation induced colonic hypersensitivity is associated with increased flagellin fecal content and colonocytes toll-like receptor 5 expression.
A: Levels of fecal flagellin (FliC) assayed with toll-like receptor 5 (TLR5) reporter cells; B: Levels of fecal lipopolysaccharide assayed with TLR4 reporter cells; C: Colonocytes mRNA expression of TLR5 in non-handled (NH), neonatal maternal separated non-sensitized (NMS NS) and neonatal maternal separated sensitized (NMS S) mice at week 12. Values are expressed as relative expression of TLR5 mRNA compared to HPRT expression; D: Correlation between NMS colonocytes TLR5 expression and area under the curve (AUC) corresponding of the intracolonic pressure variation (IPV) for highest colorectal distension pressures (60, 80 and 100 mmHg). A and B: NH: n = 6; NMS NS: n = 9; NMS S: n = 9. aP < 0.05 vs NH group; and dP < 0.05 vs NMS NS group. C and D: NH: n = 5; NMS NS: n = 6; NMS S: n = 5. dP < 0.05 vs NMS NS. For FliC quantification TLR5 mRNA relative expression, each dot represents one mouse and red lines represent means and for correlation between TLR5 expression and AUC of IPV, each dot represents one mouse and red line represents the linear regression curve.
- Citation: Mallaret G, Lashermes A, Meleine M, Boudieu L, Barbier J, Aissouni Y, Gelot A, Chassaing B, Gewirtz AT, Ardid D, Carvalho FA. Involvement of toll-like receptor 5 in mouse model of colonic hypersensitivity induced by neonatal maternal separation. World J Gastroenterol 2022; 28(29): 3903-3916
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v28/i29/3903.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v28.i29.3903