Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 7, 2022; 28(29): 3854-3868
Published online Aug 7, 2022. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i29.3854
Published online Aug 7, 2022. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i29.3854
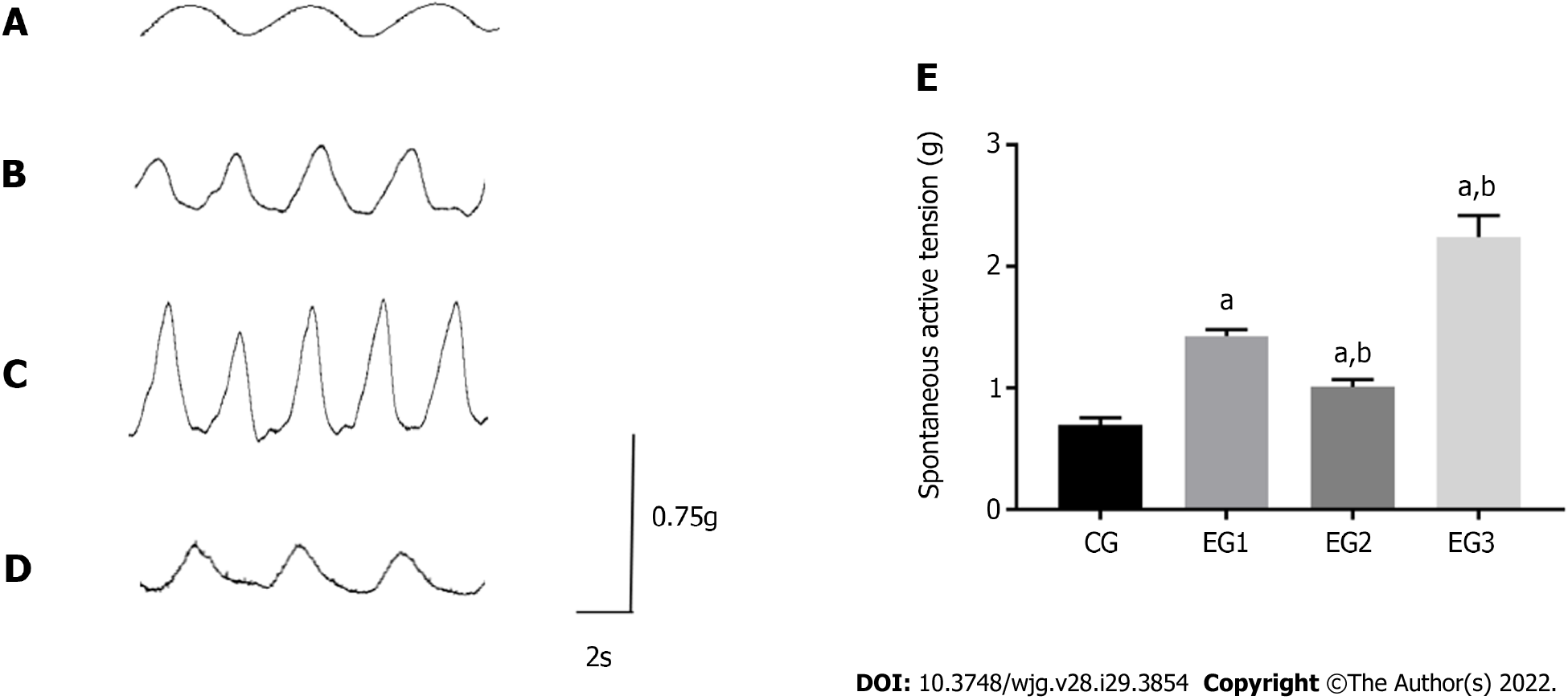
Figure 7 Comparison of isolated colonic longitudinal muscle contraction tension.
A-D: Contraction amplitude of the colonic longitudinal muscle of CG (A), EG1 (B), EG2 (C), and EG3 (D) rats; E: Comparison of the contraction tension of the colonic longitudinal muscle among rats from the four groups: CG (0.69 ± 0.02 g), EG1 (1.4 2 ± 0.02 g), EG2 (2.24 ± 0.07 g), and EG3 (1.01 ± 0.02 g). All differences were statistically significant between EG groups and CG group (aP < 0.0001) and between EG2-3 groups and EG1 group (bP < 0.001). CG: Control group; UC: Ulcerative colitis; NOS: Nitric oxide synthase; L-NMMA: NG-monomethyl-L-arginine monoacetate; EG1: UC group; EG2: UC + NOS agonist TP508TFA group; EG3: UC + NOS inhibitor L-NMMA group; LM: Longitudinal muscle.
- Citation: Li YR, Li Y, Jin Y, Xu M, Fan HW, Zhang Q, Tan GH, Chen J, Li YQ. Involvement of nitrergic neurons in colonic motility in a rat model of ulcerative colitis. World J Gastroenterol 2022; 28(29): 3854-3868
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v28/i29/3854.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v28.i29.3854