Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 7, 2022; 28(29): 3814-3824
Published online Aug 7, 2022. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i29.3814
Published online Aug 7, 2022. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i29.3814
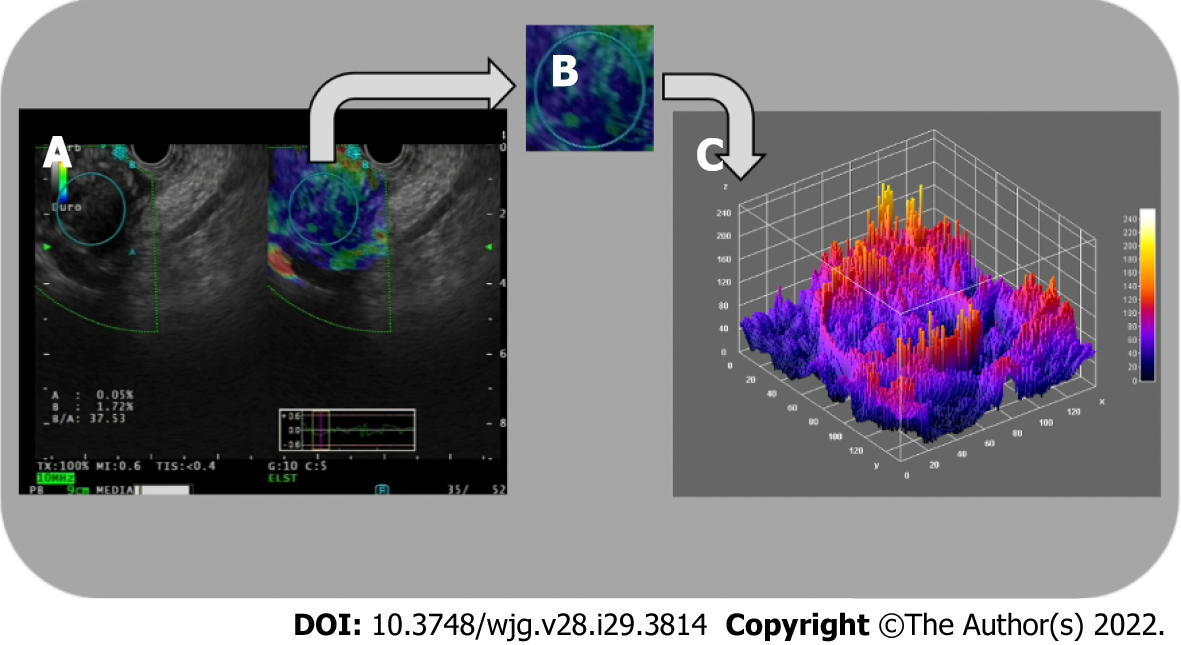
Figure 3 Three-dimensional surface fractal dimension estimate.
A and B: Endoscopic ultrasound-elastography images (A) are used to highlight representative parenchymal regions (B) of solid pancreatic lesions; C: A computer-aided image analysis system generates an irregularly-shaped three-dimensional surface as a “shape matrix” of points with the column and row numbers proportional to the x and y coordinates and with the depth information z (x, y) stored as a matrix element. The three-dimensional fractal dimension, which is an index of the “surface roughness”, is automatically determined using the box-counting algorithm. The fractal dimension of a surface is expressed by a real number greater than 2 (the Euclidean dimension of a two-dimensional surface) and less than 3 (the Euclidean dimension of a solid). A surface with a higher surface fractal dimension is wrinkled than one with a lower dimension.
- Citation: Spadaccini M, Koleth G, Emmanuel J, Khalaf K, Facciorusso A, Grizzi F, Hassan C, Colombo M, Mangiavillano B, Fugazza A, Anderloni A, Carrara S, Repici A. Enhanced endoscopic ultrasound imaging for pancreatic lesions: The road to artificial intelligence. World J Gastroenterol 2022; 28(29): 3814-3824
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v28/i29/3814.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v28.i29.3814