Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 28, 2022; 28(28): 3627-3636
Published online Jul 28, 2022. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i28.3627
Published online Jul 28, 2022. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i28.3627
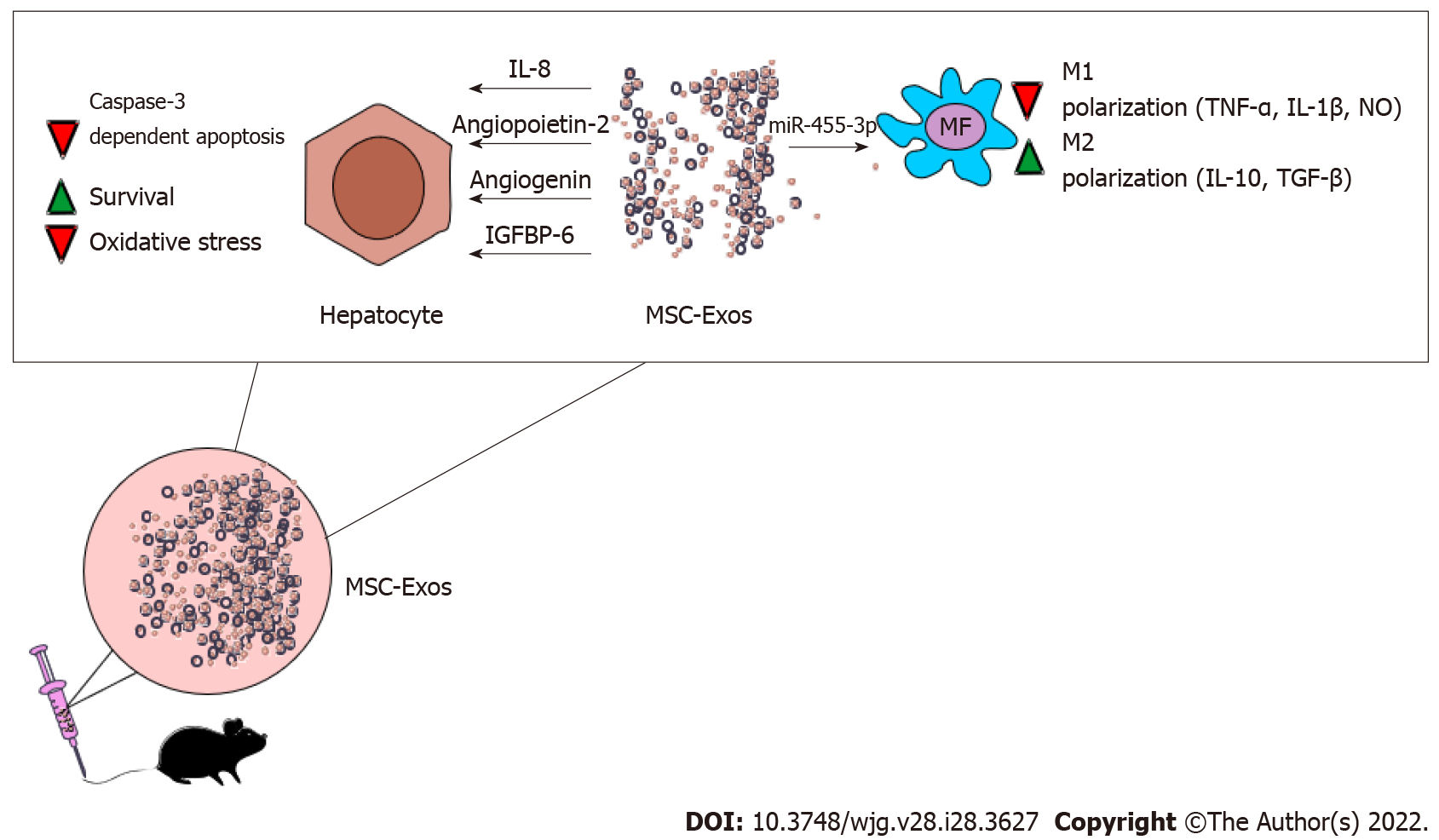
Figure 2 Molecular mechanisms responsible for the beneficial effects of mesenchymal stem cell derived exosomes in attenuation of acute liver failure.
By delivering interleukin (IL)-8, angiopoietin-2, angiogenin, insulin-like growth factor binding protein-6, mesenchymal stem cell derived exosomes (MSC-Exos) attenuate oxidative stress, suppress caspase-3-dependent apoptosis and promoted survival of hepatocytes in acutely injured livers. MSC-Exos, in miRNA-455-3p-dependent manner, alleviate on-going liver inflammation by inhibiting inflammatory, tumor necrosis factor alpha, IL-1β and nitric oxide-producing M1 macrophages and by promoting generation of immunosuppressive, transforming growth factor beta-β and IL-10-producing M2 macrophages. Abbreviations: MSC-Exos: Mesenchymal stem cell derived exosomes; IL: Interleukin; IGFBP6: Insulin like growth factor binding protein 6; TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor alpha; NO: Nitric oxide.
- Citation: Harrell CR, Pavlovic D, Djonov V, Volarevic V. Therapeutic potential of mesenchymal stem cells in the treatment of acute liver failure. World J Gastroenterol 2022; 28(28): 3627-3636
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v28/i28/3627.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v28.i28.3627