Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 21, 2022; 28(27): 3422-3434
Published online Jul 21, 2022. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i27.3422
Published online Jul 21, 2022. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i27.3422
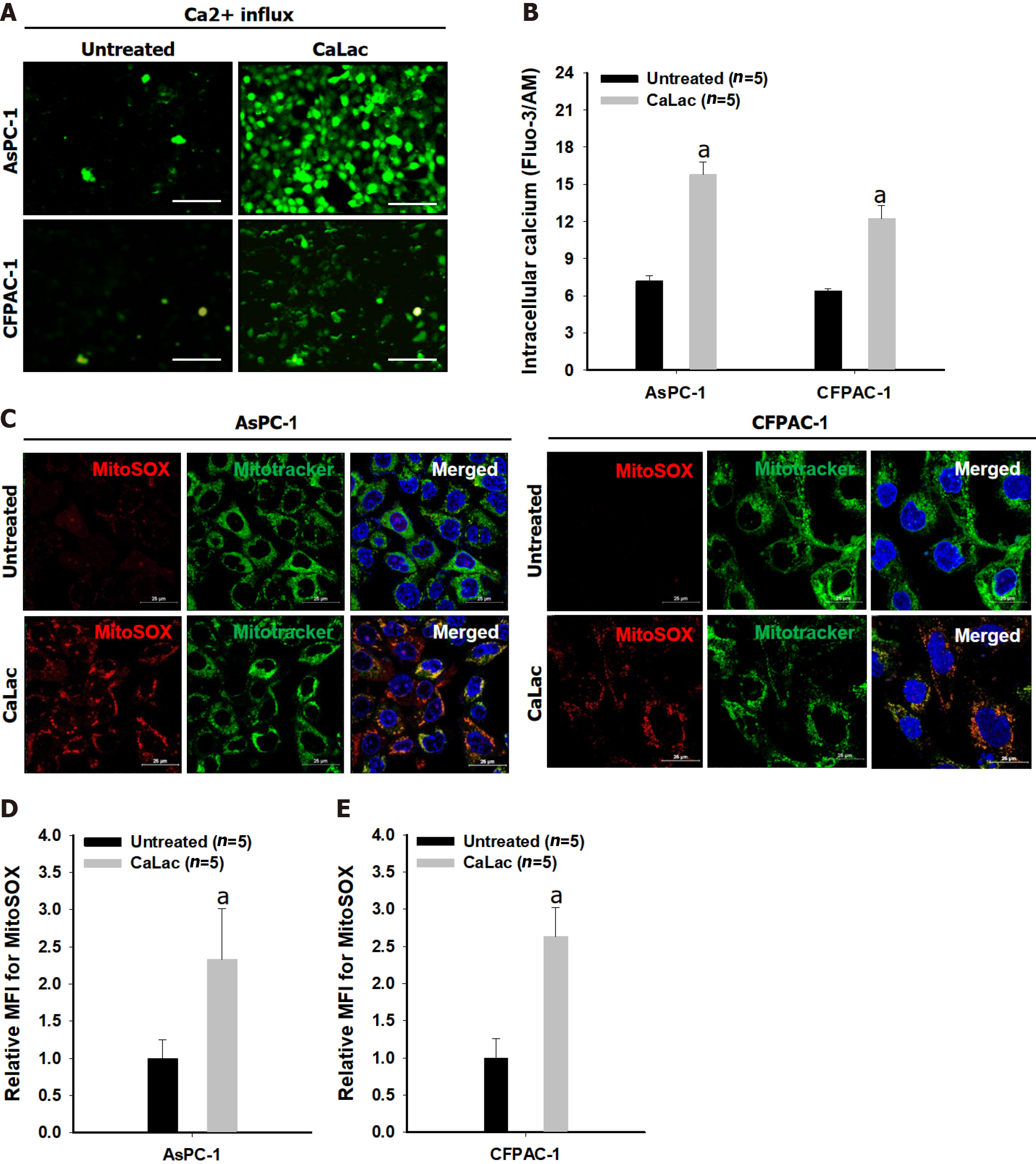
Figure 1 Confirmation of mitochondrial reactive oxygen species generation by sustained calcium supply.
A: Fluorescent calcium imaging following lactate calcium salt (CaLac) treatment of pancreatic cancer cells (AsPC-1 and CFPAC-1). Scale bars: 100 μm; B: Quantitative analysis of the fluorescence intensity of calcium; C: Confocal imaging of mitochondrial reactive oxygen species (ROS) in pancreatic cancer cells. Red dye: Mitochondrial superoxide indicator; Green dye: Mitochondrial indicator. Scale bars: 25 μm; D: Quantitative analysis of the fluorescence intensity of mitochondrial ROS in AsPC-1; E: Quantitative analysis of the fluorescence intensity of mitochondrial ROS in CFPAC-1. The fluorescence intensity was calculated by the mean fluorescence intensity. The cells were treated with 2.5 mM CaLac for 72 h. Results represent the mean ± SD. aP < 0.001 vs untreated. CaLac: Lactate calcium salt; MitoSOX: Mitochondrial superoxide indicator.
- Citation: Jeong KY, Sim JJ, Park M, Kim HM. Accumulation of poly (adenosine diphosphate-ribose) by sustained supply of calcium inducing mitochondrial stress in pancreatic cancer cells. World J Gastroenterol 2022; 28(27): 3422-3434
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v28/i27/3422.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v28.i27.3422