Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 14, 2022; 28(26): 3201-3217
Published online Jul 14, 2022. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i26.3201
Published online Jul 14, 2022. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i26.3201
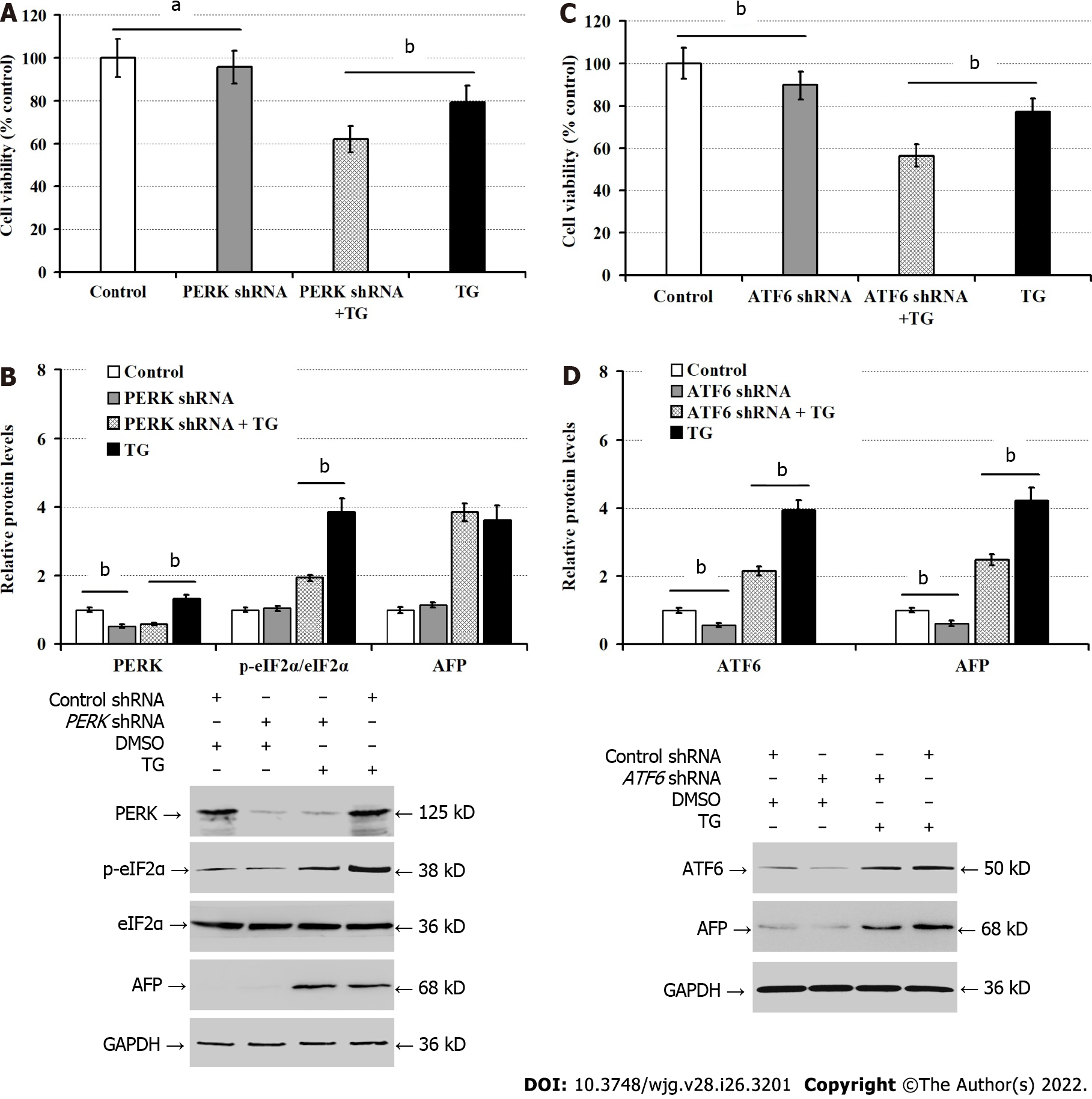
Figure 4 Activating transcription factor-6 silencing inhibits the expression of alpha-fetoprotein induced by thapsigargin invitro.
LO2 cells were transfected with control shRNA, protein kinase R-like endoplasmic reticulum kinase (PERK)-shRNA, or activating transcription factor-6 (ATF6)-shRNA for 48 h, and treated with dimethyl sulfoxide (control) or thapsigargin for 24 h. A: Cell counting kit-8 (CCK-8) analysis of cell viability; B: Western blot analysis of p-PERK, phosphorylated eukaryotic translational initiation factor 2 alpha, and alpha-fetoprotein expression; C: CCK-8 analysis of cell viability; D: Western blot analysis of the relative levels of ATF6 and AFP protein expression. AFP: Alpha-fetoprotein; ATF6: Activating transcription factor-6; CCK-8: Cell counting kit-8; DMSO: Dimethyl sulfoxide; p-eIF2α: Phosphorylated eukaryotic translational initiation factor 2 alpha; p-PERK: Phosphorylated protein kinase R-like endoplasmic reticulum kinase; TG: Thapsigargin. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, compared with these two groups.
- Citation: Chen YF, Liu SY, Cheng QJ, Wang YJ, Chen S, Zhou YY, Liu X, Jiang ZG, Zhong WW, He YH. Intracellular alpha-fetoprotein mitigates hepatocyte apoptosis and necroptosis by inhibiting endoplasmic reticulum stress. World J Gastroenterol 2022; 28(26): 3201-3217
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v28/i26/3201.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v28.i26.3201