Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 14, 2022; 28(26): 3201-3217
Published online Jul 14, 2022. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i26.3201
Published online Jul 14, 2022. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i26.3201
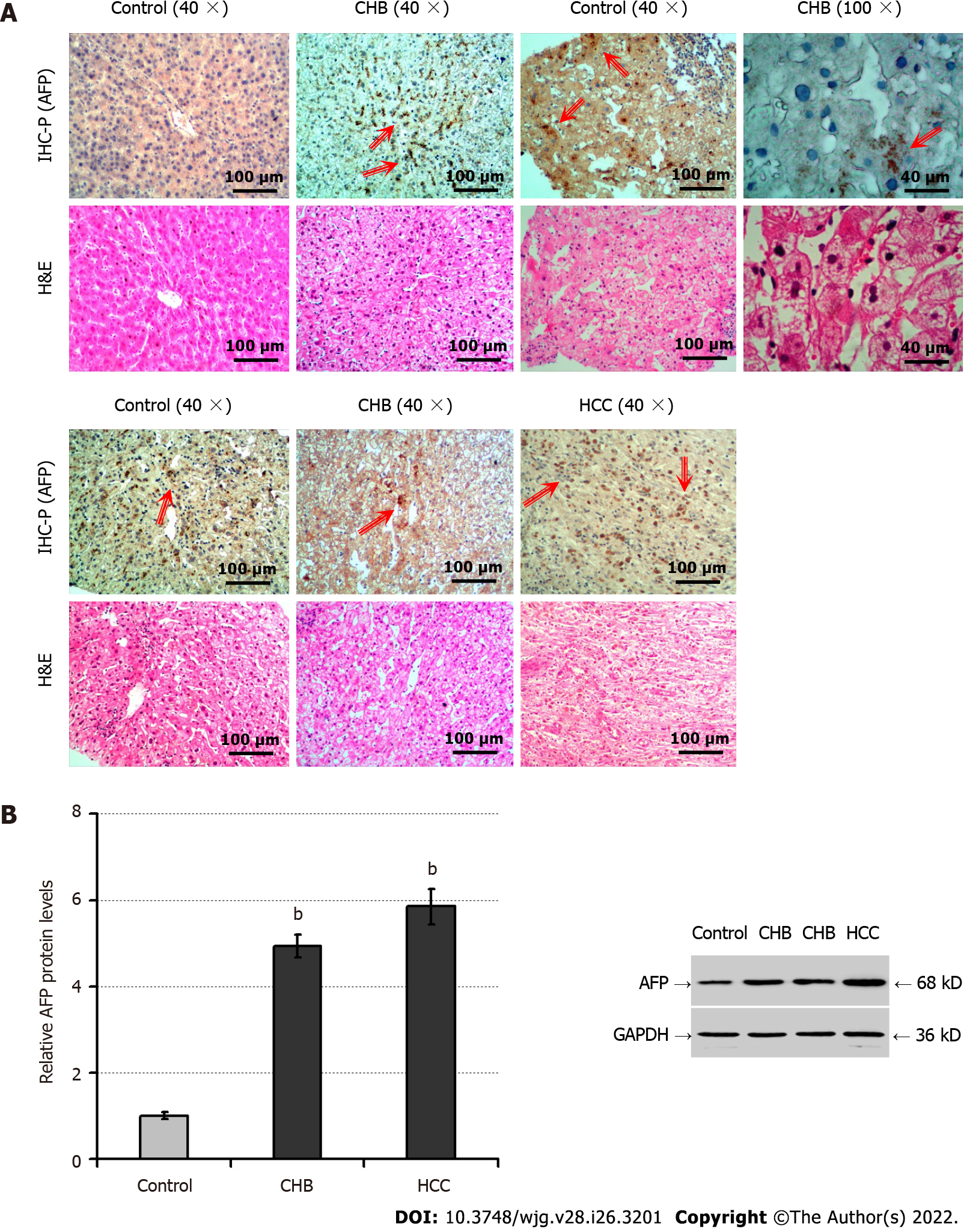
Figure 1 The intrahepatic levels of alpha-fetoprotein protein are elevated in injured livers.
A: Immunohistochemistry and hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining analyzed alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) expression and pathological changes, respectively, in liver tissues of patients with chronic hepatitis B (CHB, n = 34), trauma (n = 8) or hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC, the positive control group, n = 8). The upper panels display immunohistochemical staining, and the lower panels exhibit H&E staining in sequential tissue sections. The positive expression of AFP was stained with brownish yellow by immunohistochemistry and indicated by the arrows; B: The relative levels of AFP protein expression were analyzed by Western blot in the liver specimens indicated. H&E: Hematoxylin and eosin; IHC-P: Immunohistochemistry-paraffin; AFP: Alpha-fetoprotein; HCC: Hepatocellular carcinoma; CHB: Chronic hepatitis B. bP < 0.01, compared with the control group.
- Citation: Chen YF, Liu SY, Cheng QJ, Wang YJ, Chen S, Zhou YY, Liu X, Jiang ZG, Zhong WW, He YH. Intracellular alpha-fetoprotein mitigates hepatocyte apoptosis and necroptosis by inhibiting endoplasmic reticulum stress. World J Gastroenterol 2022; 28(26): 3201-3217
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v28/i26/3201.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v28.i26.3201