Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 14, 2022; 28(26): 3150-3163
Published online Jul 14, 2022. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i26.3150
Published online Jul 14, 2022. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i26.3150
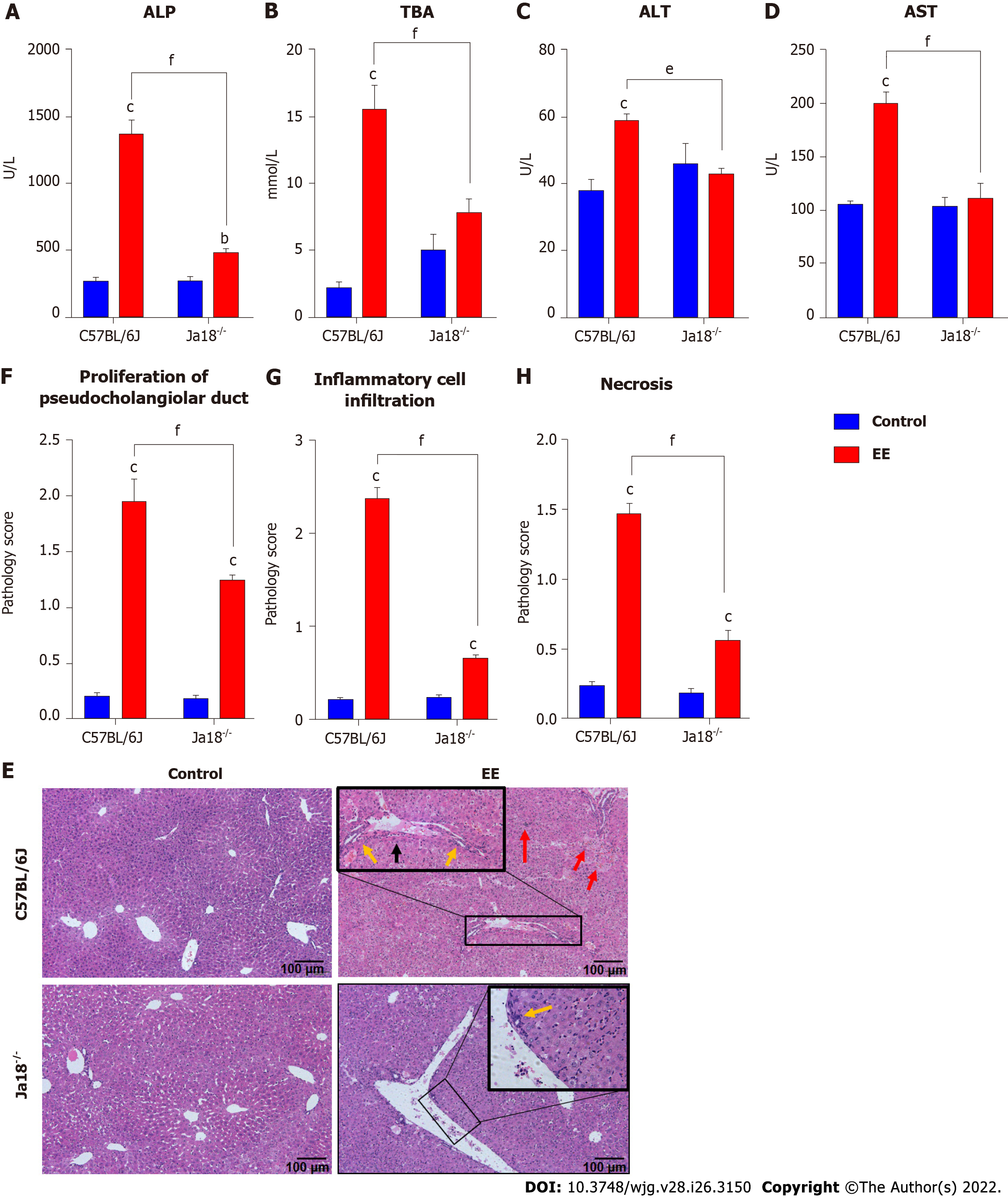
Figure 2 Invariant natural killer T cells exacerbate ethinylestradiol-induced cholestatic liver damage.
A-D: The serum levels of ALP (A), TBA (B), ALT (C) and AST (D); E: Liver sections stained with hematoxylin and eosin (10×); F: Proliferation of pseudocholangiolar duct (yellow arrows); G and H: Inflammatory cell infiltration (G, red arrows) and hepatocyte necrosis (H, black arrows) were compared as pathology scores. All values are the means ± SE (n = 4-6). bP < 0.01, cP < 0.001 vs control; eP < 0.01, fP < 0.001 vs C57BL/6J group.
- Citation: Zou MZ, Kong WC, Cai H, Xing MT, Yu ZX, Chen X, Zhang LY, Wang XZ. Activation of natural killer T cells contributes to Th1 bias in the murine liver after 14 d of ethinylestradiol exposure. World J Gastroenterol 2022; 28(26): 3150-3163
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v28/i26/3150.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v28.i26.3150