Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 14, 2022; 28(26): 3116-3131
Published online Jul 14, 2022. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i26.3116
Published online Jul 14, 2022. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i26.3116
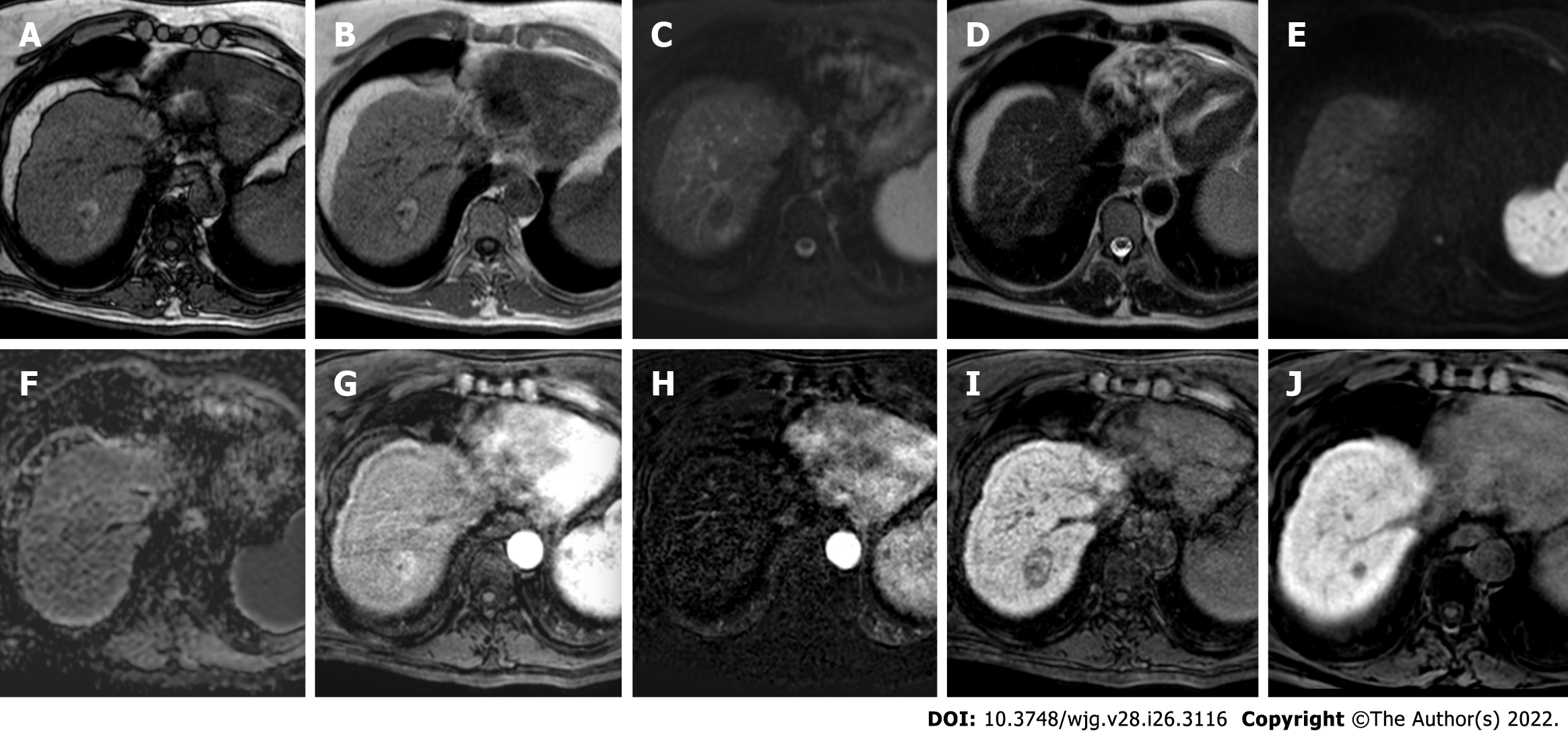
Figure 1 hree-month follow-up liver magnetic resonance imaging of a 69-yr-old male post radiofrequency ablation of right hepatic lobe hepatocellular carcinoma (segment VII).
A: Out-phase T1-weighted image; B: In-phase T1-weighted image; C: T2-spectral attenuated inversion recovery; D: T2-weighted image; E: High b-value diffusion weighted imaging; F: Apparent diffusion coefficient map; G: Arterial phase magnetic resonance imaging (MRI); H: Arterial phase MRI with image subtraction technique; I and J: Hepatobiliary phase MRI. Follow-up MRI (A-I) after 3 mo post treatment revealed a good outcome characterized by inhomogeneous high signal hyperintensity in T1 sequences due to the presence of coagulative necrosis with associated signal hypointensity in T2 weighted sequences and the absence signal hyperintensity in diffusion weighted imaging. Dynamic study showed no enhancement in arterial phase with inhomogeneous hypointensity during hepatobiliary excretion. Findings are suggestive of complete tumor ablation also when compared to the similar pre-treatment sequences (J).
- Citation: Gatti M, Maino C, Darvizeh F, Serafini A, Tricarico E, Guarneri A, Inchingolo R, Ippolito D, Ricardi U, Fonio P, Faletti R. Role of gadoxetic acid-enhanced liver magnetic resonance imaging in the evaluation of hepatocellular carcinoma after locoregional treatment. World J Gastroenterol 2022; 28(26): 3116-3131
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v28/i26/3116.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v28.i26.3116