Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 14, 2022; 28(26): 3008-3026
Published online Jul 14, 2022. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i26.3008
Published online Jul 14, 2022. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i26.3008
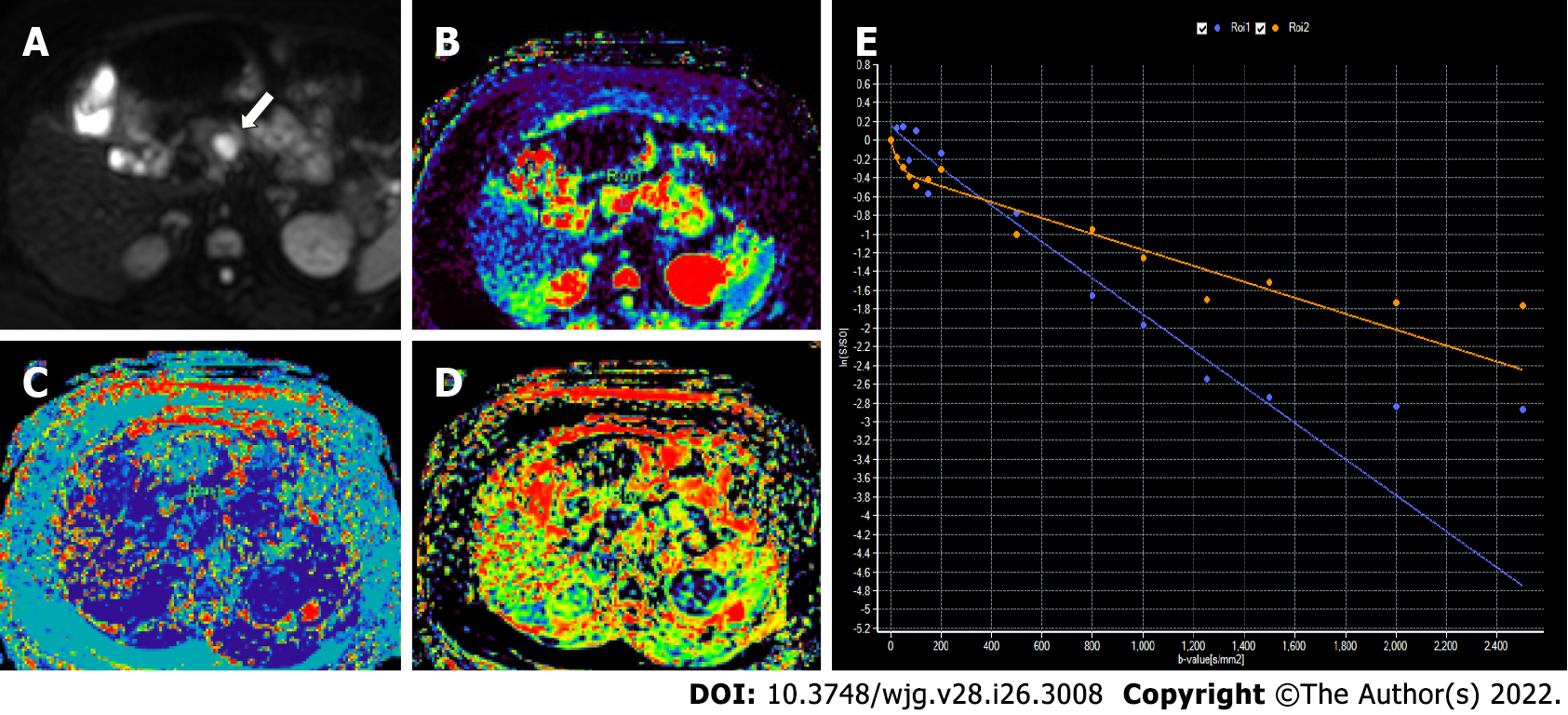
Figure 7 Intravoxel incoherent motion diffusion-weighted imaging in a 46-year-old woman with proven grade 1 pancreatic neuroe
- Citation: Ramachandran A, Madhusudhan KS. Advances in the imaging of gastroenteropancreatic neuroendocrine neoplasms. World J Gastroenterol 2022; 28(26): 3008-3026
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v28/i26/3008.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v28.i26.3008