Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 14, 2022; 28(26): 3008-3026
Published online Jul 14, 2022. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i26.3008
Published online Jul 14, 2022. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i26.3008
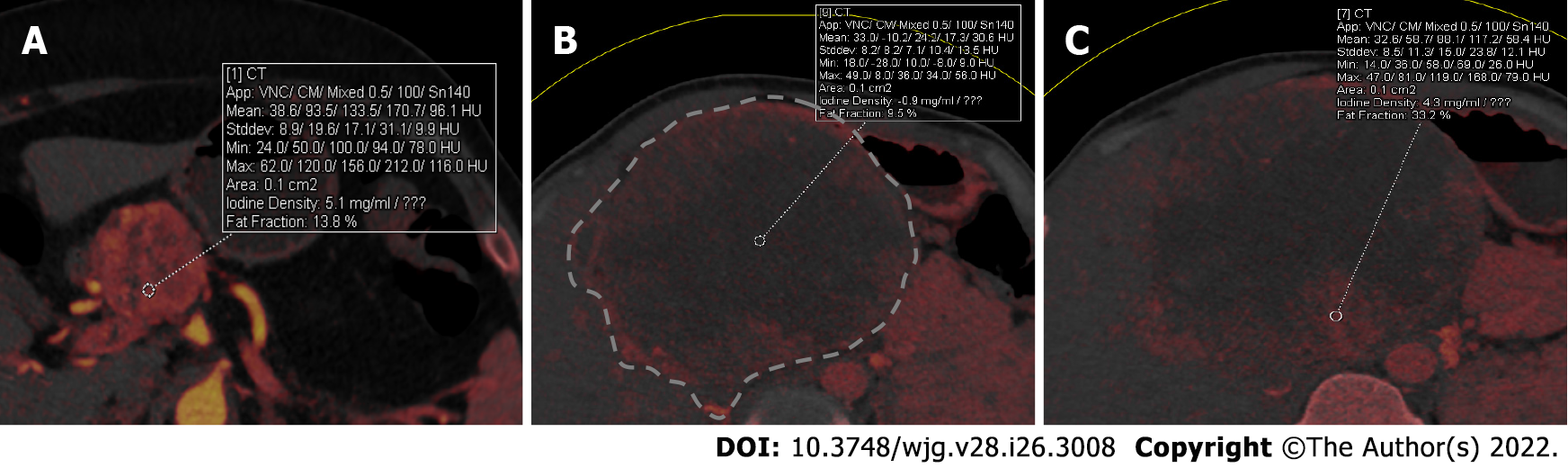
Figure 3 Dual-energy computed tomography in grading the pancreatic neuroendocrine neoplasms.
A: Iodine overlay dual-energy computed tomography (CT) map of a 40-year-old woman with low-grade (grade 2) pancreatic neuroendocrine neoplasms (PNEN) in head of pancreas shows hyperenhancement of the tumor with an iodine concentration of 5.1 mg/mL; B and C: Iodine overlay dual energy CT maps of a 29-year-old man with grade 3 PNEN (outlined in B) shows large hypoenhancing areas with low iodine concentration (0.9 mg/mL) and peripheral bright areas with iodine concentration of 4.3 mg/mL (C). Measuring iodine concentration helps in objectively assessing the grade of the tumor.
- Citation: Ramachandran A, Madhusudhan KS. Advances in the imaging of gastroenteropancreatic neuroendocrine neoplasms. World J Gastroenterol 2022; 28(26): 3008-3026
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v28/i26/3008.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v28.i26.3008