Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 7, 2022; 28(25): 2937-2954
Published online Jul 7, 2022. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i25.2937
Published online Jul 7, 2022. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i25.2937
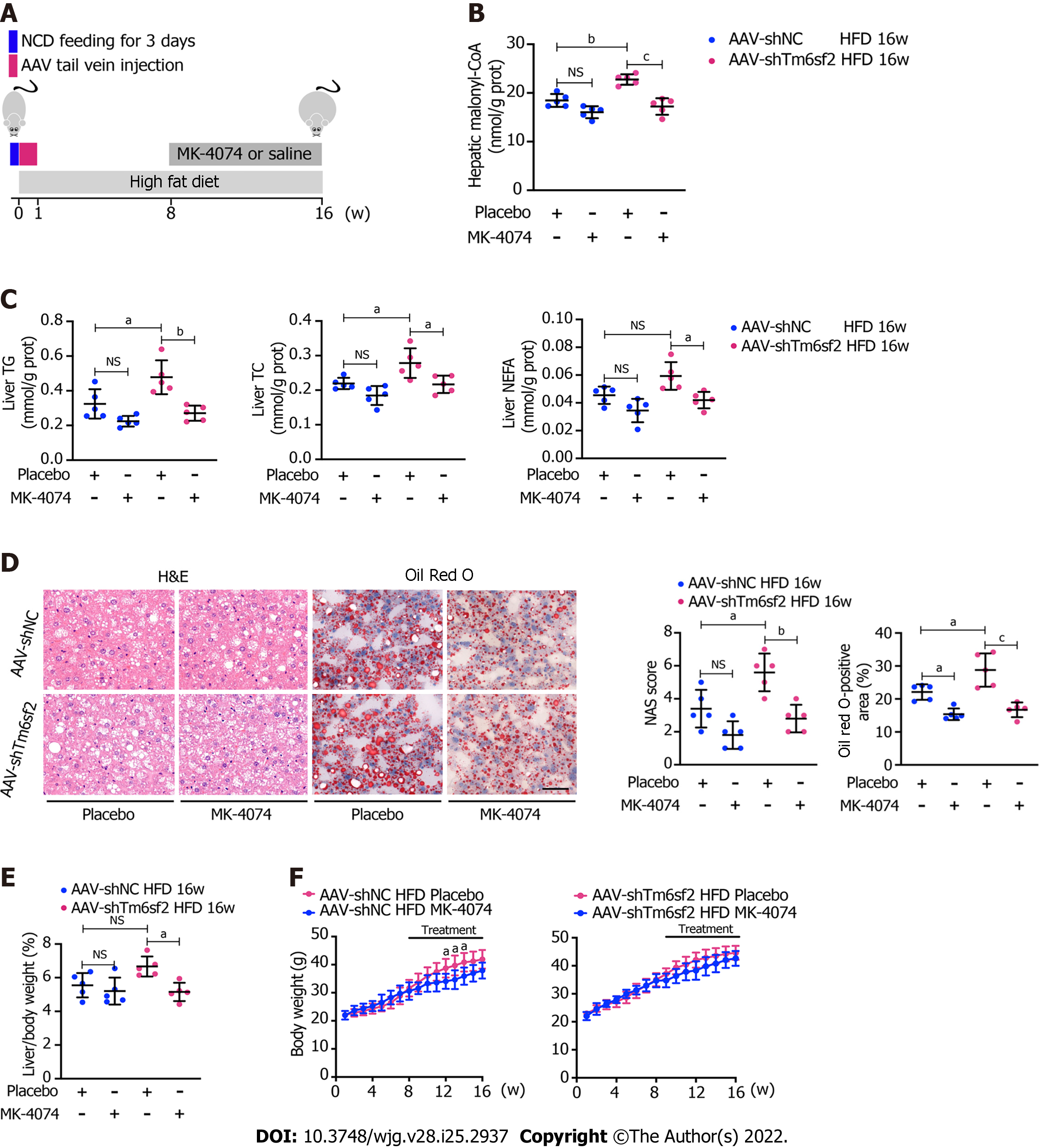
Figure 8 Therapeutic potential of MK-4074 on nonalcoholic fatty liver disease caused by TM6SF2 deficiency.
A: Schematic representation of animal experiments; B-D: Two groups (AAV-shNC and AAV-shTm6sf2) of mice were fed a high-fat diet (HFD) for 8 wk to induce nonalcoholic fatty liver disease phenotypes and then each subgroup was dosed with MK-4074 (10 mg/kg/day) or placebo orally for additional 8 wk. The hepatic malonyl-CoA levels (B) and lipid content (C) as well as results of hematoxylin and eosin-staining and Oil Red O-staining of liver sections (D) were shown; E and F: The liver/body weight ratio (E) and the body weight (F) of HFD-fed AAV-shNC and AAV-shTm6sf2 mice with or without MK-4074 treatment (n = 5 mice per group) were shown. aP < 0.05; bP < 0.01; cP < 0.001. NS: Not significant; H&E: Hematoxylin and eosin; NCD: Normal chow diet; HFD: High-fat diet; TG: Triglyceride; TC: Total cholesterol; NEFA: Non-esterified fatty acids.
- Citation: Li ZY, Wu G, Qiu C, Zhou ZJ, Wang YP, Song GH, Xiao C, Zhang X, Deng GL, Wang RT, Yang YL, Wang XL. Mechanism and therapeutic strategy of hepatic TM6SF2-deficient non-alcoholic fatty liver diseases via in vivo and in vitro experiments. World J Gastroenterol 2022; 28(25): 2937-2954
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v28/i25/2937.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v28.i25.2937