Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 7, 2022; 28(25): 2937-2954
Published online Jul 7, 2022. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i25.2937
Published online Jul 7, 2022. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i25.2937
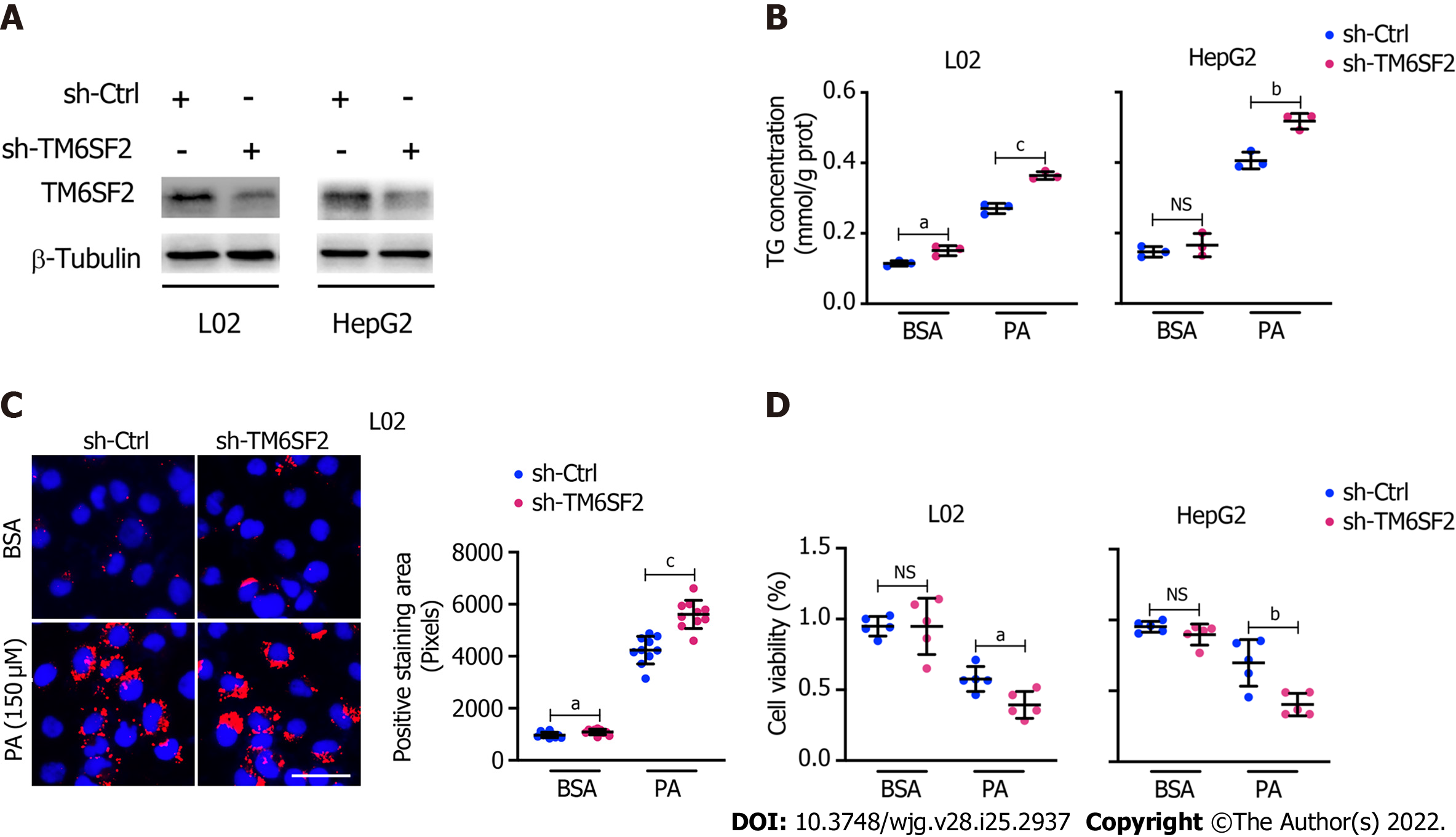
Figure 3 Knockdown of TM6SF2 promotes intracellular lipid accumulation and lipid-overload induced cell death.
A: The efficiency of TM6SF2 knockdown in two cell lines; B: Intracellular triglyceride levels (n = 3) in TM6SF2-knockdown cells were examined after palmitic acid (PA) (150 μmol/L) or bovine serum albumin (BSA) (fatty acid free) treatment for 24 h; C: Nile red staining (left, nuclei labeled with DAPI, blue) and quantification of lipid accumulation (right) of sh-Ctrl or sh-TM6SF2 L02 cells after PA or BSA treatment. Scale bars: 50 μm; D: TM6SF2-knockdown cells were incubated with PA (150 μmol/L) or BSA for 24 h. The cellular viability was examined (n = 5). aP < 0.05; bP < 0.01; cP < 0.001. NS: Not significant; BSA: Bovine serum albumin; PA: Palmitic acid; TG: Triglyceride; μM: μmol/L.
- Citation: Li ZY, Wu G, Qiu C, Zhou ZJ, Wang YP, Song GH, Xiao C, Zhang X, Deng GL, Wang RT, Yang YL, Wang XL. Mechanism and therapeutic strategy of hepatic TM6SF2-deficient non-alcoholic fatty liver diseases via in vivo and in vitro experiments. World J Gastroenterol 2022; 28(25): 2937-2954
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v28/i25/2937.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v28.i25.2937